Abstract
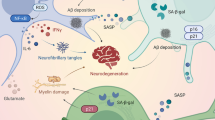
Cdk5 kinase, a cyclin-dependent kinase family member, is a key regulator of cytoskeletal remodeling in the brain. Cdk5 is essential for brain development during embryogenesis. After birth, it is essential for numerous neuronal processes such as learning and memory formation, drug addiction, pain signaling, and long-term behavior changes, all of which rely on rapid alterations in the cytoskeleton. Cdk5 activity is deregulated in various brain disorders including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and ischemic stroke, resulting in profound remodeling of the neuronal cytoskeleton, loss of synapses, and ultimately neurodegeneration. This review focuses on the “good and bad” Cdk5 in the brain and its pleiotropic contribution in regulating neuronal actin cytoskeletal remodeling. A vast majority of physiological and pathological Cdk5 substrates are associated with the actin cytoskeleton. Thus, our special emphasis is on the numerous Cdk5 substrates identified in the past two decades such as ephexin1, p27, Mst3, CaMKv, kalirin-7, RasGRF2, Pak1, WAVE1, neurabin-1, TrkB, 5-HT6R, talin, drebrin, synapsin I, synapsin III, CRMP1, GKAP, SPAR, PSD-95, and LRRK2. These substrates have unraveled the molecular mechanisms by which Cdk5 plays divergent roles in regulating neuronal actin cytoskeletal dynamics both in healthy and diseased states.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
β-Amyloid
- CAK:
-
Cdk-activating kinase
- CaMKv:
-
Calmodulin kinase-like vesicle-associated
- Cdk:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase
- Cdk1:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase-1
- Cdk2:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase-2
- Cdk5:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase-5
- CKI:
-
Cdk inhibitor protein
- CRMP1:
-
Collapsin response mediator protein-1
- EphA:
-
Ephrin receptor A
- GAP:
-
GTPase-activating protein
- GEF:
-
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
- GSTP1:
-
Glutathione S-transferase pi 1
- 5-HT6R:
-
5-Hydroxytryptamine-6 receptor
- LIMK:
-
LIM kinase
- LTD:
-
Long-term depression
- LTP:
-
Long-term potentiation
- MLCK:
-
Myosin light-chain kinase
- MT:
-
Microtubule
- Myt1:
-
Membrane-associated tyrosine- and threonine-specific cdc2-inhibitory kinase isoform 1
- NMDA:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate
- NMDAR:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor
- Pak1:
-
p21 activated kinase
- p21Cip1:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A
- p27Kip1:
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- TrkB:
-
Tropomyosin receptor kinase B
- VGCC:
-
Voltage-gated calcium channels
- WAVE1:
-
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP)-family verprolin homologous protein 1
References
Malumbres M, Harlow E, Hunt T, Hunter T, Lahti JM, Manning G, Morgan DO, Tsai LH et al (2009) Cyclin-dependent kinases: a family portrait. Nat Cell Biol 11:1275–1276. doi:10.1038/ncb1109-1275
Morgan DO (2007) The cell cycle: principles of control. New Science Press Ltd., London
Dhavan R, Tsai LH (2001) A decade of CDK5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(10):749–759. doi:10.1038/35096019
Shah K, Lahiri DK (2014) Cdk5 activity in the brain—multiple paths of regulation. J Cell Sci 127(11):2391–2400. doi:10.1242/jcs.147553
Shah K, Lahiri DK (2017) A tale of the good and bad: remodeling of the microtubule network in the brain by Cdk5. Mol Neurobiol 54(3):2255–2268. doi:10.1007/s12035-016-9792-7
Tsai LH, Delalle I, Caviness VS Jr, Chae T, Harlow E. (1994) p35 is a neural-specific regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. 371(6496), 419-23. doi: 10.1038/371419a0.
Tang D, Yeung J, Lee KY, Matsushita M, Matsui H, Tomizawa K, Hatase O, Wang JH. (1995) An isoform of the neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) activator. J Biol Chem. (45), 26897-903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.45.26897.
