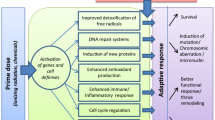
Abstract
Humans are continuously exposed to ionizing radiation throughout life from natural sources that include cosmic, solar, and terrestrial. Much harsher natural radiation and chemical environments existed during our planet’s early years. Mammals survived the harsher environments via evolutionarily-conserved gifts ̶ a continuously evolving system of stress-induced natural protective measures (i.e., activated natural protection [ANP]). The current protective system is differentially activated by stochastic (i.e., variable) low-radiation-dose thresholds and when optimally activated in mammals includes antioxidants, DNA damage repair, p53-related apoptosis of severely-damaged cells, reactive-oxygen-species (ROS)/reactive-nitrogen-species (RNS)- and cytokine-regulated auxiliary apoptosis that selectively removes aberrant cells (e.g., precancerous cells), suppression of disease promoting inflammation, and immunity against cancer cells. The intercellular-signaling-based protective system is regulated at least in part via epigenetic reprogramming of adaptive-response genes. When the system is optimally activated, it protects against cancer and some other diseases, thereby leading to hormetic phenotypes (e.g., reduced disease incidence to below the baseline level; reduced pain from inflammation-related problems). Here, some expressed radiation hormesis phenotypes and related mechanisms are discussed along with their implications for disease prevention and therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADCC :
-
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity
- ANP :
-
activated natural protection
- B[a]P :
-
benzo[a]pyrene
- BPDE :
-
benzo[a]pyrene diolepoxide
- CAF :
-
cancer-associated fibroblasts
- CCL2 :
-
chmokine system CC ligand 2
- CCR2 :
-
receptor CC 2
- CIA :
-
collagen-induced arthritis
- CLF1 :
-
cytokine-like factor 1
- CNTFR :
-
ciliary neurotropic factor receptor
- DNA :
-
deoxyribonucleic acid
- epiactivation :
-
epigenetic activation
- epiregulated :
-
epigenetically regulated
- epicellcom :
-
epigenetically regulated cell community wide
- epireprogramming :
-
epigenetic reprogramming
- episilencing :
-
epigenetically silencing
- γ-GCS :
-
γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase
- GPx :
-
glutathione peroxidase
- GR :
-
glutathione reductase
- GSH :
-
reduced glutathione
- HBEC :
-
human bronchial epithelial cells
- HRR :
-
hormetic relative risk
- IFN-γ :
-
interferon-gamma
- IL-6 :
-
interleukin-6
- IL-6R :
-
interleukin-6 receptor
- p53 :
-
tumor protein
- LET :
-
linear energy transfer
- MC :
-
methylcholanthrene
- MC4R :
-
melanocortin 4 receptor
- miRNA :
-
microRNA
- NK :
-
natural killer
- PAM :
-
protective-apoptosis-mediated
- OVA :
-
ovalbumin
- RNS :
-
reactive nitrogen species
- ROS :
-
reactive oxygen species
- SiRNA :
-
small interfering RNA
- SOD :
-
superoxide dismutase
- SPF :
-
specific pathogen free
- STAT 3 :
-
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- TGF-β :
-
transforming growth factor β
- TNF-α :
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha
- Tregs :
-
regulatory T cells
- TRX :
-
thioredoxin
References
Averbeck D (2009) Does scientific evidence support a change from the LNT model for low-dose radiation risk extrapolation? Health Phys 95:493–504
Azzam EI, de Toledo SM, Raaphorst GP, Mitchel RE (1996) Low-dose ionizing radiation decreases the frequency of neoplastic transformation to a level below the spontaneous rate in C3H 10T1/2 cells. Radiat Res 146:369–373
Bauer G (2007) Low dose radiation and intercellular induction of apoptosis: potential implications for control of oncogenesis. Int J Radiat Biol 83:873–888
Bernal AJ, Dolinoy DC, Huang D, Skaar DA, Weinhouse C, Jirtle RL (2013) Adaptive radiation-induced epigenetic alterations mitigated by antioxidants. FASEB J 27(2):665–671
Bhatia AL (2008) Radiation exposure and evolutionary perspectives with special reference to neutral theory. Int J Low Radiat 5(2):113–122
Bruce V, Belinsky SA, Gott K, Liu Y, March T, Scott B, Wilder J (2012) Low-dose gamma-radiation inhibits benzo[a]pyrene-induced lung adenoma development in A/J mice. Dose Response 10:516–526
