Abstract
Obesity, defined as excess fat mass, increases risks for multiple chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and several types of cancer. Beyond adiposity per se, the pattern of fat distribution, android or truncal as compared to gynoid or peripheral, has a profound influence on systemic metabolism and hence risk for obesity complications. Not only factors as genetics, environment, gender, and age account for the apparent compartmentalization of white adipose tissue (WAT) in the body. Indeed, the heterogeneity among different anatomical depots also appears to stem from their intrinsic diversity, including cellular developmental origin, proliferative capacity, glucose and lipid metabolism, insulin sensitivity, cytokine pattern, thermogenic ability, and vascularization. Under the obese condition, these depot-specific differences translate into specific WAT distribution patterns, giving rise to different cardiometabolic consequences. This review summarizes the clinical and mechanistic evidence for the depot-specific differences and the phenotypic characteristics of different WAT depots that link their depot-specific biology to obesity-specific complications.

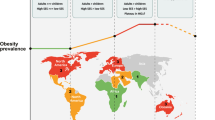
Modified from [9]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sacks FM, Bray GA, Carey VJ, Smith SR, Ryan DH, Anton SD, McManus K, Champagne CM, Bishop LM, Laranjo N, Leboff MS, Rood JC, de Jonge L, Greenway FL, Loria CM, Obarzanek E, Williamson DA (2009) Comparison of weight-loss diets with different compositions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. N Engl J Med 360(9):859–873. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0804748
Lombardo M, Bellia A, Padua E, Annino G, Guglielmi V, D’Adamo M, Iellamo F, Sbraccia P (2014) Morning meal more efficient for fat loss in a 3-month lifestyle intervention. J Am Coll Nutr 33(3):198–205. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2013.863169
Bellia A, Salli M, Lombardo M, D’Adamo M, Guglielmi V, Tirabasso C, Giordani L, Federici M, Lauro D, Foti C, Sbraccia P (2014) Effects of whole body vibration plus diet on insulin-resistance in middle-aged obese subjects. Int J Sports Med 35(6):511–516. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1354358
Jakicic JM, Otto AD (2005) Physical activity considerations for the treatment and prevention of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 82(1 Suppl):226S–229S
Lombardo M, Bellia A, Mattiuzzo F, Franchi A, Ferri C, Padua E, Guglielmi V, D’Adamo M, Annino G, Gentileschi P, Iellamo F, Lauro D, Federici M, Sbraccia P (2015) Frequent follow-up visits reduce weight regain in long-term management after bariatric surgery. Bariatric Surg Pract Patient Care 10(3):119–125. https://doi.org/10.1089/bari.2015.0021
Frikke-Schmidt H, O’Rourke RW, Lumeng CN, Sandoval DA, Seeley RJ (2016) Does bariatric surgery improve adipose tissue function? Obes Rev 17(9):795–809. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12429
Tilg H, Moschen AR (2006) Adipocytokines: mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 6(10):772–783. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1937
Guglielmi V, D’Adamo M, Bellia A, Ciotto RT, Federici M, Lauro D, Sbraccia P (2015) Iron status in obesity: an independent association with metabolic parameters and effect of weight loss. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 25(6):541–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2015.02.012
Kwok KH, Lam KS, Xu A (2016) Heterogeneity of white adipose tissue: molecular basis and clinical implications. Exp Mol Med 48:e215. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2016.5
Smith SR, Lovejoy JC, Greenway F, Ryan D, deJonge L, de la Bretonne J, Volafova J, Bray GA (2001) Contributions of total body fat, abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments, and visceral adipose tissue to the metabolic complications of obesity. Metabolism 50(4):425–435. https://doi.org/10.1053/meta.2001.21693
Geer EB, Shen W (2009) Gender differences in insulin resistance, body composition, and energy balance. Gend Med 6 Suppl 1:60–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genm.2009.02.002
Ramirez ME, McMurry MP, Wiebke GA, Felten KJ, Ren K, Meikle AW, Iverius PH (1997) Evidence for sex steroid inhibition of lipoprotein lipase in men: comparison of abdominal and femoral adipose tissue. Metabolism 46(2):179–185
