Abstract
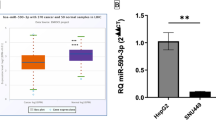
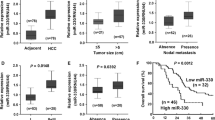
MicroRNA 144 (miR-144), a small non-coding RNA, is frequently dysregulated in human several tumour progression, but its role and the underlying mechanisms in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is poorly investigated. In the present study, the expression of miR-144 was firstly analysed in datasets derived from GSE21362 and TCGA, and then detected in HCC tissues and cell lines by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis. MiR-144 was shown to be significantly down-regulated in HCC tissues and cell lines. Subsequently, overexpression of miR-144 was transfected into HCC cell lines so as to investigate its biological function, including MTT, colony formation, and transwell assays. Gain of function assay revealed miR-144 remarkably inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion. In addition, bioinformatical analysis and luciferase reporter assay identified ZFX as a novel target of miR-144 in HCC cells, as confirmed by qRT-PCR and Western blot. Furthermore, ZFX was found to be significantly up-regulated using Oncomine database analysis. Loss of function assay further indicated knockdown of ZFX had similar effects of miR-144-mediated HCC cell proliferation and invasion. Therefore, miR-144 has been demonstrated to act as a tumour suppressor in HCC cell growth and motility by directly targeting ZFX, which implicates its potential applications in the development of HCC treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bao RF, Shu YJ, Hu YP, Wang XA, Zhang F, Liang HB, Ye YY, Li HF et al. 2016 miR-101 targeting ZFX suppresses tumor proliferation and metastasis by regulating the MAPK/Erk and smad pathways in gallbladder carcinoma. Oncotarget 19 22339--22354
Bartel DP 2009 MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136 215–233
Dhanasekaran R et al. 2012 Hepatocellular carcinoma: current trends in worldwide epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis, and therapeutics. Hepat. Med. Evid. Res. 4 19–37
Hao W et al. 2015 Zinc finger X-chromosomal protein (ZFX) is a significant prognostic indicator and promotes cellular malignant potential in gallbladder cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 16 1462–1470
Higashi T et al. 2015 miR-9-3p plays a tumour-suppressor role by targeting TAZ (WWTR1) in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 113 252–258
Iwaya T et al. 2012 Downregulation of miR-144 is associated with colorectal cancer progression via activation of mTOR signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 33 2391–2397
Jiang J, et al. 2015 Zinc finger protein X-linked is overexpressed in colorectal cancer and is associated with poor prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 10 810
Lai KP et al. 2014 Overexpression of ZFX confers self-renewal and chemoresistance properties in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 135 1790–1799
Li C et al. 2014 ZFX is a strong predictor of poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 21 3380–3385
Li K et al. 2013 ZFX knockdown inhibits growth and migration of non-small cell lung carcinoma cell line H1299. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 6 2460–2467
Liu M et al. 2016 Downregulating microRNA-144 mediates a metabolic shift in lung cancer cells by regulating GLUT1 expression. Oncol. Lett. 11 3772–3776
Paranjape T et al. 2009 MicroRNAs: tools for cancer diagnostics. Gut. 58 1546–1554
Rossing M et al. 2012 Down-regulation of microRNAs controlling tumourigenic factors in follicular thyroid carcinoma. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 48 11–23
Shukla GC et al. 2011 MicroRNAs: processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory functions. Mol. Cell. Pharmacol. 3 83–92
Song G et al. 2010 MicroRNAs control hepatocyte proliferation during liver regeneration. Hepatology 51 1735–1743
Song X et al. 2015 Loss of miR-532-5p in vitro promotes cell proliferation and metastasis by influencing CXCL2 expression in HCC. Am. J. Transl. Res. 7 2254–2261
Tang B et al. 2013 Stable isotope dimethyl labeling combined with LTQ mass spectrometric detection, a quantitative proteomics technology used in liver cancer research. Biomed. Rep. 1 549–554
Voorhoeve PM 2010 MicroRNAs: oncogenes, tumor suppressors or master regulators of cancer heterogeneity? Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1805 72–86
Xiang C, Cui SP and Ke Y 2016 MiR-144 inhibits cell proliferation of renal cell carcinoma by targeting MTOR. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 36 186–192
Xiao R et al. 2015 miRNA-144 suppresses proliferation and migration of colorectal cancer cells through GSPT1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 74 138–144
Xie BH et al. 2016 Mir-765 promotes cell proliferation by downregulating INPP4B expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 16 405–413
Yang X et al. 2014 MicroRNA-26a suppresses angiogenesis in human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting hepatocyte growth factor-cMet pathway. Hepatology 59 1874–1885
Zhang B et al. 2007 microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors (Inc: John Wiley & Sons)
Zhang LY et al. 2012 MicroRNA-144 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma through repression of PTEN. Carcinogenesis 34 454–463
Zhou J et al. 2011 Analysis of microRNA expression profiling identifies microRNA-503 regulates metastatic function in hepatocellular cancer cell. J. Surg. Oncol. 104 278–283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Bao H, Li X, Li H, Xing H, Xu B, Zhang X and Liu Z 2017 MicroRNA-144 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting ZFX. J. Biosci.]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, H., Li, X., Li, H. et al. MicroRNA-144 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation, invasion and migration by targeting ZFX. J Biosci 42, 103–111 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-016-9662-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-016-9662-5