Calabrese EJ, Baldwin LA (1999) Reevaluation of the fundamental dose–response relationship. A new database suggests that the u-shaped, rather than the sigmoidal, curve predominates. BioSci 49(9):725–732
Calabrese EJ, Baldwin LA (2003) The hormetic dose–response model is more common than the threshold model in toxicology. Toxicol Sci 71:246–250
Calabrese EJ, Calabrese V (2013) Reduction of arthritic symptoms by low-dose radiation therapy (LD-RT) is associated with an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Int J Radiat Biol 89:278–l286
Calabrese EJ, Dhawan G (2014) Historical use of x-rays: treatment of inner ear infections and prevention of deafness. Hum Exp Toxicol 33(5):542–553
Calabrese EJ, Bachmann KA, Bailer AJ et al (2007) Biological stress response terminology: Integrating the concepts of adaptive response ad preconditioning stress within a hormetic dose–response framework. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 222:122–128
Cheda A, Wrembel-Wargocka J, Lisiak E, Nowosielska EM, Marciniak M, Janiak MK (2004a) Single low does of X-rays inhibit development of experimental tumor metastases and trigger the activities of NK cells in mice. Radiat Res 161:335–340
Cheda A, Wrembel-Wargocka J, Lisiak E, Marciniak M, Nowosielska EM, Janiak MK (2004b) Inhibition of the development of pulmonary tumor nodules and stimulation of the activity of NK cells and macrophages in mice by single low doses of low-LET radiation. Int J Low Radiat 1:171–179
Chen WL, Luan YC, Shieh MC, Chen ST, Kung HT, Soong KL, Yeh YC, Chou TS, Mong SH, Wu JT, Sun CP, Deng WP, Wu MF, Shen ML (2007) Effects of cobalt-60 exposure on health of Taiwan residents suggest new approach needed in radiation protection. Dose Response 5:63–75
Chen W, Xu X, Bai L, Padilla MT, Gott KM, Leng S, Tellez CS, Wilder JA, Belinsky SA, Scott BR, Lin Y (2012) Low dose gamma-irradiation inhibits IL-6 secretion from human lung fibroblasts that promotes bronchial epithelial cell transformation by cigarette-smoke carcinogens. Carcinogenesis 33(7):1368–1374
Cohen BL (2008) The linear no-threshold theory of radiation carcinogenesis should be rejected. J Am Phys Surg 13(3):70–76
Cuttler JM (2010) Commentary on using LNT for radiation protection and risk assessment. Dose Response 8(3):378–383
Day TK, Zeng G, Hooker AM, Bhat M, Scott BR, Turner DR, Sykes PJ (2007) Adaptive response for chromosomal inversions in pKZ1 mouse prostate induced by low doses of X radaition delivered after a high dose. Radiat Res 167(6):682–692
Ducoff HS (1975) Forms of increased longevity of Tribolium after X-irradiation. Exp Gerontol 10:189–193
Ducoff HS (2002) Radiation hormesis: incredible or inevitable? Korean J Biol Sci 6:187–193
Duhl DM, Vrieling H, Miller KA, Wolff GL, Barsh GS (1994) Neomorphic agouti mutations in obese yellow mice. Nat Genet 8:6–11
Elmore E, Lao XY, Kapadia R, Giedzinski E, Limoli C, Redpath JL (2008) Low doses of very low-dose-rate low-LET radiation suppress radiation-induced neoplastic transformation in vitro and induce an adaptive response. Radiat Res 169(3):311–318
Feinendegen LE, Paretzke HG, Neumann RD (2007a) Damage propagation in complex biological systems following exposure to low doses of ionizing radiation. Atoms Peace 1:336–354
Feinendegen LE, Pollycove M, Neumann RD (2007b) Whole-body responses to low-level radiation exposure: new concepts in mammalian radiobiology. Exp Hematol 35(Suppl 1):37–46
Fornalski KW, Dobrzyński L (2012) The cancer mortality rate in high natural radiation areas in Poland. Dose Response 10(4):541–562
Hart J (2010) Mean cancer mortality rates in low versus high elevation counties in Texas. Dose Response 8(4):448–455
Hart J (2011a) Cancer mortality for a single race in low versus high elevation counties in the U.S. Dose response 9(3):348–355
Hart J (2011b) Lung cancer in Oregon. Dose Response 9(3):410–415
Hashimoto S, Shirato H, Hosokawa M, Nishioka T, Kuramitsu Y, Matsushita K, Kobayashi M, Miyasaka K (1999) The suppression of metastases and the change in host immune response after low-dose total-body irradiation in tumor-bearing rats. Radiat Res 151:717–724