Pedersen SB, Kristensen K, Hermann PA, Katzenellenbogen JA, Richelsen B (2004) Estrogen controls lipolysis by up-regulating alpha2A-adrenergic receptors directly in human adipose tissue through the estrogen receptor alpha. Implications for the female fat distribution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(4):1869–1878. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2003-031327
Singh R, Artaza JN, Taylor WE, Braga M, Yuan X, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF, Bhasin S (2006) Testosterone inhibits adipogenic differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells: nuclear translocation of androgen receptor complex with beta-catenin and T-cell factor 4 may bypass canonical Wnt signaling to down-regulate adipogenic transcription factors. Endocrinology 147(1):141–154. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2004-1649
Lacasa D, Le Liepvre X, Ferre P, Dugail I (2001) Progesterone stimulates adipocyte determination and differentiation 1/sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c gene expression. potential mechanism for the lipogenic effect of progesterone in adipose tissue. J Biol Chem 276(15):11512–11516. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M008556200
Wajchenberg BL (2000) Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr Rev 21(6):697–738. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv.21.6.0415
White UA, Tchoukalova YD (2014) Sex dimorphism and depot differences in adipose tissue function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842(3):377–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.05.006
Yang X, Schadt EE, Wang S, Wang H, Arnold AP, Ingram-Drake L, Drake TA, Lusis AJ (2006) Tissue-specific expression and regulation of sexually dimorphic genes in mice. Genome Res 16(8):995–1004. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.5217506
Lee MJ, Wu Y, Fried SK (2013) Adipose tissue heterogeneity: implication of depot differences in adipose tissue for obesity complications. Mol Aspects Med 34(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2012.10.001
Anand SS, Tarnopolsky MA, Rashid S, Schulze KM, Desai D, Mente A, Rao S, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC, Sharma AM (2011) Adipocyte hypertrophy, fatty liver and metabolic risk factors in South Asians: the Molecular Study of Health and Risk in Ethnic Groups (mol-SHARE). PLoS One 6(7):e22112. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0022112
Guglielmi V, Maresca L, D’Adamo M, Di Roma M, Lanzillo C, Federici M, Lauro D, Preziosi P, Bellia A, Sbraccia P (2014) Age-related different relationships between ectopic adipose tissues and measures of central obesity in sedentary subjects. PLoS One 9(7):e103381. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103381
Lundgren M, Svensson M, Lindmark S, Renstrom F, Ruge T, Eriksson JW (2007) Fat cell enlargement is an independent marker of insulin resistance and ‘hyperleptinaemia’. Diabetologia 50(3):625–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-006-0572-1
Tchkonia T, Tchoukalova YD, Giorgadze N, Pirtskhalava T, Karagiannides I, Forse RA, Koo A, Stevenson M, Chinnappan D, Cartwright A, Jensen MD, Kirkland JL (2005) Abundance of two human preadipocyte subtypes with distinct capacities for replication, adipogenesis, and apoptosis varies among fat depots. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 288(1):E267–E277. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00265.2004
Tchkonia T, Giorgadze N, Pirtskhalava T, Thomou T, DePonte M, Koo A, Forse RA, Chinnappan D, Martin-Ruiz C, von Zglinicki T, Kirkland JL (2006) Fat depot-specific characteristics are retained in strains derived from single human preadipocytes. Diabetes 55(9):2571–2578. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-0540
Gesta S, Bluher M, Yamamoto Y, Norris AW, Berndt J, Kralisch S, Boucher J, Lewis C, Kahn CR (2006) Evidence for a role of developmental genes in the origin of obesity and body fat distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(17):6676–6681. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0601752103
Guglielmi V, D’Adamo M, Menghini R, Cardellini M, Gentileschi P, Federici M, Sbraccia P (2017) MicroRNA 21 is up-regulated in adipose tissue of obese diabetic subjects. Nutr Healthy Aging 4:141–145. https://doi.org/10.3233/NHA-160020
Gilad S, Meiri E, Yogev Y, Benjamin S, Lebanony D, Yerushalmi N, Benjamin H, Kushnir M, Cholakh H, Melamed N, Bentwich Z, Hod M, Goren Y, Chajut A (2008) Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS One 3(9):e3148. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0003148
