Abstract
Background
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the second most common type of male cancer in western. Despite key roles of brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1-associated protein like 2 (BAIAP2L2) in several cancers, the function of BAIAP2L2 in PCa is never reported.
Objective
We aimed to investigate the role of BAIAP2L2 in the progression of PCa and decipher the underlying mechanisms.
Methods
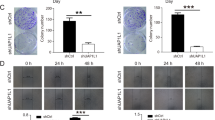
RNA sequencing data from TCGA database were used to evaluate the expression of BAIAP2L2 in PCa. Survival analysis and Cox regression model analysis were conducted to evaluate the prognostic value of BAIAP2L2. BAIAP2L2-associated pathways were preliminary analyzed by Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) method and confirmed by western blot assays. Cell proliferation and transwell assays were performed to determine biological behaviors in BAIAP2L2 knocked-down or overexpressed PCa cell lines including LNCaP and PC-3 cells.
Results
In our study, BAIAP2L2 was significantly up-regulated in PCa tissues and cell lines and independently associated with the poor prognosis of PCa patients. Knockdown of BAIAP2L2 notably repressed proliferation, migration and invasion of PCa cells. And overexpression of BAIAP2L2 obtained the contrary results. Mechanically, GSEA method and western blot results of key molecules in signaling pathways implicated that the depletion of BAIAP2L2 inactivated the vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) and induced apoptosis signaling pathways in PCa cells.
Conclusions
Overall, these findings revealed that BAIAP2L2 may support tumorigenesis and malignant development of prostate cancer cells via VEGF and apoptosis signaling pathways, and it could be considered as a promising biomarker and independent prognostic predictor of prostate cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albasri A, Fadhil W, Scholefield JH, Durrant LG, Ilyas M (2014) Nuclear expression of phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase is associated with poor prognosis in human colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 34:3969–3974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2014.05.010
Amundson SA, Myers TG, Scudiero D, Kitada S, Reed JC, Fornace AJ Jr (2000) An informatics approach identifying markers of chemosensitivity in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 60:6101–6110. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-5394.2000.86010.x
Anai S, Shiverick K, Medrano T, Nakamura K, Goodison S, Brown BD, Rosser CJ (2007) Downregulation of BCL-2 induces downregulation of carbonic anhydrase IX, vascular endothelial growth factor, and pAkt and induces radiation sensitization. Urology 70:832–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2007.06.1118
Bender RJ, Mac Gabhann F (2015) Dysregulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor and semaphorin ligand-receptor families in prostate cancer metastasis. BMC Syst Biol 9:55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12918-015-0201-z
Chao A, Tsai CL, Jung SM, Chuang WC, Kao C, Hsu A, Chen SH, Lin CY, Lee YC, Lee YS et al (2015) BAI1-associated orotein 2-Like 1 (BAIAP2L1) is a potential biomarker in ovarian cancer. PLoS One 10:e0133081. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133081
Domigan CK, Ziyad S, Iruela-Arispe ML (2015) Canonical and noncanonical vascular endothelial growth factor pathways: new developments in biology and signal transduction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 35:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303215
Goel HL, Mercurio AM (2013) VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer 13:871–882. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3627
Hayes JH, Barry MJ (2014) Screening for prostate cancer with the prostate-specific antigen test: a review of current evidence. JAMA 311:1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.2085
Hu X, Li YQ, Li QG, Ma YL, Peng JJ, Cai SJ (2018) Osteoglycin-induced VEGF inhibition enhances T lymphocytes infiltrating in colorectal cancer. EBioMedicine 34:35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.07.021
Hu W, Wang G, Yarmus LB, Wan Y (2020) Combined methylome and transcriptome analyses reveals potential therapeutic targets for EGFR wild type lung cancers with low PD-L1 expression. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092496
Huey KA, Smith SA, Sulaeman A, Breen EC (2016) Skeletal myofiber VEGF is necessary for myogenic and contractile adaptations to functional overload of the plantaris in adult mice. J Appl Physiol (1985) 120:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00638.2015
Izdebska M, Zielińska W (2020) Involvement of actin and actin-binding proteins in carcinogenesis. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102245
Jelińska M, Skrajnowska D, Wrzosek M, Domanska K, Bielecki W, Zawistowska M, Bobrowska Korczak B (2020) Inflammation factors and element supplementation in cancer. J Trace Elem Med Biol 59:126450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2019.126450
Jiang H, Xu S, Chen C (2020) A ten-gene signature-based risk assessment model predicts the prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 20:782. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-07235-z
Jin W, Fei X, Wang X, Song Y, Chen F (2020) Detection and prognosis of prostate cancer using blood-based biomarkers. Mediators Inflamm 2020:8730608. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8730608