Hayase H, Ohshima Y, Takahashi M, Kojima S (2013) The enhancement of Th1 immunity and the suppression tumor growth by low-dose γ-radiation. Int J of Low Radiat 5:275–298
Jaworowski Z. (1999) Radiation risk and ethics. Phys Today, September:24 − 29
Jaworowski A (2008) The paradigm that failed. Int J Low Radiat 5(2):151–155
Jaworowski Z (2010a) Observations of the Chernobyl disaster and LNT. Dose Response 8(2):148–171
Jaworowski Z (2010b) Radiation hormesis − a remedy for fear. Hum Exp Toxicol 29:263–270
Karam PA, Leslie SA (1999) Calculation of background beta-gamma radiation dose through geologic time. Health Phys 77(6):662–667
Kataoka T (2013) Study of the antioxidative effects and anti-inflammatory effects in mice due to low-dose X-irradiation or radon inhalation. J Radiat Res 54(4):587–596
Katz R, Waligorski MPR (1994) On the linear extrapolation to low doses. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 52(1–4):197–199
Kawakita Y, Ikekita M, Kurozumi R et al (2003) Increase of intracellular glutathione by low-dose gamma-ray irradiation is mediated by transcription factor AP-1 in RAW 264.7 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 36:19–23
Koana T, Okada MO, Ogura K, Tsujimura H, Sakai K (2007) Reduction of background mutations by low-dose X irradiation of Drosophila spermatocytes at a low dose rate. Radiat Res 167:217–221
Kojima S, Matsuki O, Nomura T et al (1998a) Induction of mRNAs for glutathione synthesis-related proteins in mouse liver by low doses of γ-rays. Biochem Biophys Acta 1381:312–318
Kojima S, Matsuki O, Nomura T et al (1998b) Localization of glutathione and induction of glutathione synthesis-related proteins in mouse brain by low doses of γ rays. Brain Res 808:262–269
Kojima S, Ishida H, Takahasji M, Yamaoka K (2002) Elevation of glutathione induced by low-dose gamma rays and its involvement in increased natural killer activity. Radiat Res 157:275–280
Kojima S, Nakayama K, Ishida H (2004) Low dose γ-rays activate immune function via induction of glutathione and delay tumor growth. J Radiat Res 45:33–39
Kondo S (1993) Health effects of low-level radiation. Kinki University Press, Osaka, Japan, Medical Physics Publishing, Madison, WI, USA
Kondo S (1998) Apoptotic repair of genotoxic tissue damage and the role of p53 gene. Mutat Res 402:311–319
Lacoste-Collin L, Jozan S, Cances-Lauwers V, Pipy B, Gasset G, Caratero C, Courtade-Saïdo M (2007) Effect of continuous irradiation with very low doses of gamma rays on life span and the immune system in SJL mice prone to B-cell lymphoma. Radiat Res 168:725–732
Leung AKL, Sharp PA (2010) MicroRNA functions in stress responses. Mol Cell 40:205–215
Liu S-Z (2007) Cancer control related to stimulation of immunity by low-dose radiation. Dose Response 5:39–47
Luckey TD (1980) Hormesis with ionizing radiation. CRC Press, Florida
Luckey TD (1991) Radiation Hormesis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Makinodan T, James SJ (1990) T cell potentiation by low dose ionizing radiation: possible mechanisms. Health Phys 59(1):29–34
Mifune M, Sobue T, Arimoto H, Komoto Y, Kondo S, Tanooka H (1992) Cancer mortality survey in a spa area (Misasa, Japan) with a high radon background. Jpn J Cancer Res 83:1–5
Mitchel REJ, Jackson JS, Morrison DP, Carlisle SM (2003) Low doses of radiation increase the latency of spontaneous lymphomas and spinal osteosarcomas in cancer prone, radiation sensitive Trp53 heterozygous mice. Radiat Res 159:320–327
Mitsunobu F, Yamaoka K, Hanamoto K, Kojima S, Hosaki Y, Ashida K, Sugita K, Tanizaki Y (2003) Elevation of antioxidant enzymes in the clinical effects of radon and thermal therapy for bronchial asthma. J Radiat Res 44:95–99
Miura Y (2004) Oxidative stress, radiation adaptive responses, and aging. J Radiat Res 45(3):357–372
Muller HJ (1927) Artificial transmutation of the gene. Science 46:84–87
Muller HJ (1954) The manner of production of mutations by radiation. Radiat Biol, vol 1. Chap. 8, McGraw-Hill Book Co. Inc.: 475 − 626
Nakatsukasa H, Tsukimoto M, Ohshima Y, Tago F, Masada A, Kojima S (2008) Suppressing effect of low-dose gamma-ray irradiation on collagen-induced arthritis. J Radiat Res 49:381–389