Joe AW, Yi L, Even Y, Vogl AW, Rossi FM (2009) Depot-specific differences in adipogenic progenitor abundance and proliferative response to high-fat diet. Stem Cells 27(10):2563–2570. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.190
Spalding KL, Arner E, Westermark PO, Bernard S, Buchholz BA, Bergmann O, Blomqvist L, Hoffstedt J, Naslund E, Britton T, Concha H, Hassan M, Ryden M, Frisen J, Arner P (2008) Dynamics of fat cell turnover in humans. Nature 453(7196):783–787. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06902
Skurk T, Alberti-Huber C, Herder C, Hauner H (2007) Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92 (3):1023–1033. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-1055
Giordano A, Murano I, Mondini E, Perugini J, Smorlesi A, Severi I, Barazzoni R, Scherer PE, Cinti S (2013) Obese adipocytes show ultrastructural features of stressed cells and die of pyroptosis. J Lipid Res 54(9):2423–2436. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M038638
Strissel KJ, Stancheva Z, Miyoshi H, Perfield JW, 2nd, DeFuria J, Jick Z, Greenberg AS, Obin MS (2007) Adipocyte death, adipose tissue remodeling, and obesity complications. Diabetes 56 (12):2910–2918. https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-0767
Pellegrinelli V, Carobbio S, Vidal-Puig A (2016) Adipose tissue plasticity: how fat depots respond differently to pathophysiological cues. Diabetologia 59(6):1075–1088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-016-3933-4
Kim SM, Lun M, Wang M, Senyo SE, Guillermier C, Patwari P, Steinhauser ML (2014) Loss of white adipose hyperplastic potential is associated with enhanced susceptibility to insulin resistance. Cell Metab 20(6):1049–1058. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.10.010
Cinti S (2017) UCP1 protein: the molecular hub of adipose organ plasticity. Biochimie 134:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2016.09.008
Vijgen GH, Bouvy ND, Teule GJ, Brans B, Schrauwen P, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD (2011) Brown adipose tissue in morbidly obese subjects. PLoS One 6(2):e17247. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017247
Virtanen KA, Lidell ME, Orava J, Heglind M, Westergren R, Niemi T, Taittonen M, Laine J, Savisto NJ, Enerback S, Nuutila P (2009) Functional brown adipose tissue in healthy adults. N Engl J Med 360(15):1518–1525. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0808949
Cypess AM, Lehman S, Williams G, Tal I, Rodman D, Goldfine AB, Kuo FC, Palmer EL, Tseng YH, Doria A, Kolodny GM, Kahn CR (2009) Identification and importance of brown adipose tissue in adult humans. N Engl J Med 360(15):1509–1517. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0810780
Vitali A, Murano I, Zingaretti MC, Frontini A, Ricquier D, Cinti S (2012) The adipose organ of obesity-prone C57BL/6J mice is composed of mixed white and brown adipocytes. J Lipid Res 53(4):619–629. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M018846
Cousin B, Cinti S, Morroni M, Raimbault S, Ricquier D, Penicaud L, Casteilla L (1992) Occurrence of brown adipocytes in rat white adipose tissue: molecular and morphological characterization. J Cell Sci 103(Pt 4):931–942
De Matteis R, Lucertini F, Guescini M, Polidori E, Zeppa S, Stocchi V, Cinti S, Cuppini R (2013) Exercise as a new physiological stimulus for brown adipose tissue activity. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 23(6):582–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2012.01.013
Wang QA, Tao C, Gupta RK, Scherer PE (2013) Tracking adipogenesis during white adipose tissue development, expansion and regeneration. Nat Med 19(10):1338–1344. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3324
Giordano A, Frontini A, Cinti S (2016) Convertible visceral fat as a therapeutic target to curb obesity. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15(6):405–424. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.31
Seale P, Bjork B, Yang W, Kajimura S, Chin S, Kuang S, Scime A, Devarakonda S, Conroe HM, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Rudnicki MA, Beier DR, Spiegelman BM (2008) PRDM16 controls a brown fat/skeletal muscle switch. Nature 454(7207):961–967. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07182
Frontini A, Vitali A, Perugini J, Murano I, Romiti C, Ricquier D, Guerrieri M, Cinti S (2013) White-to-brown transdifferentiation of omental adipocytes in patients affected by pheochromocytoma. Biochim Biophys Acta 1831(5):950–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2013.02.005