Brinkkoetter PT, Pippin JW, Shankland SJ (2010) Cyclin I-Cdk5 governs survival in post-mitotic cells. Cell Cycle 9(9):1729–1731. doi:10.4161/cc.9.9.11471
Sun KH, Chang KH, Clawson S, Ghosh S, Mirzaei H, Regnier F, Shah K (2011) Glutathione-S-transferase P1 is a critical regulator of Cdk5 kinase activity. J Neurochem 118(5):902–914. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07343.x
Modi PK, Komaravelli N, Singh N, Sharma P (2012) Interplay between MEK-ERK signaling, cyclin D1, and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 regulates cell cycle reentry and apoptosis of neurons. Mol Biol Cell 23(18):3722–3730. doi:10.1091/mbc.E12-02-0125
Odajima J, Wills ZP, Ndassa YM, Terunuma M, Kretschmannova K, Deeb TZ, Geng Y, Gawrzak S et al (2011) Cyclin E constrains Cdk5 activity to regulate synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Dev Cell 21(4):655–668. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2011.08.009
Fu WY, Chen Y, Sahin M, Zhao XS, Shi L, Bikoff JB, Lai KO, Yung WH et al (2007) Cdk5 regulates EphA4-mediated dendritic spine retraction through an ephexin1-dependent mechanism. Nat Neurosci 10(1):67–76. doi:10.1038/nn1811
Zukerberg LR, Patrick GN, Nikolic M, Humbert S, Wu CL, Lanier LM, Gertler FB, Vidal M et al (2000) Cables links Cdk5 and c-Abl and facilitates Cdk5 tyrosine phosphorylation, kinase upregulation, and neurite outgrowth. Neuron 26(3):633–646. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(00)81200-3
Sasaki Y, Cheng C, Uchida Y, Nakajima O, Ohshima T, Yagi T, Taniguchi M, Nakayama T et al (2002) Fyn and Cdk5 mediate semaphorin-3A signaling, which is involved in regulation of dendrite orientation in cerebral cortex. Neuron 35(5):907–920. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00857-7
Kobayashi H, Saito T, Sato K, Furusawa K, Hosokawa T, Tsutsumi K, Asada A, Kamada S et al (2014) Phosphorylation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) at Tyr-15 is inhibited by Cdk5 activators and does not contribute to the activation of Cdk5. J Biol Chem 289(28):19627–19636. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.501148
McLinden KA, Trunova S, Giniger E (2012) At the fulcrum in health and disease: Cdk5 and the balancing acts of neuronal structure and physiology. Brain Disord Ther (Suppl 1):001. doi:10.4172/2168-975X
Fischer A, Sananbenesi F, Schrick C, Spiess J, Radulovic J (2002) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is required for associative learning. J Neurosci 22(9):3700–3707. doi:10.3389/fnbeh.2013.00216
Takahashi S, Ohshima T, Cho A, Sreenath T, Iadarola MJ, Pant HC, Kim Y, Nairn AC et al (2005) Increased activity of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 leads to attenuation of cocaine-mediated dopamine signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(5):1737–1742. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409456102
Hawasli AH, Benavides DR, Nguyen C, Kansy JW, Hayashi K, Chambon P, Greengard P, Powell CM et al (2007) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 governs learning and synaptic plasticity via control of NMDAR degradation. Nat Neurosci 10(7):880–886. doi:10.1038/nn1914
Hisanaga S, Endo R (2010) Regulation and role of cyclin-dependent kinase activity in neuronal survival and death. J Neurochem 115(6):1309–1321. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.07050.x
Xi ZQ, Xiao F, Yuan J, Wang XF, Wang L, Quan FY, Liu GW (2009) Gene expression analysis on anterior temporal neocortex of patients with intractable epilepsy. Synapse 63(11):1017–1028. doi:10.1002/syn.20681
Drerup JM, Hayashi K, Cui H, Mettlach GL, Long MA, Marvin M, Sun X, Goldberg MS et al (2010) Attention-deficit/hyperactivity phenotype in mice lacking the cyclin-dependent kinase 5 cofactor p35. Biol Psychiatry 68(12):1163–1171. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.07.016
