Abstract
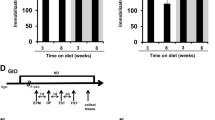
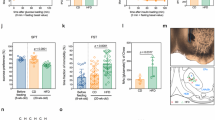
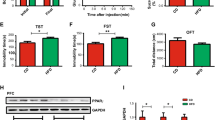
Obesity is considered as a risk factor for mood disorders including depression. Nevertheless, the mechanisms underlying this association are not clearly understood. To address this issue, we investigated the impact of high-fat (HF)-diet-induced obesity on depressive-like behavior and on serotonin (5-HT)-dependent Akt/glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) signaling in the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus, which has been associated with mood regulation. We first showed that a HF diet induced significant overweight and hyperglycemia as well as a depressive-like behavior in adult Wistar rats. By using an ex vivo approach on brain slices, we demonstrated that 5-HT activates the Akt/GSK3β cascade in the DG of control chow (C) diet-fed animals and that a 16-week HF diet feeding abolishes this activation, concurrently with a desensitization of leptin and insulin signaling in the same region. Furthermore, depressive-like behavior inversely correlated with 5-HT-induced phosphorylation of GSK3β in the subgranular neurons of the DG. Interestingly, a substitution of HF with C diet for 6 weeks induced a total loss of depressive symptoms, whereas body weight and glycemia remained significantly higher compared to control rats. In addition, food restoration led to a recovery of the Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway activation in the DG. In parallel, we observed a negative correlation between body weight and cell proliferation in the subgranular zone of the DG. To conclude, we provide evidence for a desensitization of 5-HT-induced Akt/GSK3β signaling and an impaired cell proliferation in the DG by HF diet, suggesting novel molecular mechanisms linking obesity to depression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malik VS, Willett WC, Hu FB (2013) Global obesity: trends, risk factors and policy implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 9(1):13–27
Faith MS, Butryn M, Wadden TA, Fabricatore A, Nguyen AM, Heymsfield SB (2011) Evidence for prospective associations among depression and obesity in population-based studies. Obes Rev 12(5):e438–e453
Wittchen HU, Jacobi F, Rehm J, Gustavsson A, Svensson M, Jonsson B, Olesen J, Allgulander C, Alonso J, Faravelli C, Fratiglioni L, Jennum P, Lieb R, Maercker A, van Os J, Preisig M, Salvador-Carulla L, Simon R, Steinhausen HC (2011) The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 21(9):655–679
Shomaker LB, Tanofsky-Kraff M, Stern EA, Miller R, Zocca JM, Field SE, Yanovski SZ, Hubbard VS, Yanovski JA (2011) Longitudinal study of depressive symptoms and progression of insulin resistance in youth at risk for adult obesity. Diabetes Care 34(11):2458–2463
Pan A, Keum N, Okereke OI, Sun Q, Kivimaki M, Rubin RR, Hu FB (2012) Bidirectional association between depression and metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Diabetes Care 35(5):1171–1180
Luppino FS, de Wit LM, Bouvy PF, Stijnen T, Cuijpers P, Penninx BW, Zitman FG (2010) Overweight, obesity, and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 67(3):220–229
Sutherland C, Leighton IA, Cohen P (1993) Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta by phosphorylation: new kinase connections in insulin and growth-factor signalling. Biochem J 296(Pt 1):15–19
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129(7):1261–1274
Benzler J, Ganjam GK, Kruger M, Pinkenburg O, Kutschke M, Stohr S, Steger J, Koch CE, Olkrug R, Schwartz MW, Shepherd PR, Grattan DR, Tups A (2012) Hypothalamic glycogen synthase kinase 3beta has a central role in the regulation of food intake and glucose metabolism. Biochem J 447(1):175–184
Konner AC, Bruning JC (2012) Selective insulin and leptin resistance in metabolic disorders. Cell Metab 16(2):144–152
Li X, Jope RS (2010) Is glycogen synthase kinase-3 a central modulator in mood regulation? Neuropsychopharmacology 35(11):2143–2154
Adli M, Hollinde DL, Stamm T, Wiethoff K, Tsahuridu M, Kirchheiner J, Heinz A, Bauer M (2007) Response to lithium augmentation in depression is associated with the glycogen synthase kinase 3-beta -50 T/C single nucleotide polymorphism. Biol Psychiatry 62(11):1295–1302
Ackermann TF, Kempe DS, Lang F, Lang UE (2010) Hyperactivity and enhanced curiosity of mice expressing PKB/SGK-resistant glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3). Cell Physiol Biochem 25(6):775–786