Cheng W, Zhu Z, Jin X, Chen L, Zhuang H, Li F (2012) Intense FDG activity in the brown adipose tissue in omental and mesenteric regions in a patient with malignant pheochromocytoma. Clin Nucl Med 37(5):514–515. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0b013e31824d2121
Dong A, Wang Y, Lu J, Zuo C (2014) Hypermetabolic mesenteric brown adipose tissue on dual-time point FDG PET/CT in a patient with benign retroperitoneal pheochromocytoma. Clin Nucl Med 39(3):e229–e232. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0b013e3182816515
Arner P, Lithell H, Wahrenberg H, Bronnegard M (1991) Expression of lipoprotein lipase in different human subcutaneous adipose tissue regions. J Lipid Res 32(3):423–429
Karpe F, Pinnick KE (2015) Biology of upper-body and lower-body adipose tissue—link to whole-body phenotypes. Nat Rev Endocrinol 11(2):90–100. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2014.185
Veilleux A, Blouin K, Rheaume C, Daris M, Marette A, Tchernof A (2009) Glucose transporter 4 and insulin receptor substrate-1 messenger RNA expression in omental and subcutaneous adipose tissue in women. Metabolism 58(5):624–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2008.12.007
Virtanen KA, Lonnroth P, Parkkola R, Peltoniemi P, Asola M, Viljanen T, Tolvanen T, Knuuti J, Ronnemaa T, Huupponen R, Nuutila P (2002) Glucose uptake and perfusion in subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue during insulin stimulation in nonobese and obese humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(8):3902–3910. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.87.8.8761
Arner P (1999) Catecholamine-induced lipolysis in obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 23(Suppl 1):10–13
Van Harmelen V, Lonnqvist F, Thorne A, Wennlund A, Large V, Reynisdottir S, Arner P (1997) Noradrenaline-induced lipolysis in isolated mesenteric, omental and subcutaneous adipocytes from obese subjects. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 21(11):972–979
Nielsen S, Guo Z, Johnson CM, Hensrud DD, Jensen MD (2004) Splanchnic lipolysis in human obesity. J Clin Invest 113(11):1582–1588. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI21047
Dolinkova M, Dostalova I, Lacinova Z, Michalsky D, Haluzikova D, Mraz M, Kasalicky M, Haluzik M (2008) The endocrine profile of subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue of obese patients. Mol Cell Endocrinol 291(1–2):63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2008.05.001
Alvehus M, Buren J, Sjostrom M, Goedecke J, Olsson T (2010) The human visceral fat depot has a unique inflammatory profile. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18(5):879–883. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2010.22
Donath MY, Shoelson SE (2011) Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11(2):98–107. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri2925
Altintas MM, Azad A, Nayer B, Contreras G, Zaias J, Faul C, Reiser J, Nayer A (2011) Mast cells, macrophages, and crown-like structures distinguish subcutaneous from visceral fat in mice. J Lipid Res 52(3):480–488. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M011338
Guglielmi V, Cardellini M, Cinti F, Corgosinho F, Cardolini I, D’Adamo M, Zingaretti MC, Bellia A, Lauro D, Gentileschi P, Federici M, Cinti S, Sbraccia P (2015) Omental adipose tissue fibrosis and insulin resistance in severe obesity. Nutr Diabetes 5:e175. https://doi.org/10.1038/nutd.2015.22
Wernstedt Asterholm I, Tao C, Morley TS, Wang QA, Delgado-Lopez F, Wang ZV, Scherer PE (2014) Adipocyte inflammation is essential for healthy adipose tissue expansion and remodeling. Cell Metab 20(1):103–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.05.005
Khan T, Muise ES, Iyengar P, Wang ZV, Chandalia M, Abate N, Zhang BB, Bonaldo P, Chua S, Scherer PE (2009) Metabolic dysregulation and adipose tissue fibrosis: role of collagen VI. Mol Cell Biol 29(6):1575–1591. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01300-08
Michaud A, Tordjman J, Pelletier M, Liu Y, Laforest S, Noel S, Le Naour G, Bouchard C, Clement K, Tchernof A (2016) Relevance of omental pericellular adipose tissue collagen in the pathophysiology of human abdominal obesity and related cardiometabolic risk. Int J Obes (Lond) 40(12):1823–1831. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2016.173