Venturin M, Guarnieri P, Natacci F, Stabile M, Tenconi R, Clementi M, Hernandez C, Thompson P et al (2004) Mental retardation and cardiovascular malformations in NF1 microdeleted patients point to candidate genes in 17q11.2. J Med Genet 41:35–41. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8817.2005.00203.x
Engmann O, Hortobágyi T, Pidsley R, Troakes C, Bernstein HG, Kreutz MR, Mill J, Nikolic M et al (2011) Schizophrenia is associated with dysregulation of a Cdk5 activator that regulates synaptic protein expression and cognition. Brain 134(Pt 8):2408–2421. doi:10.1093/brain/awr155
Cheung ZH, Ip NY (2012) Cdk5: a multifaceted kinase in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Cell Biol 22(3):169–175. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2011.11.003
Shukla V, Skuntz S, Pant HC (2012) Deregulated Cdk5 activity is involved in inducing Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Med Res 43(8):655–662. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2012.10.015
Meyer DA, Torres-Altoro MI, Tan Z, Tozzi A, Di Filippo M, DiNapoli V, Plattner F, Kansy JW et al (2014) Ischemic stroke injury is mediated by aberrant Cdk5. J Neurosci 34(24):8259–8267. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4368-13.2014
Lee MS, Kwon YT, Li M, Peng J, Friedlander RM, Tsai LH (2000) Neurotoxicity induces cleavage of p35 to p25 by calpain. Nature 405(6784):360–364. doi:10.1038/35012636
Sun KH, de Pablo Y, Vincent F, Johnson EO, Chavers AK, Shah K (2008) Novel genetic tools reveal Cdk5’s major role in Golgi fragmentation in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Biol Cell 19(7):3052–3069. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-11-1106
Sun KH, de Pablo Y, Vincent F, Shah K (2008) Deregulated Cdk5 promotes oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. J Neurochem 10:265–278. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05616.x
Sun KH, Lee HG, Smith MA, Shah K (2009) Direct and indirect roles of Cdk5 as an upstream regulator in the JNK cascade: relevance to neurotoxic insults in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Biol Cell 20(21):4611–4619. doi:10.1091/mbc.E09-05-0433
Chang KH, Pablo Y, Lee H, Lee H, Smith M, Shah K (2010) Cdk5 is a major regulator of p38 cascade: relevance to neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 113(5):1221–1229. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06687.x
Chang KH, Multani PS, Sun KH, Vincent F, de Pablo Y, Ghosh S, Gupta R, Lee HP et al (2011) Nuclear envelope dispersion triggered by deregulated Cdk5 precedes neuronal death. Mol Biol Cell 22(9):1452–1462. doi:10.1091/mbc.E10-07-0654
Chang KH, Vincent F, Shah K (2012) Deregulated Cdk5 triggers aberrant activation of cell cycle kinases and phosphatases inducing neuronal death. J Cell Sci 125(Pt 21):5124–5137. doi:10.1242/jcs.108183
Shi C, Viccaro K, Lee HG, Shah K (2016) Cdk5-FOXO3a axis: initially neuroprotective, eventually neurodegenerative in Alzheimer’s disease models. J Cell Sci 129:1815–1830. doi:10.1242/jcs.185009
Fletcher DA, Mullins RD (2010) Cell mechanics and the cytoskeleton. Nature 463(7280):485–492. doi:10.1038/nature08908
Ito Y, Asada A, Kobayashi H, Takano T, Sharma G, Saito T, Ohta Y, Amano M et al (2014) Preferential targeting of p39-activated Cdk5 to Rac1-induced lamellipodia. Mol Cell Neurosci 61:34–45. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2014.05.006
He L, Zhang Z, Yu Y, Ahmed S, Cheung NS, Qi RZ (2011) The neuronal p35 activator of Cdk5 is a novel F-actin binding and bundling protein. Cell Mol Life Sci 68(9):1633–1643. doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0562-9
Xu J, Tsutsumi K, Tokuraku K, Estes KA, Hisanaga S, Ikezu T (2011) Actin interaction and regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5/p35 complex activity. J Neurochem 116(2):192–204. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06824.x
