Abstract
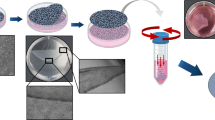
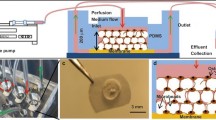
Bone is a complex, highly structured, mechanically active, three-dimensional (3-D) tissue composed of cellular and matrix elements. We previously published a report on in situ collagen gelation using a rotary 3-D culture system (CG–RC system) for the construction of large tissue specimens. The objective of the current study was to evaluate the feasibility of bone tissue engineering using our CG–RC system. Osteoblasts from the calvaria of newborn Wistar rats were cultured in the CG–RC system for up to 3 wk. The engineered 3-D tissues were implanted into the backs of nude mice and calvarial round bone defects in Wistar rats. Cell metabolic activity, mineralization, and bone-related proteins were measured in vitro in the engineered 3-D tissues. Also, the in vivo histological features of the transplanted, engineered 3-D tissues were evaluated in the animal models. We found that metabolic activity increased in the engineered 3-D tissues during cultivation, and that sufficient mineralization occurred during the 3 wk in the CG–RC system in vitro. One mo posttransplantation, the transplants to nude mice remained mineralized and were well invaded by host vasculature. Of particular interest, 2 mo posttransplantation, the transplants into the calvarial bone defects of rats were replaced by new mature bone. Thus, this study shows that large 3-D osseous tissue could be produced in vitro and that the engineered 3-D tissue had in vivo osteoinductive potential when transplanted into ectopic locations and into bone defects. Therefore, this system should be a useful model for bone tissue engineering.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, T. L.; Goodwin, T. J. Three-dimensional culture of bovine chondrocytes in rotating-wall vessels. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 33:358–365; 1997
Chung, C.-H.; Golub, F. E.; Forbes, E.; Tokuoka, T.; Shapiro, I. M. Mechanism of action of β−glycerophosphate on bone cell mineralization. Calcif Tissue Int 51:305–311; 1992
Dahl, L. K. A simple and sensitive histochemical method for calcium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 80:474–479; 1952
Doolin, E. J.; Geldziler, B.; Strande, L.; Kain, M.; Hewitt, C. Effects of microgravity on growing cultured skin constructs. Tissue Eng 5:573–582; 1999
Eiselt, P.; Kim, B. S.; Chacko, B.; Isenberg, B.; Peters, M. C.; Greene, K. G.; Roland, W. D.; Loebsack, A. B.; Burg, K. J.; Culberson, C.; Halberstadt, C. R.; Holder, W. D.; Mooney, D. J. Development of technologies aiding large-tissue engineering. Biotechnol Prog 14:134–140; 1998
Ferrera, D.; Poggi, S.; Biassoni, C.; Dickson, G. R.; Astigiano, S.; Barbieri, O.; Favre, A.; Franzi, A. T.; Strangio, A.; Federici, A.; Manduca, P. Three-dimensional cultures of normal human osteoblasts: proliferation and differentiation potential in vitro and upon ectopic implantation in nude mice. Bone 30:718–725; 2002
Freed, L. E.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Microgravity tissue engineering. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 33:381–385; 1997
Freed, L. E.; Hollander, A. P.; Martin, I.; Barry, J. R.; Langer, R.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Chondrogenesis in a cell-polymer-bioreactor system. Exp Cell Res 240:58–65; 1998
Freeman, E.; Turnbull, R. S. The value of osseous coagulum as a graft material. J Periodontal Res 8:229–236; 1973
Goldstein, A. S.; Juarez, T. M.; Helmke, C. D.; Gustin, M. C.; Mikos, A. G. Effect of convection on osteoblastic cell growth and function in biodegradable polymer foam scaffolds. Biomaterials 22:1279–1288; 2001
Granet, C.; Laroche. N.; Vico, L.; Alexandre, C.; Lafage-Proust, M. H. Rotating-wall vessels, promising bioreactors for osteoblastic cell culture: comparison with other 3D conditions. Med Biol Eng Comput 36:513–519; 1998
Gronowicz, G.; Woodiel, F. N.; McCarthy, M. B.; Raisz, L. G. In vitro mineralization of fetal rat parietal bones in defined serum-free medium: effect of β-glycerol phosphate. J Bone Miner Res 4(3):313–324; 1989
Hollinger, J. O.; Kleinschmidt, J. C. The critical size defect as an experimental model to test bone repair materials. J Craniofac Surg 1(1):60–68; 1990
