Abstract
Viral myocarditis (VM) is an inflammatory disease of the myocardium associated with heart failure, which is caused by common viral infections. A majority of the infections are initiated by coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have a major role in various biological processes, including gene expression, cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis, as well as viral infection and antiviral immune responses. Although, miRNAs have been found to regulate viral infections, their role in CVB3 infection remains poorly understood. In the previous study, miRNA microarray results showed that miR-324-3p expression levels were significantly increased when cells and mice were infected with CVB3. It was also found that miR-324-3p downregulated TRIM27 and decreased CVB3 replication in vitro and in vivo. In vitro, analysis of downstream signaling of TRIM27 revealed that, miR-324-3p inhibited CVB3 infection, and reduced cytopathic effect and viral plaque formation by reducing the expression of TRIM27. In vivo, miR-324-3p decreased the expression of TRIM27, reduced cardiac viral replication and load, thereby strongly attenuating cardiac injury and inflammation. Taken together, this study suggests that miR-324-3p targets TRIM27 to inhibit CVB3 replication and viral load, thereby reducing the cardiac injury associated with VM.







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 October 2021
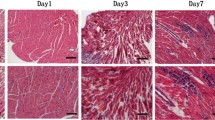
Error in Figure 1 has been corrected.
References
Amitava M, Morosky SA, Elizabeth DA, Naomi DS, Steven M, Tianyi W, Coyne CB (2011) The coxsackievirus B 3C protease cleaves MAVS and TRIF to attenuate host type I interferon and apoptotic signaling. PLoS Pathog 7:1311
Amy J, Skotheim JM (2013) Start and the restriction point. Cell Biol 25:717–723
Blauwet LA, Cooper LT (2009) Myocarditis. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 52:274–288
Bowles NE, Richardson PJ, Olsen EG, Archard LC (1986) Detection of coxsackie-B-virus-specific RNA sequences in myocardial biopsy samples from patients with myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. Lancet 327:1120–1123
Cao H, Yang B, Zhao Y, Deng X, Shen X (2020) The pro-apoptosis and pro-inflammation role of LncRNA HIF1A-AS1 in Coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis via targeting miR-138. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther 10:1245–1255
Corsten M, Papageorgiou A, Verhesen W, Carai P, Lindow M, Obad S, Summer G, Coort S, Hazebroek M, van Leeuwen R, Gijbels M, Wijnands E, Biessen E, De Winther M, Stassen F, Carmeliet P, Kauppinen S, Schroen B, Heymans S (2012) MicroRNA profiling identifies microRNA-155 as an adverse mediator of cardiac injury and dysfunction during acute viral myocarditis. Circ Res 111:415–425
Corsten MF, Heggermont W, Papageorgiou AP, Deckx S, Tijsma A, Verhesen W, van Leeuwen R, Carai P, Thibaut HJ, Custers K, Summer G, Hazebroek M, Verheyen F, Neyts J, Schroen B, Heymans S (2015) The microrna-221/-222 cluster balances the antiviral and inflammatory response in viral myocarditis. Eur Heart J 36:2909–2919
Cullen BR (2006) Viruses and micrornas. Nat Genet 38(Suppl):S25
Esfandiarei M, McManus BM (2008) Molecular biology and pathogenesis of viral myocarditis. Annu Rev Pathol 3:127–155
Feuer R, Whitton JL (2008) Preferential coxsackievirus replication in proliferating/activated cells: Implications for virus tropism, persistence, and pathogenesis. Microbiol Immunol 323:149–173
Feuer R, Mena I, Pagarigan RR, Hassett DE, Whitton JLJMM (2004) Coxsackievirus replication and the cell cycle: A potential regulatory mechanism for viral persistence/latency. Immunol 193:83–90
Garmaroudi FS, Marchant D, Si X, Khalili A, Bashashati A, Wong BW, Tabet A, Ng RT, Murphy K, Luo H, Janes KA, McManus BM (2010) Pairwise network mechanisms in the host signaling response to coxsackievirus b3 infection. Natl Acad Sci 107:17053–17058
Grist NR, Reid D (1997) Organisms in myocarditis/endocarditis viruses. J Infect 34:155
Hatakeyama S (2017) Trim family proteins: Roles in autophagy, immunity, and carcinogenesis. Trends Biochem Sci 42:297
Kawai T, Akira S (2011) Regulation of innate immune signalling pathways by the tripartite motif (trim) family proteins. EMBO Mol Med 3:513–527