O’Brien WT, Harper AD, Jove F, Woodgett JR, Maretto S, Piccolo S, Klein PS (2004) Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta haploinsufficiency mimics the behavioral and molecular effects of lithium. J Neurosci 24(30):6791–6798
Kaidanovich-Beilin O, Milman A, Weizman A, Pick CG, Eldar-Finkelman H (2004) Rapid antidepressive-like activity of specific glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitor and its effect on beta-catenin in mouse hippocampus. Biol Psychiatry 55(8):781–784
Gould TD, Einat H, Bhat R, Manji HK (2004) AR-A014418, a selective GSK-3 inhibitor, produces antidepressant-like effects in the forced swim test. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 7(4):387–390
Belmaker RH, Agam G (2008) Major depressive disorder. N Engl J Med 358(1):55–68
Polter AM, Yang S, Jope RS, Li X (2012) Functional significance of glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulation by serotonin. Cell Signal 24(1):265–271
Li X, Zhu W, Roh MS, Friedman AB, Rosborough K, Jope RS (2004) In vivo regulation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK3beta) by serotonergic activity in mouse brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 29(8):1426–1431
Polter A, Beurel E, Yang S, Garner R, Song L, Miller CA, Sweatt JD, McMahon L, Bartolucci AA, Li X, Jope RS (2010) Deficiency in the inhibitory serine-phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 increases sensitivity to mood disturbances. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(8):1761–1774
Mamounas LA, Mullen CA, O’Hearn E, Molliver ME (1991) Dual serotoninergic projections to forebrain in the rat: morphologically distinct 5-HT axon terminals exhibit differential vulnerability to neurotoxic amphetamine derivatives. J Comp Neurol 314(3):558–586
Berumen LC, Rodriguez A, Miledi R, Garcia-Alcocer G (2012) Serotonin receptors in hippocampus. Scientific World Journal 2012:823493
Omata N, Chiu CT, Moya PR, Leng Y, Wang Z, Hunsberger JG, Leeds P, Chuang DM (2011) Lentivirally mediated GSK-3beta silencing in the hippocampal dentate gyrus induces antidepressant-like effects in stressed mice. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 14(5):711–717
Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, Weisstaub N, Lee J, Duman R, Arancio O, Belzung C, Hen R (2003) Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science 301(5634):805–809
Boldrini M, Hen R, Underwood MD, Rosoklija GB, Dwork AJ, Mann JJ, Arango V (2012) Hippocampal angiogenesis and progenitor cell proliferation are increased with antidepressant use in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 72(7):562–571
Vacher CM, Gassmann M, Desrayaud S, Challet E, Bradaia A, Hoyer D, Waldmeier P, Kaupmann K, Pevet P, Bettler B (2006) Hyperdopaminergia and altered locomotor activity in GABAB1-deficient mice. J Neurochem 97(4):979–991
Vacher CM, Hardin-Pouzet H, Steinbusch HW, Calas A, De Vente J (2003) The effects of nitric oxide on magnocellular neurons could involve multiple indirect cyclic GMP-dependent pathways. Eur J Neurosci 17(3):455–466
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 5th edn. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam; Boston
Couvreur O, Aubourg A, Crepin D, Degrouard J, Gertler A, Taouis M, Vacher CM (2012) The anorexigenic cytokine ciliary neurotrophic factor stimulates POMC gene expression via receptors localized in the nucleus of arcuate neurons. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 302(4):E458–E467
Cope EC, Morris DR, Scrimgeour AG, VanLandingham JW, Levenson CW (2011) Zinc supplementation provides behavioral resiliency in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Physiol Behav 104(5):942–947
Sclafani A, Abrams M (1986) Rats show only a weak preference for the artificial sweetener aspartame. Physiol Behav 37(2):253–256
Slattery DA, Cryan JF (2012) Using the rat forced swim test to assess antidepressant-like activity in rodents. Nat Protoc 7(6):1009–1014
Yamada N, Katsuura G, Ochi Y, Ebihara K, Kusakabe T, Hosoda K, Nakao K (2011) Impaired CNS leptin action is implicated in depression associated with obesity. Endocrinology 152(7):2634–2643
Sharma S, Fulton S (2012) Diet-induced obesity promotes depressive-like behaviour that is associated with neural adaptations in brain reward circuitry. Int J Obes (Lond) 37:382–389