Nakatsukasa H, Tsukimoto M, Tokuaga A, Kojima S (2010) Repeated gamma irradiation attenuates collagen-induced arthritis via up-regulation of regulator T cells but not by damaging lymphocytes directly. Radiat Res 174:313–324
Nomura T, Sakai K, Ogata H, Magae J (2013) Prolongation of life span in the accelerated aging klotho mouse model, by low-dose-rate continuous γ irradiation. Radiat Res 179:717–724
Nowosielska EM, Wrembel-Wargocka J, Cheda A, Lisiak E, Janiak MK (2006) Enhanced cytotoxic activity of macrophages and suppressed tumor metastases in mice irradiated with low dose x-rays. J Radiat Res 47:229–236
Nowosielska EM, Cheda A, Wrembel-Wargochka J, Janiak MK (2010) Immunological mechanism of the low-dose radiation-induced suppression of cancer metastases in a mouse model. Dose Response 8(2):209–226
Ogura K, Magae J, Kawakami Y, Koana T (2009) Reduction in mutation frequency by very low-dose gamma irradiation of Drosophila melanogaster germ cells. Radiat Res 171:1–8
Orient J (2014) Fukushima and reflections on radiation as a terror weapon. J Am Phys Surg 19(2):48–55
Park BS, Hong GU, Ro JY (2013) Foxp3 + -Treg cells enhanced by repeated low-dose gamma-irradiation attenuate ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma in mice. Radiat Res 179(5):570–583
Pollycove M (2006) Radiobiological basis of low-dose irradiation in prevention and therapy of cancer. Dose Response 5(1):26–38
Pollycove M, Feinendegen L (2008) Low dose radioimmunotherapy for cancer. Hum Exp Toxicol 27(2):169–175
Portess DI, Bauer G, Hill M et al (2007) Low-dose irradiation of nontransformed cells stimulate the selective removal of precancerous cells via intercellular induction of apoptosis. Cancer Res 67:1246–1253
Redpath JL, Antoniono RJ (1998) Induction of an adaptive response against spontaneous neoplastic transformation in vitro by low-dose gamma radiation. Radiat Res 149(5):517–520
Redpath JL, Liang D, Taylor TH, James C, Christie E, Elmore E (2001) The shape of the dose–response curve for radiation-induced neoplastic transformation in vitro: Evidence for an adaptive response against neoplastic transformation at low doses of low-LET radiation. Radiat Res 156:700–707
Redpath JL, Short SC, Woodcock M, Johnston PJ (2003) Low-dose reduction in transformation frequency compared to unirradiated controls: the role of hyper-radiosensitivity to cell death. Radiat Res 159(3):433–436
Rithidech K, Scott BR (2008) Evidence for radiation hormesis after in vitro exposure of human lymphocytes to low doses of ionizing radiation. Dose Response 6:252–271
Rödel F, Frey B, Gaipl U, Keilholz L, Fournier C, Manda K, Scöllnberger H, Hildebrandt G, Rödel C (2012) Modulation of inflammatory immune reactions by low-dose radiation: molecular mechanisms and clinical application. Curr Med Chem 19:1741–1750
Rothkamm K, Löbrich M (2003) Evidence for a lack of DNA double-strand break repair in human cells exposed to very low x-ray doses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(9):5057–5062
Sakai K (2006) Enhancement of bio-protective functions by low dose/dose-rate radiation. Dose Response 4:327–332
Sakai K, Hoshi Y, Nomura T, Oda T, Iwasaki T, Fujita K, Yamada T, Tanooka H (2003) Suppression of carcinogenic process in mice by chronic low dose rate gamma-irradiation. Int J Low Radiat 1:142–146
Sanders CL (2010) Radiation hormesis and the linear-no-threshold assumption, 1st edn. Springer, Heidelberg
Sanders CL, Scott BR (2008) Smoking and hormesis as confounding factors in radiation pulmonary carcinogenesis. Dose Response 6:53–79
Sawat A (2000) The immunobiology of low-dose total-body irradiation: more questions than answers. Radiat Res 153:599–604
Scott BR (2004) A biological-based model that links genomic instability, bystander effects, and adaptive response. Mutat Res 568(1):129–143
Scott BR (2005) Stochastic thresholds: a novel explanation of nonlinear dose–response relationships for stochastic radiobiological effects. Dose Response 3(4):547–567
Scott BR (2008a) It’s time for a new low-dose-radiation risk assessment paradigm − one that acknowledges hormesis. Dose Response 6:333–351