Kast DJ, Dominguez R (2019a) IRSp53 coordinates AMPK and 14-3-3 signaling to regulate filopodia dynamics and directed cell migration. Mol Biol Cell 30:1285–1297. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E18-09-0600
Kast DJ, Dominguez R (2019b) Mechanism of IRSp53 inhibition by 14-3-3. Nat Commun 10:483. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08317-8
Liu J, Shangguan Y, Sun J, Cong W, Xie Y (2020) BAIAP2L2 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via AKT/mTOR and Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 129:110414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110414
Lu RM, Chiu CY, Liu IJ, Chang YL, Liu YJ, Wu HC (2019) Novel human Ab against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 shows therapeutic potential for leukemia and prostate cancer. Cancer Sci 110:3773–3787. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14208
Melegh Z, Oltean S (2019) Targeting angiogenesis in prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112676
Millard TH, Bompard G, Heung MY, Dafforn TR, Scott DJ, Machesky LM, Futterer K (2005) Structural basis of filopodia formation induced by the IRSp53/MIM homology domain of human IRSp53. EMBO J 24:240–250. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600535
Mohammad RM, Muqbil I, Lowe L, Yedjou C, Hsu HY, Lin LT, Siegelin MD, Fimognari C, Kumar NB, Dou QP et al (2015) Broad targeting of resistance to apoptosis in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 35 Suppl:S78–S103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.03.001
Pidgeon GP, Lysaght J, Krishnamoorthy S, Reynolds JV, O’Byrne K, Nie D, Honn KV (2007) Lipoxygenase metabolism: roles in tumor progression and survival. Cancer Metast Rev 26:503–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9098-3
Pykalainen A, Boczkowska M, Zhao H, Saarikangas J, Rebowski G, Jansen M, Hakanen J, Koskela EV, Peranen J, Vihinen H et al (2011) Pinkbar is an epithelial-specific BAR domain protein that generates planar membrane structures. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:902–907. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2079
Quigley DA, Dang HX, Zhao SG, Lloyd P, Aggarwal R, Alumkal JJ, Foye A, Kothari V, Perry MD, Bailey AM et al (2018) Genomic hallmarks and structural variation in metastatic prostate cancer. Cell 175:889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.019
Recher C, Ysebaert L, Beyne-Rauzy O, Mansat-De Mas V, Ruidavets JB, Cariven P, Demur C, Payrastre B, Laurent G, Racaud-Sultan C (2004) Expression of focal adhesion kinase in acute myeloid leukemia is associated with enhanced blast migration, increased cellularity, and poor prognosis. Cancer Res 64:3191–3197. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3005
Rudzińska M, Mikula M, Arczewska KD (2019) Transcription factor prospero homeobox 1 (PROX1) as a potential angiogenic regulator of follicular thyroid cancer dissemination. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225619
Rybalov M, Ananias HJ, Hoving HD, van der Poel HG, Rosati S, de Jong IJ (2014) PSMA, EpCAM, VEGF and GRPR as imaging targets in locally recurrent prostate cancer after radiotherapy. Int J Mol Sci 15:6046–6061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15046046
Safari F, Suetsugu S (2012) The BAR domain superfamily proteins from subcellular structures to human diseases. Membranes (Basel) 2:91–117. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes2010091
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2020) Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 70:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21590
Sulzmaier FJ, Jean C, Schlaepfer DD (2014) FAK in cancer: mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat Rev Cancer 14:598–610. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3792
Wang YP, Huang LY, Sun WM, Zhang ZZ, Fang JZ, Wei BF, Wu BH, Han ZG (2013) Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate activates EGFR/ERK signalling pathway and promotes cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 337:96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.019
Xu L, Du H, Zhang Q, Wang C, Yan L, Tian G, Fu X (2019) BAI1associated protein 2like 2 is a potential biomarker in lung cancer. Oncol Rep 41:1304–1312. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6883
Zhang X, Pan Y, Fu H, Zhang J (2019) microRNA-205 and microRNA-338-3p reduces cell apoptosis in prostate carcinoma tissue and LNCaP prostate carcinoma cells by directly targeting the B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) gene. Med Sci Monit 25:1122–1132. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.912148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: YS and MZ; Methodology: YS and GZ; Formal analysis and investigation: GZ; Writing-original draft preparation: YS, GZ and JL; Writing-review and editing: YS and MZ; Approval of the manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Yuanzi Song, Guishan Zhuang, Jiazhen Li and Mingqing Zhang declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13258_2021_1061_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. 1 Linoleic acid metabolism signaling pathway was significantly enriched in BAIAP2L2 high-expression group (P < 0.05)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Zhuang, G., Li, J. et al. BAIAP2L2 facilitates the malignancy of prostate cancer (PCa) via VEGF and apoptosis signaling pathways. Genes Genom 43, 421–432 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01061-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-021-01061-8