Pasarica M, Sereda OR, Redman LM, Albarado DC, Hymel DT, Roan LE, Rood JC, Burk DH, Smith SR (2009) Reduced adipose tissue oxygenation in human obesity: evidence for rarefaction, macrophage chemotaxis, and inflammation without an angiogenic response. Diabetes 58(3):718–725. https://doi.org/10.2337/db08-1098
Gealekman O, Guseva N, Hartigan C, Apotheker S, Gorgoglione M, Gurav K, Tran KV, Straubhaar J, Nicoloro S, Czech MP, Thompson M, Perugini RA, Corvera S (2011) Depot-specific differences and insufficient subcutaneous adipose tissue angiogenesis in human obesity. Circulation 123(2):186–194. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.970145
Goossens GH, Blaak EE (2015) Adipose tissue dysfunction and impaired metabolic health in human obesity: a matter of oxygen? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 6:55. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2015.00055
St-Pierre J, Lemieux I, Perron P, Brisson D, Santure M, Vohl MC, Despres JP, Gaudet D (2007) Relation of the “hypertriglyceridemic waist” phenotype to earlier manifestations of coronary artery disease in patients with glucose intolerance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol 99(3):369–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2006.08.041
Coutinho T, Goel K, Correa de Sa D, Kragelund C, Kanaya AM, Zeller M, Park JS, Kober L, Torp-Pedersen C, Cottin Y, Lorgis L, Lee SH, Kim YJ, Thomas R, Roger VL, Somers VK, Lopez-Jimenez F (2011) Central obesity and survival in subjects with coronary artery disease: a systematic review of the literature and collaborative analysis with individual subject data. J Am Coll Cardiol 57(19):1877–1886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2010.11.058
Bray GA, Jablonski KA, Fujimoto WY, Barrett-Connor E, Haffner S, Hanson RL, Hill JO, Hubbard V, Kriska A, Stamm E, Pi-Sunyer FX (2008) Relation of central adiposity and body mass index to the development of diabetes in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Am J Clin Nutr 87(5):1212–1218
Fabbrini E, Magkos F, Mohammed BS, Pietka T, Abumrad NA, Patterson BW, Okunade A, Klein S (2009) Intrahepatic fat, not visceral fat, is linked with metabolic complications of obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(36):15430–15435. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0904944106
Karastergiou K, Fried SK (2013) Multiple adipose depots increase cardiovascular risk via local and systemic effects. Curr Atheroscler Rep 15(10):361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-013-0361-5
Pramyothin P, Karastergiou K (2016) What can we learn from interventions that change fat distribution? Curr Obes Rep 5(2):271–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-016-0215-x
Hernandez TL, Bessesen DH, Cox-York KA, Erickson CB, Law CK, Anderson MK, Wang H, Jackman MR, Van Pelt RE (2015) Femoral lipectomy increases postprandial lipemia in women. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 309(1):E63–E71. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00080.2015
Cameron AJ, Magliano DJ, Soderberg S (2013) A systematic review of the impact of including both waist and hip circumference in risk models for cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and mortality. Obes Rev 14(1):86–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2012.01051.x
Lombardi F, Gullotta F, Columbaro M, Filareto A, D’Adamo M, Vielle A, Guglielmi V, Nardone AM, Azzolini V, Grosso E, Lattanzi G, D’Apice MR, Masala S, Maraldi NM, Sbraccia P, Novelli G (2007) Compound heterozygosity for mutations in LMNA in a patient with a myopathic and lipodystrophic mandibuloacral dysplasia type A phenotype. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(11):4467–4471. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-0116
Guglielmi V, D’Adamo M, D’Apice MR, Bellia A, Lauro D, Federici M, Lauro R, Novelli G, Sbraccia P (2010) Elbow deformities in a patient with mandibuloacral dysplasia type A. Am J Med Genet A 152A(11):2711–2713. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.33700
McLaughlin TM, Liu T, Yee G, Abbasi F, Lamendola C, Reaven GM, Tsao P, Cushman SW, Sherman A (2010) Pioglitazone increases the proportion of small cells in human abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue. Obesity (Silver Spring) 18(5):926–931. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2009.380
Bosello O, Donataccio MP, Cuzzolaro M (2016) Obesity or obesities? Controversies on the association between body mass index and premature mortality. Eat Weight Disord 21(2):165–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-016-0278-4