Scott BR (2008b) Low-dose risk extrapolation fallacy associated with the linear-no-threshold model. Hum Exp Toxicol 27:163–168
Scott BR (2011a) Modeling DNA double-strand break repair kinetics as an epiregulated cell-community-wide (epicellcom) response to radiation stress. Dose Response 9:579–601
Scott BR (2011b) Residential radon appears to prevent lung cancer. Dose Response 9:444–464
Scott BR (2013) First generation stochastic gene episilencing (STEP1) model and applications to in vitro cancinogen exposure. Dose Response 11:9–28
Scott BR, Sanders CL, Mitchel REJ, Boreham DR (2008) CT scans may reduce rather than increase the risk of cancer. J Am Phys Surg 13:8–11
Scott BR, Belinsky SA, Leng S, Lin L, Wilder JA, Damiani LA (2009) Radiation-stimulated epigenetic reprogramming of adaptive-response genes in the lung: an evolutionary gift for mounting adaptive protection against lung cancer. Dose Response 7:104–131
Takahashi M, Kojima S (2006) Suppression of atopic dermatitis and tumor metastasis in mice by small amounts of radon. Radiat Res 165:337–342
Takatori M, Hattori S, Yagi M (2010) Clinical significance of low-dose radiation therapy: radiation hormesis. Int J Low Rad 7(6):51–519
Thompson RE, Nelson DF, Popkin JH, Popkin Z (2008) Case–control study of lung cancer risk from residential radon exposure in Worchester County, Massachusetts. Health Phys 94(3):228–241
Tremme J, Bauer G (2013) Low-dose gamma irradiation enhances superoxide anion production by nonirradiated cells through TGF-β1-dependent bystander signaling. Radiat Res 179:422–432
Tubiana M (2008) The 2007 Marie Curie prize: the linear no threshold relationship and advances in our understanding of carcinogenesis. Int J Low Radiat 5(3):173–204
Tubiana MF, Feinendegen LE, Yang C, Kaminski JM (2009) The linear no-threshold relationship is inconsistent with radiation biologic and experimental data. Radiology 251:13–22
Vaiserman AM (2011) Hormesis and epigenetics: is there a link? Ageing Res Rev 10:413–421
Vicent S, Sayles LC, Vaka D, Khatri P, Gavaert O, Chen R, Zheng Y, Gillespie AK, Clarke N, Xu Y, Shrager J, Hoang CD, Plevritis S, Butte AJ, Seweet-Cordero EA (2012) Cross-species functional analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts identifies a critical role for CLCF1 and IL-6 in non-small cell lung cancer in vivo. Cancer Res 72(22):5744–5756
Wei L-C, Ding Y-X, Liu Y-H, Duan L, Bai Y, Shi M, Chen L-W (2012) Low-dose radiation stimulates Wtn/β-catenin signaling, neural stem cell proliferation and neurogenesis of the mouse hippocampus in vitro and in vivo. Curr Alzheimer Res 9:278–289
Wolf S (1992) “Is radiation all bad? The search for adaptation”, the Failla memorial lecture. Radiat Res 131(2):117–123
Wolff S (1998) The adaptive response in radiobiology: evolving insights and implications. Environ Health Perspect 106:277–283
Yamaoka K, Kojima S, Takahashi M et al (1998) Change in glutathione peroxidase synthesis along with that of superoxide dismutase synthesis in mice spleens after low-dose X-ray irradiation. Biochem Biophys Acta 1381:265–270
Acknowledgments
The preparation of this manuscript was supported in part by the Office of Science (BER), U.S. Department of Energy, Grant No. DE-FG02-09ER64783 and in part by Lovelace Respiratory Research Institute. The paper is dedicated to the memory of Professor Howard Ducoff who made numerous important contributions to radiation hormesis research through his work with insects as well as through the work of those he mentored during his life, including the author of this paper. The author (BRS) is a founder member of Scientists for Accurate Radiation Information (SARI; www.radiationeffects.org), a group that includes several authors of radiation hormesis publications. The author confirms independence from the sponsors; the content of the article has not been influenced by the sponsors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, B.R. Radiation-hormesis phenotypes, the related mechanisms and implications for disease prevention and therapy. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 8, 341–352 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-014-0250-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-014-0250-x