Inoda, H.; Yamamoto, G.; Hattori, T. Histological investigation of osteoinductive properties of rh-BMP2 in a rat calvarial bone defect model. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 32(6):365–369; 2004
Khouja, H. I.; Bevington, A.; Kemp, G. J.; Russell, R. G. Calcium and orthophosphate deposits in vitro do not imply osteoblast-mediated mineralization: mineralization by betaglycerophosphate in the absence of osteoblasts. Bone 11:385–391; 1990
Klement, B. J.; Spooner, B. S. Utilization of microgravity bioreactors for differentiation of mammalian skeletal tissue. J Cell Biochem 51:252–256; 1993
Klement, B. J.; Young, Q. M.; George, B. J.; Nokkaew, M. Skeletal tissue growth, differentiation and mineralization in the NASA rotating wall vessel. Bone 34:478–498; 2004
Langer, R.; Vacanti, J. P. Tissue engineering. Science 260:920–926; 1993
Molnar, G.; Schroedl, N. A.; Gonda, S. R.; Hartzell, C. R. Skeletal muscle satellite cells cultured in simulated microgravity. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 33:386–391; 1997
Mulliken, J. B.; Glowacki, J. Induced osteogenesis for repair and construction in the craniofacial region. Plast Reconstr Surg 65:553–560; 1980
Ohsawa, K.; Neo, M.; Matsuoka, H.; Akiyama, H.; Ito, H.; Kohno, H.; Nakamura, T. The expression of bone matrix protein mRNAs around beta-TCP particles implanted into bone. J Biomed Mater Res 52:460–466; 2000
Parikh, S. N. Bone graft substitutes: past, present, future. J Postgrad Med 48:142–148; 2002
Pei, M.; Solchaga, L. A.; Seidel, J.; Zeng, L.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G.; Caplan, A. I.; Freed, L. E. Bioreactors mediate the effectiveness of tissue engineering scaffolds. FASEB J 16:1691–1694; 2002
Qiu, Q. Q.; Ducheyne, P.; Ayyaswamy, P. S. 3D bone tissue engineered with bioactive microspheres in simulated microgravity. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 37:157–165; 2001
Rattner, A.; Sabido, O.; Le, J.; Vico, L.; Massoubrem, C.; Frey, J.; Chamson, A. Mineralization and alkaline phosphatase activity in collagen lattices populated by human osteoblasts. Calcif Tissue Int 66:35–42; 2000
Sarber, R.; Hull, B.; Merrill, C.; Soranno, T.; Bell, E. Regulation of proliferation of fibroblasts of low and high population doubling levels grown in collagen lattices. Mech Ageing Dev 17:107–117; 1981
Schmitz, J. P.; Hollinger, J. O. The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res 205:299–308; 1986
Schwarz, R. P.; Goodwin, T. J.; Wolf, D. A. Cell culture for three-dimensional modeling in rotating-wall vessels: an application of simulated microgravity. J Tissue Cult Methods 14:51–57; 1992
Sikavitsas, V. I.; Bancroft, G. N.; Mikos, A. G. Formation of three-dimensional cell/polymer constructs for bone tissue engineering in a spinner flask and a rotating wall vessel bioreactor. J Biomed Mater Res 62:136–148; 2002
Spurr, A. R. A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43; 1969
Su, GN-C.; Hidaka, M.; Kimura, Y.; Yamamoto, G. In situ collagen gelation: a new method for constructing large tissue in rotary culture vessels. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 39:368–374; 2003
Yamaguchi, A.; Komori, T.; Suda, T. Regulation of osteoblast differentiation mediated by bone morphogenetic proteins, hedgehogs, and Cbfa1. Endocr Rev 21:393–441; 2000
Yu, X.; Botchwey, E. A.; Levine, E. M.; Pollack, S. R.; Laurencin, C. T. Bioreactor-based bone tissue engineering: the influence of dynamic flow on osteoblast phenotypic expression and matrix mineralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(31):11203–11208; 2004
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank Mr. T. Yamamoto in the Central Research Laboratory, Shiga University of Medical Science, Japan for his excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hidaka, M., Su, G.NC., Chen, J.KH. et al. Transplantation of engineered bone tissue using a rotary three-dimensional culture system. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 43, 49–58 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-006-9005-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11626-006-9005-1