Hotulainen P, Hoogenraad CC (2010) Actin in dendritic spines: connecting dynamics to function. J Cell Biol 189(4):619–629. doi:10.1083/jcb.201003008
Cingolani LA, Goda Y (2008) Actin in action: the interplay between the actin cytoskeleton and synaptic efficacy. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:344–356. doi:10.1038/nrn2373
Bourne JN, Harris KM (2008) Balancing structure and function at hippocampal dendritic spines. Annu Rev Neurosci 31:47–67. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.31.060407.125646
Yoshihara Y, De Roo M, Muller D (2009) Dendritic spine formation and stabilization. Curr Opin Neurobiol 19(2):146–153. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2009.05.013
Alvarez VA, Sabatini BL (2007) Anatomical and physiological plasticity of dendritic spines. Annu Rev Neurosci 30:79–97. doi:10.1146/annurev.neuro.30.051606.094222
Sheng M, Hoogenraad CC (2007) The postsynaptic architecture of excitatory synapses: a more quantitative view. Annu Rev Biochem 76:823–847. doi:10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.060805.160029
Renner M, Specht CG, Triller A (2008) Molecular dynamics of postsynaptic receptors and scaffold proteins. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18(5):532–540. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2008.09.009
Nikolic M, Dudek H, Kwon YT, Ramos YF, Tsai LH (1996) The cdk5/p35 kinase is essential for neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation. Genes Dev 10(7):816–825
Humbert S, Dhavan R, Tsai L (2000) p39 activates cdk5 in neurons, and is associated with the actin cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 6):975–983
Norrholm SD, Bibb JA, Nestler EJ, Ouimet CC, Taylor JR, Greengard P (2003) Cocaine-induced proliferation of dendritic spines in nucleus accumbens is dependent on the activity of cyclin-dependent kinase-5. Neuroscience 116(1):19–22. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(02)00560-2
Nobes CD, Hall A (1995) Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 81:53–62. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90370-4
Heasman SJ, Ridley AJ (2008) Mammalian Rho GTPases: new insights into their functions from in vivo studies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:690–701. doi:10.1038/nrm2476
Spiering D, Hodgson L (2011) Dynamics of the Rho-family small GTPases in actin regulation and motility. Cell Adhes Migr 5(2):170–180. doi:10.4161/cam.5.2.14403
Tashiro A, Minden A, Yuste R (2000) Regulation of dendritic spine morphology by the Rho family of small GTPases: antagonistic roles of Rac and Rho. Cereb Cortex 10:927–938. doi:10.1093/cercor/10.10.927
Fujita Y, Yamashita T (2014) Axon growth inhibition by RhoA/ROCK in the central nervous system. Front Neurosci 8:338. doi:10.3389/fnins.2014.00338
Liang Z, Zhan Y, Shen Y, Wong CC, Yates JR 3rd, Plattner F, Lai KO, Ip NY (2016) The pseudokinase CaMKv is required for the activity-dependent maintenance of dendritic spines. Nat Commun 7:13282. doi:10.1038/ncomms13282
Kawauchi T, Chihama K, Nabeshima Y, Hoshino M (2006) Cdk5 phosphorylates and stabilizes p27kip1 contributing to actin organization and cortical neuronal migration. Nat Cell Biol 8(1):17–26. doi:10.1038/ncb1338
Besson A, Gurian-West M, Schmidt A, Hall A, Roberts JM (2004) p27Kip1 modulates cell migration through the regulation of RhoA activation. Genes Dev 18(8):862–876. doi:10.1101/gad.1185504
Tang J, Ip JP, Ye T, Ng YP, Yung WH, Wu Z, Fang W, Fu AK et al (2014) Cdk5-dependent Mst3 phosphorylation and activity regulate neuronal migration through RhoA inhibition. J Neurosci 34(22):7425–7436. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5449-13.2014