Li YC, Chen GY, Ge LS, Xing C, Tian XQ, Lin C, Dai XY, Yang XJ (2016) The Protective Effects of Ivabradine in Preventing Progression from Viral Myocarditis to Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Front Pharmacol 7:408
Liao Y, Chen KH, Dong XM, Fang Y, Li WG, Huang GY, Song W (2015) A role of pre-mir-10a coding region variant in host susceptibility to coxsackie virus-induced myocarditis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19:3500
Maisch B, Portig I, Ristic A, Hufnagel G, Pankuweit S (2000) Definition of inflammatory cardiomyopathy (myocarditis): On the way to consensus. Herz 25:200–209
Márquez-González H, López-Gallegos D, González-Espinosa AM, Zamudio-López JO, Yáñez-Gutiérrez L (2016) Effect of immune therapy in the prognosis of viral myocarditis in pediatric patients. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc 54:S296 (in Spanish)
Martin AB, Webber S, Fricker FJ, Jaffe R, Demmler G, Kearney D, Zhang YH, Bodurtha J, Gelb B, Ni J (1994) Acute myocarditis. Rapid diagnosis by pcr in children. Circulation 90:330–339
McCarthy RE 3rd, Boehmer JP, Hruban RH, Hutchins GM, Kasper EK, Hare JM, Baughman KL (2000) Long-term outcome of fulminant myocarditis as compared with acute (nonfulminant) myocarditis. N Engl J Med 342:690–695
Mehta A, Baltimore D (2016) Micrornas as regulatory elements in immune system logic. Nat Rev Immunol 16:279
Meroni G, Diez-Roux G (2010) TRIM/RBCC, a novel class of “single protein RING finger” E3 ubiquitin ligases. BioEssays 27:1147–1157
Mohamud Y, Qu J, Xue YC, Liu H, Deng H, Luo H (2019) Calcoco2/ndp52 and sqstm1/p62 differentially regulate coxsackievirus b3 propagation. Cell Death Differ 26:1062–1076
Nisole S, Stoye JP, Saïb A (2005) Trim family proteins: Retroviral restriction and antiviral defence. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:799–808
O’Connell RM, Rao DS, Chaudhuri AA, Baltimore D (2010) Physiological and pathological roles for micrornas in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 10:111–122
Rienks M, Papageorgiou A, Wouters K, Verhesen W, Leeuwen RV, Carai P, Summer G, Westermann D, Heymans S (2017) A novel 72-kda leukocyte-derived osteoglycin enhances the activation of toll-like receptor 4 and exacerbates cardiac inflammation during viral myocarditis. Cell Mol Life Sci 74:1511–1525
Schang LM (2003) The cell cycle, cyclin-dependent kinases, and viral infections: New horizons and unexpected connections. Prog Cell Cycle Res 5:103
Singaravelu R, Ahmed N, Quan C, Srinivasan P, Ablenas CJ, Roy DG, Pezacki JP (2019) A conserved miRNA-183 cluster regulates the innate antiviral response. J Biol Chem 294:19785–19794
Small EM, Olson ENJN (2011) Pervasive roles of micrornas in cardiovascular biology. Nature 469:336–342
Stein EA, Pinkert S, Becher PM, Geisler A, Zeichhardt H, Klopfleisch R, Poller W, Tschöpe C, Lassner D, Fechner H, Kurreck J (2015) Combination of RNA interference and virus receptor trap exerts additive antiviral activity in coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis in mice. J Infect Dis 211:613–622
Tong L, Lin L, Wu S, Guo Z, Wang T, Qin Y, Wang R, Zhong X, Wu X, Wang Y, Luan T, Wang Q, Li Y, Chen X, Zhang F, Zhao W, Zhong Z (2013) Mir-10a* up-regulates coxsackievirus b3 biosynthesis by targeting the 3d-coding sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 41:3760–3771
Van Linthout S, Savvatis K, Miteva K, Peng J, Ringe J, Warstat K, Schmidt-Lucke C, Sittinger M, Schultheiss HP, Tschöpe C (2011) Mesenchymal stem cells improve murine acute coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. Eur Heart J 32:2168–2178
Van Linthout S, Tschöpe C, Schultheiss HP (2014) Lack in treatment options for virus-induced inflammatory cardiomyopathy: Can ips-derived cardiomyocytes close the gap? Circ Res 115:540–541
Wang L, Qin Y, Tong L, Wu S, Wang Q, Jiao Q, Guo Z, Lin L, Wang R, Zhao W, Zhong Z (2012) MiR-342-5p suppresses coxsackievirus B3 biosynthesis by targeting the 2C-coding region. Antiviral Res 93:270–279
Wang F, Qiu Y, Zhang HM, Hanson P, Ye X, Zhao G, Xie R, Tong L, Yang D (2017) Heat shock protein 70 promotes coxsackievirus B3 translation initiation and elongation via Akt-mTORC1 pathway depending on activation of p70S6K and Cdc2. Cell Microbiol 19:e12725
Wang Y, Jia L, Shen J, Wang Y, Fu Z, Su SA, Cai Z, Wang JA, Xiang M (2018) Cathepsin b aggravates coxsackievirus b3-induced myocarditis through activating the inflammasome and promoting pyroptosis. PLoS Pathog 14:e1006872