Detke MJ, Lucki I (1996) Detection of serotonergic and noradrenergic antidepressants in the rat forced swimming test: the effects of water depth. Behav Brain Res 73(1–2):43–46
Drossopoulou G, Antoniou K, Kitraki E, Papathanasiou G, Papalexi E, Dalla C, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z (2004) Sex differences in behavioral, neurochemical and neuroendocrine effects induced by the forced swim test in rats. Neuroscience 126(4):849–857
Abildgaard A, Solskov L, Volke V, Harvey BH, Lund S, Wegener G (2011) A high-fat diet exacerbates depressive-like behavior in the Flinders Sensitive Line (FSL) rat, a genetic model of depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36(5):623–633
Grillo CA, Piroli GG, Kaigler KF, Wilson SP, Wilson MA, Reagan LP (2011) Downregulation of hypothalamic insulin receptor expression elicits depressive-like behaviors in rats. Behav Brain Res 222(1):230–235
Guo M, Huang TY, Garza JC, Chua SC, Lu XY (2012) Selective deletion of leptin receptors in adult hippocampus induces depression-related behaviours. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:857–867
Garza JC, Guo M, Zhang W, Lu XY (2012) Leptin restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis in a chronic unpredictable stress model of depression and reverses glucocorticoid-induced inhibition of GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Psychiatry 17(8):790–808
Hilakivi-Clarke LA, Wozniak KM, Durcan MJ, Linnoila M (1990) Behavior of streptozotocin-diabetic mice in tests of exploration, locomotion, anxiety, depression and aggression. Physiol Behav 48(3):429–433
Standaert ML, Kanoh Y, Sajan MP, Bandyopadhyay G, Farese RV (2002) Cbl, IRS-1, and IRS-2 mediate effects of rosiglitazone on PI3K, PKC-lambda, and glucose transport in 3T3/L1 adipocytes. Endocrinology 143(5):1705–1716
Sharma AN, Elased KM, Lucot JB (2012) Rosiglitazone treatment reversed depression—but not psychosis-like behavior of db/db diabetic mice. J Psychopharmacol 26(5):724–732
Scott MM, Lachey JL, Sternson SM, Lee CE, Elias CF, Friedman JM, Elmquist JK (2009) Leptin targets in the mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 514(5):518–532
Farrar CE, Huang CS, Clarke SG, Houser CR (2005) Increased cell proliferation and granule cell number in the dentate gyrus of protein repair-deficient mice. J Comp Neurol 493(4):524–537
Folli F, Bonfanti L, Renard E, Kahn CR, Merighi A (1994) Insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) distribution in the rat central nervous system. J Neurosci 14(11 Pt 1):6412–6422
Papazoglou I, Berthou F, Vicaire N, Rouch C, Markaki EM, Bailbe D, Portha B, Taouis M, Gerozissis K (2012) Hypothalamic serotonin-insulin signaling cross-talk and alterations in a type 2 diabetic model. Mol Cell Endocrinol 350(1):136–144
Banasr M, Hery M, Printemps R, Daszuta A (2004) Serotonin-induced increases in adult cell proliferation and neurogenesis are mediated through different and common 5-HT receptor subtypes in the dentate gyrus and the subventricular zone. Neuropsychopharmacology 29(3):450–460
Stranahan AM, Arumugam TV, Cutler RG, Lee K, Egan JM, Mattson MP (2008) Diabetes impairs hippocampal function through glucocorticoid-mediated effects on new and mature neurons. Nat Neurosci 11(3):309–317
Kim WY, Wang X, Wu Y, Doble BW, Patel S, Woodgett JR, Snider WD (2009) GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis. Nat Neurosci 12(11):1390–1397
Fabricatore AN, Wadden TA, Higginbotham AJ, Faulconbridge LF, Nguyen AM, Heymsfield SB, Faith MS (2011) Intentional weight loss and changes in symptoms of depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Obes (Lond) 35(11):1363–1376
Acknowledgments
We thank Alain Aubourg for technical assistance. We also thank Dr. Valérie Grange-Messent for her advice in designing the ex vivo brain slice experiments and Dr. Daniel Toledano for his help in performing the circular corridor test. We also thank Dr. Cristina Dalla for providing Observador ethological software and for her useful advice in analysis FST data and Joël Lefebvre for animal caring. This work was supported by the University Paris-Sud 11 and CNRS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papazoglou, I.K., Jean, A., Gertler, A. et al. Hippocampal GSK3β as a Molecular Link Between Obesity and Depression. Mol Neurobiol 52, 363–374 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8863-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8863-x