Ma XM, Johnson RC, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2001) Expression of kalirin, a neuronal GDP/GTP exchange factor of the trio family, in the central nervous system of the adult rat. J Comp Neurol 429:388–402. doi:10.1002/1096-9861(20010115)429:3<388::AID-CNE3>3.0.CO;2-I
Penzes P, Johnson RC, Alam MR, Kambampati V, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2000) An isoform of kalirin, a brain-specific GDP/GTP exchange factor, is enriched in the postsynaptic density fraction. J Biol Chem 275:6395–6403. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.9.6395
Penzes P, Jones KA (2008) Dendritic spine dynamics—a key role for kalirin-7. Trends Neurosci 31(8):419–427. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2008.06.001
Ma XM, Huang J, Wang Y, Eipper BA, Mains RE (2003) Kalirin, a multifunctional Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor, is necessary for maintenance of hippocampal pyramidal neuron dendrites and dendritic spines. J Neurosci 23:10593–10603
Cahill ME, Xie Z, Day M, Photowala H, Barbolina MV, Miller CA, Weiss C, Radulovic J et al (2009) Kalirin regulates cortical spine morphogenesis and disease-related behavioral phenotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(31):13058–13063. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904636106
Ma XM (2010) Kalirin-7 is a key player in the formation of excitatory synapses in hippocampal neurons. Sci World J 10:1655–66. doi:10.1100/tsw.2010.148
Xin X, Wang Y, Ma XM, Rompolas P, Keutmann HT, Mains RE, Eipper BA (2008) Regulation of kalirin by Cdk5. J Cell Sci 121(Pt 15):2601–2611. doi:10.1242/jcs.016089
Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM, Gill GN (1999) Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat Cell Biol 1(5):253–259. doi:10.1038/12963
Singer BF, Neugebauer NM, Forneris J, Rodvelt KR, Li D, Bubula N, Vezina P (2014) Locomotor conditioning by amphetamine requires cyclin-dependent kinase 5 signaling in the nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology 85:243–252. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.05.033
Kesavapany S, Amin N, Zheng YL, Nijhara R, Jaffe H, Sihag R, Gutkind JS, Takahashi S et al (2004) p35/cyclin-dependent kinase 5 phosphorylation of ras guanine nucleotide releasing factor 2 (RasGRF2) mediates Rac-dependent extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activity, altering RasGRF2 and microtubule-associated protein 1b distribution in neurons. J Neurosci 24(18):4421–4431. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0690-04.2004
Causeret F, Jacobs T, Terao M, Heath O, Hoshino M, Nikolic M (2004) Neurabin-I is phosphorylated by Cdk5: implications for neuronal morphogenesis and cortical migration. Mol Biol Cell 18(11):4327–4342. doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-04-0372
Nikolic M, Chou MM, Lu W, Mayer BJ, Tsai LH (1998) The p35/Cdk5 kinase is a neuron-specific Rac effector that inhibits Pak1 activity. Nature 395(6698):194–198. doi:10.1038/26034
Sanders LC, Matsumura F, Bokoch GM, de Lanerolle P (1999) Inhibition of myosin light chain kinase by p21-activated kinase. Science 283(5410):2083–2085. doi:10.1126/science.283.5410.2083
Kim Y, Sung JY, Ceglia I, Lee KW, Ahn JH, Halford JM, Kim AM, Kwak SP et al (2006) Phosphorylation of WAVE1 regulates actin polymerization and dendritic spine morphology. Nature 442(7104):814–817. doi:10.1038/nature04976
Sung JY, Engmann O, Teylan MA, Nairn AC, Greengard P, Kim Y (2008) WAVE1 controls neuronal activity-induced mitochondrial distribution in dendritic spines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(8):3112–3116. doi:10.1073/pnas.0712180105
Ligon LA, Steward O (2000) Role of microtubules and actin filaments in the movement of mitochondria in the axons and dendrites of cultured hippocampal neurons. J Comp Neurol 427:351–361. doi:10.1002/1096-9861(20001120)427:3<351::AID-CNE3>3.0.CO;2-R