Wang Y, Zhao S, Chen Y, Wang T, Dong C, Wo X, Zhang J, Dong Y, Xu W, Feng X, Qu C, Wang Y, Zhong Z, Zhao W (2019) The capsid protein vp1 of coxsackievirus b induces cell cycle arrest by up-regulating heat shock protein 70. Front Microbiol 10:1633
Wu X, Wu S, Tong L, Luan T, Lin L, Lu S, Zhao W, Ma Q, Liu H, Zhong Z (2009) miR-122 affects the viability and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Scand J Gastroentero 44:1332–1339
Wu S, Wang Y, Lin L, Si X, Wang T, Zhong X, Tong L, Luan Y, Chen Y, Li X, Zhang F, Zhao W, Zhong Z (2014) Protease 2A induces stress granule formation during coxsackievirus B3 and enterovirus 71 infections. Virol J 11:192
Ye X, Hemida MG, Qiu Y, Hanson PJ, Zhang HM, Yang D (2013) MiR-126 promotes coxsackievirus replication by mediating cross-talk of ERK1/2 and Wnt/β-catenin signal pathways. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:4631–4644
Ye X, Zhang HM, Qiu Y, Hanson PJ, Hemida MG, Wei W, Hoodless PA, Chu F, Yang D (2014) Coxsackievirus-induced miR-21 disrupts cardiomyocyte interactions via the downregulation of intercalated disk components. PLoS Pathog 10:e1004070
Yu M, Long Q, Li HH, Liang W, Liao YH, Yuan J, Cheng X (2016) IL-9 inhibits viral replication in coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. Front Immunol 7:409
Yuan J, Liu Z, Lim T, Zhang H, He J, Walker E, Shier C, Wang Y, Su Y, Sall A, McManus B, Yang D (2009) CXCL10 inhibits viral replication through recruitment of natural killer cells in coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis. Circ Res 104:628–638
Zhang H, Yang D (2013) MiR-126 promotes coxsackievirus replication by mediating cross-talk of ERK1/2 and Wnt/β-catenin signal pathways. CMLS 70:4631–4644
Zhang X, Gao X, Hu J, Xie Y, Zuo Y, Xu H, Zhu S (2019) ADAR1p150 forms a complex with dicer to promote miRNA-222 activity and regulate PTEN expression in CVB3-induced viral myocarditis. Int J Mol Sci 20:407
Zhang C, Xiong Y, Zeng L, Peng Z, Liu Z, Zhan H, Yang Z (2020a) The role of non-coding RNAs in viral myocarditis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 10:312
Zhang Y, Li X, Wang C, Zhang M, Yang H, Lv K (2020b) lncRNA AK085865 promotes macrophage M2 polarization in CVB3-induced VM by regulating ILF2-ILF3 complex-mediated miRNA-192 biogenesis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 21:441–451
Zheng Q, Hou J, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Cao X (2015a) Type I IFN-inducible downregulation of MicroRNA-27a feedback inhibits antiviral innate response by upregulating Siglec1/TRIM27. J Immunol 196:1317–1326
Zheng Q, Hou J, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Xie B, Cao X (2015b) Siglec1 suppresses antiviral innate immune. Response by inducing TBK1 degradation via the ubiquitin ligase TRIM27. Cell Res 25:1121–1136
Zheng F, Xu N, Zhang Y (2019) TRIM27 promotes hepatitis C virus replication by suppressing type I interferon response. Inflammation 42:1317–1325
Acknowledgements
The research was support by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No. 81971945 and No. 81802013 (https://isisn.nsfc.gov.cn/egrantweb/), Xuzhou Science and Technology Project, Grant No. KC1717 (http://kjj.xz.gov.cn), the Projects from Social development of Zhenjiang, Grant No. SH2019044 (http://kjj.zhenjiang.gov.cn).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HXS, SHS and HW conceived and designed the experiments. TJL, JYL, YS, JT and YL performed the experiments. TJL, HXS and HW analyzed the data. TJL, HXS, SHS, CS, HW and JYQ contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. TJL, HXS and HW wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Animal and Human Rights Statement
This study was conducted in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide to the Care and Use of Experimental Animals-Chinese Council on Animal Care. All protocols were approved by the Animal Care Committee of University Jiangsu, (protocol number: UJS-IACUC-AP-20190307087).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Tong, J., Shao, C. et al. MicroRNA-324-3p Plays A Protective Role Against Coxsackievirus B3-Induced Viral Myocarditis. Virol. Sin. 36, 1585–1599 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-021-00441-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-021-00441-4