Bellia A, Marinoni G, D’Adamo M, Guglielmi V, Lombardo M, Donadel G, Gentileschi P, Lauro D, Federici M, Lauro R, Sbraccia P (2012) Parathyroid hormone and insulin resistance in distinct phenotypes of severe obesity: a cross-sectional analysis in middle-aged men and premenopausal women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(12):4724–4732. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2012-2513
Bluher M (2014) Are metabolically healthy obese individuals really healthy? Eur J Endocrinol 171(6):R209–R219. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-14-0540
Marques-Vidal P, Pecoud A, Hayoz D, Paccaud F, Mooser V, Waeber G, Vollenweider P (2010) Normal weight obesity: relationship with lipids, glycaemic status, liver enzymes and inflammation. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 20(9):669–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2009.06.001
Badoud F, Perreault M, Zulyniak MA, Mutch DM (2015) Molecular insights into the role of white adipose tissue in metabolically unhealthy normal weight and metabolically healthy obese individuals. FASEB J 29(3):748–758. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.14-263913
Srdic B, Stokic E, Korac A, Ukropina M, Velickovic K, Breberina M (2010) Morphological characteristics of abdominal adipose tissue in normal-weight and obese women of different metabolic profiles. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 118(10):713–718. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1254165
Kloting N, Fasshauer M, Dietrich A, Kovacs P, Schon MR, Kern M, Stumvoll M, Bluher M (2010) Insulin-sensitive obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 299(3):E506–E515. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00586.2009
Item F, Konrad D (2012) Visceral fat and metabolic inflammation: the portal theory revisited. Obes Rev 13 Suppl 2:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2012.01035.x
Carobbio S, Rodriguez-Cuenca S, Vidal-Puig A (2011) Origins of metabolic complications in obesity: ectopic fat accumulation. The importance of the qualitative aspect of lipotoxicity. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 14(6):520–526. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0b013e32834ad966
Bachman ES, Dhillon H, Zhang CY, Cinti S, Bianco AC, Kobilka BK, Lowell BB (2002) BetaAR signaling required for diet-induced thermogenesis and obesity resistance. Science 297(5582):843–845. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1073160
Feldmann HM, Golozoubova V, Cannon B, Nedergaard J (2009) UCP1 ablation induces obesity and abolishes diet-induced thermogenesis in mice exempt from thermal stress by living at thermoneutrality. Cell Metab 9(2):203–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2008.12.014
Saito M, Okamatsu-Ogura Y, Matsushita M, Watanabe K, Yoneshiro T, Nio-Kobayashi J, Iwanaga T, Miyagawa M, Kameya T, Nakada K, Kawai Y, Tsujisaki M (2009) High incidence of metabolically active brown adipose tissue in healthy adult humans: effects of cold exposure and adiposity. Diabetes 58(7):1526–1531. https://doi.org/10.2337/db09-0530
Guglielmi V, Sbraccia P (2017) Type 2 diabetes: does pancreatic fat really matter? Diabetes Metab Res Rev. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.2955
Sacks HS, Fain JN (2007) Human epicardial adipose tissue: a review. Am Heart J 153(6):907–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2007.03.019
Fain JN, Sacks HS, Bahouth SW, Tichansky DS, Madan AK, Cheema PS (2010) Human epicardial adipokine messenger RNAs: comparisons of their expression in substernal, subcutaneous, and omental fat. Metabolism 59(9):1379–1386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2009.12.027
Sacks HS, Fain JN, Holman B, Cheema P, Chary A, Parks F, Karas J, Optican R, Bahouth SW, Garrett E, Wolf RY, Carter RA, Robbins T, Wolford D, Samaha J (2009) Uncoupling protein-1 and related messenger ribonucleic acids in human epicardial and other adipose tissues: epicardial fat functioning as brown fat. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(9):3611–3615. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2009-0571
Mazurek T, Zhang L, Zalewski A, Mannion JD, Diehl JT, Arafat H, Sarov-Blat L, O’Brien S, Keiper EA, Johnson AG, Martin J, Goldstein BJ, Shi Y (2003) Human epicardial adipose tissue is a source of inflammatory mediators. Circulation 108(20):2460–2466. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000099542.57313.C5