Cheung ZH, Chin WH, Chen Y, Ng YP, Ip NY (2007) Cdk5 is involved in BDNF-stimulated dendritic growth in hippocampal neurons. PLoS Biol 5(4):e63. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050063
Duhr F, Déléris P, Raynaud F, Séveno M, Morisset-Lopez S, Mannoury la Cour C, Millan MJ, Bockaert J et al (2014) Cdk5 induces constitutive activation of 5-HT6 receptors to promote neurite growth. Nat Chem Biol 10(7):590–597. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1547
Huang C, Rajfur Z, Yousefi N, Chen Z, Jacobson K, Ginsberg MH (2009) Talin phosphorylation by Cdk5 regulates Smurf1-mediated talin head ubiquitylation and cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 11(5):624–630. doi:10.1038/ncb1868
Worth DC, Daly CN, Geraldo S, Oozeer F, Gordon-Weeks PR (2013) Drebrin contains a cryptic F-actin-bundling activity regulated by Cdk5 phosphorylation. J Cell Biol 202(5):793–806. doi:10.1083/jcb.201303005
Tanabe K, Yamazaki H, Inaguma Y, Asada A, Kimura T, Takahashi J, Taoka M, Ohshima T et al (2014) Phosphorylation of drebrin by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and its role in neuronal migration. PLoS One 9(3):e92291. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0092291
Yao L, Liu YH, Li X, Ji YH, Yang XJ, Hang XT, Ding ZM, Liu F et al (2016) CRMP1 interacted with Spy1 during the collapse of growth cones induced by Sema3A and acted on regeneration after sciatic nerve crush. Mol Neurobiol 53(2):879–893. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-9049-2
Piccini A, Perlini LE, Cancedda L, Benfenati F, Giovedì S (2015) Phosphorylation by PKA and Cdk5 mediates the early effects of Synapsin III in neuronal morphological maturation. J Neurosci 35(38):13148–13159. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1379-15.2015
Pieribone VA, Porton B, Rendon B, Feng J, Greengard P, Kao HT (2002) Expression of synapsin III in nerve terminals and neurogenic regions of the adult brain. J Comp Neurol 454(2):105–114. doi:10.1002/cne.10417
Perlini LE, Szczurkowska J, Ballif BA, Piccini A, Sacchetti S, Giovedì S, Benfenati F, Cancedda L (2015) Synapsin III acts downstream of semaphorin 3A/CDK5 signaling to regulate radial migration and orientation of pyramidal neurons in vivo. Cell Rep 11(2):234–248. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.03.022
Kao HT, Porton B, Czernik AJ, Feng J, Yiu G, Häring M, Benfenati F, Greengard P (1998) A third member of the synapsin gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:4667–4672
Cesca F, Baldelli P, Valtorta F, Benfenati F (2010) The synapsins: key actors of synapse function and plasticity. Prog Neurobiol 91:313–348. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.04.006
Bykhovskaia M (2011) Synapsin regulation of vesicle organization and functional pools. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22:387–392. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2011.07.003
Verstegen AM, Tagliatti E, Lignani G, Marte A, Stolero T, Atias M, Corradi A, Valtorta F et al (2014) Phosphorylation of synapsin I by cyclin-dependent kinase-5 sets the ratio between the resting and recycling pools of synaptic vesicles at hippocampal synapses. J Neurosci 34(21):7266–7280. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3973-13.2014
Shuang R, Zhang L, Fletcher A, Groblewski GE, Pevsner J, Stuenkel EL (1998) Regulation of Munc-18/syntaxin 1A interaction by cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in nerve endings. J Biol Chem 273(9):4957–4966
Newey SE, Velamoor V, Govek EE, Van Aelst L (2005) Rho GTPases, dendritic structure, and mental retardation. J Neurobiol 64(1):58–74. doi:10.1002/neu.20153
Moncini S, Castronovo P, Murgia A, Russo S, Bedeschi MF, Lunghi M, Selicorni A, Bonati MT et al (2016) Functional characterization of CDK5 and CDK5R1 mutations identified in patients with non-syndromic intellectual disability. Hum Genet 61(4):283–293. doi:10.1038/jhg.2015.144
Imbrici P, Camerino DC, Tricarico D (2013) Major channels involved in neuropsychiatric disorders and therapeutic perspectives. Front Genet 4:76. doi:10.3389/fgene.2013.00076
Meyer DA, Richer E, Benkovic SA, Hayashi K, Kansy JW, Hale CF, Moy LY, Kim Y et al (2008) Striatal dysregulation of Cdk5 alters locomotor responses to cocaine, motor learning, and dendritic morphology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(47):18561–18566. doi:10.1073/pnas.0806078105
Chen X, Nelson CD, Li X, Winters CA, Azzam R, Sousa AA, Leapman RD, Gainer H et al (2011) PSD-95 is required to sustain the molecular organization of the postsynaptic density. J Neurosci 31(17):6329–6338. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5968-10.2011
Sugiyama Y, Kawabata I, Sobue K, Okabe S (2005) Determination of absolute protein numbers in single synapses by a GFP-based calibration technique. Nat Methods 2:677–684. doi:10.1038/nmeth783
Bats C, Groc L, Choquet D (2007) The interaction between Stargazin and PSD-95 regulates AMPA receptor surface trafficking. Neuron 53:719–734. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.01.030
Roselli F, Tirard M, Lu J, Hutzler P, Lamberti P, Livrea P, Morabito M, Almeida OF (2005) Soluble beta-amyloid1-40 induces NMDA-dependent degradation of postsynaptic density-95 at glutamatergic synapses. J Neurosci 25(48):11061–11070. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3034-05.2005
Roselli F, Livrea P, Almeida OF (2011) CDK5 is essential for soluble amyloid β-induced degradation of GKAP and remodeling of the synaptic actin cytoskeleton. PLoS One 6(7):e23097. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023097
Seeburg DP, Feliu-Mojer M, Gaiottino J, Pak DT, Sheng M (2008) Critical role of CDK5 and Polo-like kinase 2 in homeostatic synaptic plasticity during elevated activity. Neuron 58(4):571–583. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2008.03.021
Pak DT, Yang S, Rudolph-Correia S, Kim E, Sheng M (2001) Regulation of dendritic spine morphology by SPAR, a PSD-95-associated RapGAP. Neuron 31(2):289–303. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00355-5
Cookson MR (2010) The role of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(12):791–797. doi:10.1038/nrn2935
Shu Y, Ming J, Zhang P, Wang Q, Jiao F, Tian B (2016) Parkinson-related LRRK2 mutation R1628P enables Cdk5 phosphorylation of LRRK2 and upregulates its kinase activity. PLoS One 11(3):e0149739. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0149739
Parisiadou L, Xie C, Cho HJ, Lin X, Gu XL, Long CX, Lobbestael E, Baekelandt V et al (2009) Phosphorylation of ezrin/radixin/moesin proteins by LRRK2 promotes the rearrangement of actin cytoskeleton in neuronal morphogenesis. J Neurosci 29(44):13971–13980. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3799-09.2009
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIAR21AG 47447) to KS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, K., Rossie, S. Tale of the Good and the Bad Cdk5: Remodeling of the Actin Cytoskeleton in the Brain. Mol Neurobiol 55, 3426–3438 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0525-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0525-3
Keywords
- Cdk5
- p25
- p35
- β-Amyloid
- Neuronal cytoskeleton
- Actin
- Microtubules
- Remodeling
- Cdk
- Cyclins
- Neurodegeneration
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Dendritic spines
- Neurotransmitters
- Synaptic plasticity
- Learning and memory
- Neuronal migration
- Axonal growth
- Neurotransmitters
- Synaptogenesis
- Drug addiction
- Ephexin1
- p25
- Mst3
- CaMKv
- Kalirin-7
- RasGRF2
- Pak1
- WAVE1
- Neurabin-1
- TrkB
- 5-HT6R
- Talin
- Drebrin
- Synapsin I
- Synapsin III
- CRMP1
- GKAP
- SPAR
- PSD-95
- LRRK2