Iacobellis G, Cotesta D, Petramala L, De Santis V, Vitale D, Tritapepe L, Letizia C (2010) Intracoronary adiponectin levels rapidly and significantly increase after coronary revascularization. Int J Cardiol 144(1):160–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2008.12.155
Iacobellis G, Leonetti F, Singh N, A MS (2007) Relationship of epicardial adipose tissue with atrial dimensions and diastolic function in morbidly obese subjects. Int J Cardiol 115(2):272–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2006.04.016
Guglielmi V, Maresca L, Lanzillo C, Marinoni GM, D’Adamo M, Di Roma M, Preziosi P, Bellia A, Calo L, Sbraccia P (2016) Relationship between regional fat distribution and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy phenotype. PLoS One 11(7):e0158892. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0158892
Nagashima K, Okumura Y, Watanabe I, Nakai T, Ohkubo K, Kofune T, Kofune M, Mano H, Sonoda K, Hirayama A (2011) Association between epicardial adipose tissue volumes on 3-dimensional reconstructed CT images and recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation. Circ J 75(11):2559–2565
Venteclef N, Guglielmi V, Balse E, Gaborit B, Cotillard A, Atassi F, Amour J, Leprince P, Dutour A, Clement K, Hatem SN (2015) Human epicardial adipose tissue induces fibrosis of the atrial myocardium through the secretion of adipo-fibrokines. Eur Heart J 36(13):795–805. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/eht099
Guglielmi V, Sbraccia P (2017) Epicardial adipose tissue: at the heart of the obesity complications. Acta Diabetol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-017-1020-z
Galvez-Prieto B, Bolbrinker J, Stucchi P, de Las Heras AI, Merino B, Arribas S, Ruiz-Gayo M, Huber M, Wehland M, Kreutz R, Fernandez-Alfonso MS (2008) Comparative expression analysis of the renin–angiotensin system components between white and brown perivascular adipose tissue. J Endocrinol 197(1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-07-0284
Ozen G, Daci A, Norel X, Topal G (2015) Human perivascular adipose tissue dysfunction as a cause of vascular disease: focus on vascular tone and wall remodeling. Eur J Pharmacol 766:16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.09.012
Rittig K, Dolderer JH, Balletshofer B, Machann J, Schick F, Meile T, Kuper M, Stock UA, Staiger H, Machicao F, Schaller HE, Konigsrainer A, Haring HU, Siegel-Axel DI (2012) The secretion pattern of perivascular fat cells is different from that of subcutaneous and visceral fat cells. Diabetologia 55(5):1514–1525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-012-2481-9
Chatterjee TK, Stoll LL, Denning GM, Harrelson A, Blomkalns AL, Idelman G, Rothenberg FG, Neltner B, Romig-Martin SA, Dickson EW, Rudich S, Weintraub NL (2009) Proinflammatory phenotype of perivascular adipocytes: influence of high-fat feeding. Circ Res 104(4):541–549. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.182998
Thanassoulis G, Massaro JM, Corsini E, Rogers I, Schlett CL, Meigs JB, Hoffmann U, O’Donnell CJ, Fox CS (2012) Periaortic adipose tissue and aortic dimensions in the Framingham Heart Study. J Am Heart Assoc 1(6):e000885. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.112.000885
Fox CS, Massaro JM, Schlett CL, Lehman SJ, Meigs JB, O’Donnell CJ, Hoffmann U, Murabito JM (2010) Periaortic fat deposition is associated with peripheral arterial disease: the Framingham heart study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 3(5):515–519. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.110.958884
Foster MC, Hwang SJ, Porter SA, Massaro JM, Hoffmann U, Fox CS (2011) Fatty kidney, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease: the Framingham Heart Study. Hypertension 58(5):784–790. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.175315
Wagner R, Machann J, Lehmann R, Rittig K, Schick F, Lenhart J, Artunc F, Linder K, Claussen CD, Schleicher E, Fritsche A, Haring HU, Weyrich P (2012) Exercise-induced albuminuria is associated with perivascular renal sinus fat in individuals at increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 55(7):2054–2058. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-012-2551-z
Chughtai HL, Morgan TM, Rocco M, Stacey B, Brinkley TE, Ding J, Nicklas B, Hamilton C, Hundley WG (2010) Renal sinus fat and poor blood pressure control in middle-aged and elderly individuals at risk for cardiovascular events. Hypertension 56(5):901–906. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.157370
Montani JP, Carroll JF, Dwyer TM, Antic V, Yang Z, Dulloo AG (2004) Ectopic fat storage in heart, blood vessels and kidneys in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 28 Suppl 4:S58–S65. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802858
Vettor R, Milan G, Franzin C, Sanna M, De Coppi P, Rizzuto R, Federspil G (2009) The origin of intermuscular adipose tissue and its pathophysiological implications. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297(5):E987–E998. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00229.2009
Marcus RL, Addison O, Kidde JP, Dibble LE, Lastayo PC (2010) Skeletal muscle fat infiltration: impact of age, inactivity, and exercise. J Nutr Health Aging 14(5):362–366
Addison O, Marcus RL, Lastayo PC, Ryan AS (2014) Intermuscular fat: a review of the consequences and causes. Int J Endocrinol 2014:309570. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/309570
Kim JH, Jung MH, Lee JM, Son HS, Cha BY, Chang SA (2012) Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is highly associated with nontraumatic fractures in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 77(1):51–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04222.x
Gallagher D, Kuznia P, Heshka S, Albu J, Heymsfield SB, Goodpaster B, Visser M, Harris TB (2005) Adipose tissue in muscle: a novel depot similar in size to visceral adipose tissue. Am J Clin Nutr 81(4):903–910 pii]
Gallagher D, Kelley DE, Yim JE, Spence N, Albu J, Boxt L, Pi-Sunyer FX, Heshka S (2009) Adipose tissue distribution is different in type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 89(3):807–814. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.26955
Ribeiro RJ, Monteiro CP, Cunha VF, Azevedo AS, Oliveira MJ, Monteiro R, Fraga AM, Principe P, Lobato C, Lobo F, Morais A, Silva V, Sanches-Magalhaes J, Oliveira J, Guimaraes JT, Lopes CM, Medeiros RM (2012) Tumor cell-educated periprostatic adipose tissue acquires an aggressive cancer-promoting secretory profile. Cell Physiol Biochem 29(1–2):233–240. https://doi.org/10.1159/000337604
Ribeiro R, Monteiro C, Catalan V, Hu P, Cunha V, Rodriguez A, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Fraga A, Principe P, Lobato C, Lobo F, Morais A, Silva V, Sanches-Magalhaes J, Oliveira J, Pina F, Lopes C, Medeiros R, Fruhbeck G (2012) Obesity and prostate cancer: gene expression signature of human periprostatic adipose tissue. BMC Med 10:108. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-10-108
Freedland SJ, Banez LL, Sun LL, Fitzsimons NJ, Moul JW (2009) Obese men have higher-grade and larger tumors: an analysis of the duke prostate center database. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 12(3):259–263. https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2009.11
Hamrick MW, McGee-Lawrence ME, Frechette DM (2016) Fatty infiltration of skeletal muscle: mechanisms and comparisons with bone marrow adiposity. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 7:69. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2016.00069
Hardouin P, Rharass T, Lucas S (2016) Bone marrow adipose tissue: to be or not to be a typical adipose tissue? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 7:85. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2016.00085
Sadie-Van Gijsen H, Crowther NJ, Hough FS, Ferris WF (2013) The interrelationship between bone and fat: from cellular see-saw to endocrine reciprocity. Cell Mol Life Sci 70(13):2331–2349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1211-2
Iwaniec UT, Turner RT (2013) Failure to generate bone marrow adipocytes does not protect mice from ovariectomy-induced osteopenia. Bone 53(1):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2012.11.034
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by a Grant from the Ministero della Salute (Project no. 45/RF-2013-02357791).
Conflict of interest
Valeria Guglielmi declares that she has no conflict of interest. Paolo Sbraccia declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the topical collection on Italian Society of Obesity’s Reviews.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guglielmi, V., Sbraccia, P. Obesity phenotypes: depot-differences in adipose tissue and their clinical implications. Eat Weight Disord 23, 3–14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-017-0467-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-017-0467-9