Key summary points
This study aimed to compare postural control without or with dual task, in patients over 65 years,depending on the degree of arterial stiffness, measured using the carotid-femoral pulse.
AbstractSection FindingsSway path traveled and surface covered by the center of foot pressure were measured on a force platform in different postural conditions, i.e. eyes open, eyes closed and eyes open with a dual task, allowing to calculate the length function of surface (LFS), this ratio providing information about the precision (surface) of postural control and the effort made (length) by the participant. After an age-adjustment, LFS was higher in participants with high pulse wave velocity in different postural conditions especially dual task condition.
AbstractSection MessageThe difficulties in maintaining the equilibrium under a dual task condition being more pronounced in people with increased arterial stiffness, it is necessary to avoid or to limit its aggravation to reduce the number of falls, one of the main causes of mortality in the elderly.
Abstract
Purpose
Arterial stiffness generates vascular alterations that may cause balance disorders and falls. This study aimed to investigate the possible link between arterial stiffness and postural control under different sensorial conditions in patients over 65 years.
Methods
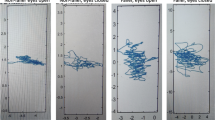
Carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (PWV) was measured in 47 participants aged over 65 years to evaluate their arterial stiffness (high PWV). Twenty-seven participants (mean age = 70.52 ± 4.02 years, 22 females) had a normal PWV (< 10 m s−1) and 20 participants (mean age = 75.93 ± 6.11 years; 15 females) had a high PWV (≥ 10 m s−1). Postural control was evaluated using a force platform in four postural conditions: eyes open (EO) 1, eyes closed (EC), eyes open with a dual task (DT) and eyes open again (EO2). Using sway path traveled and surface covered by the center of foot pressure, we calculate the length function of surface (LFS). This ratio provides information about the precision (surface) of postural control and the effort made (length) by the subjects.
Results
After an age-adjustment, LFS was lower in EO than in EC and DT in both groups (p ≤ 0.001). LFS was higher in participants with high PWV both in eyes open and eyes closed conditions (p < 0.05). LFS increased when PWV increased in EO (p < 0.01) and EC conditions (p < 0.001) but not when a dual task was performed.
Conclusion
Difficulties in maintaining equilibrium under a dual-task condition are more pronounced in people with increased arterial stiffness. These data suggest that understanding of the influence of the arterial stiffness level on specific balance control parameters could contribute to propose better balance-oriented rehabilitation programs in older adults in an attempt to prevent fall.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Salthouse TA, Somberg BL (1982) Time-accuracy relationships in young and old adults. J Gerontol 37:449–453
Mourey F, Pozzo T, Rouhier-Marcer I, Didier JP (1998) A kinematic comparison between elderly and young subjects standing up from and sitting down in a chair. Age ageing 27:137–146
Ungar A, Rivasi G, Petrovic M et al (2020) Toward a geriatric approach to patients with advanced age and cardiovascular diseases: position statement of the EuGMS special interest group on cardiovascular medicine. Eur Geriatr Med 11(1):179–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-019-00267-0
Hausdorff JM, Herman T, Baltadjieva R, Gurevich T, Giladi N (2003) Balance and gait in older adults with systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol 91:643–645
Lipsitz LA (1985) Abnormalities in blood pressure homeostasis that contribute to falls in the elderly. Clin Geriatr Med 1:637–648
Matsubayashi K, Okumya K, Wada T, Osaki Y, Fujisawa M, Doi Y, Ozama T (1997) Postural dysregulation in systolic blood pressure is associated with worsened scoring on neurobehavioral function tests and leukoaraiosis in the older elderly living in a community. Stroke 28:2169–2173
Applegate WB, Davis BR, Black HR, Smith WM, Miller ST, Burlando AJ (1991) Prevalence of postural hypotension at baseline in the systolic hypertension in the elderly program (SHEP) cohort. J Am Geriatr Soc 39:1057–1064
Van Swieten JC, Geyskes GG, Derix MM, Peeck BM, Ramos LM, van Latum JC, van Gijn J (1991) Hypertension in the elderly is associated with white matter lesions and cognitive decline. Ann Neurol 30:825–830. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.410300612
Schmidt R, Fazekas F, Koch M, Kapeller P, Augustin M, Offenbacher H, Fazekas G, Lechner H (1995) Magnetic resonance imaging cerebral abnormalities and neuropsychologic test performance in elderly hypertensive subjects. Arch Neurol 52:905–910
Scheinberg P (1988) Dementia due vascular disease: a multifactorial disorder. Stroke 19:1291–1299
Ylikoski R, Ylikoski A, Raininko R, Keskivaara P, Sulkava R, Tilvis R, Erkinjuntti T (2000) Cardiovascular disease, health status, brain imaging findings and neuropsychological functioning in neurologically healthy elderly individuals. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 30:115–130
Pfitzenmeyer P, Martin-Hunyadi C, Mourey F, d’Athis P, Baudouin N, Mischis-Troussard C (2002) Cardiovascular characteristics and cerebral CT findings in elderly subjects with psychomotor disadaptation syndrome. Aging Clin Exp Res 14:100–107
Kuo HK, Lipsitz LA (2004) Cerebral white matter changes and geriatric syndromes: is there a link? J Gerontol A Biol Sci 59:818–826
Jamet M, Deviterne D, Gauchard GC, Vançon G, Perrin P (2004) Higher visual dependency increases balance control perturbation during cognitive task in the elderly people. Neurosci Lett 25:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.02.010
Jamet M, Deviterne D, Gauchard GC, Vançon G, Perrin P (2007) Age-related part taken by attentional cognitive processes in standing postural control in dual-task context. Gait Posture 25:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2006.03.006
Rankin JK, Woollacott MH, Shumway-Cook A, Brown LA (2000) Cognitive influence on postural stability: a neuromuscular analysis in young and older adults. J Gerontol A boil Sci Med Sci 55:MI112-119
Deviterne D, Gauchard GC, Jamet M, Vançon G, Perrin P (2005) Added cognitive load through rotary auditory stimulation can improve the quality of postural control in the elderly. Brain Res Bull 64:157–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2004.10.007
Salvi P, Giuseppe L, Labat C, Ricci E, Pannier B, Benetos A (2004) Validation of a new non-invasive portable tonometer for determining arterial pressure wave and pulse wave velocity: the PulsePen device. J Hypertens 22(12):2285–2293. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004872-200412000-00010
Salvi P, Magnani E, Valbusa F, Agnoletti D, Alecu C, Joly L, Benetos A (2008) Comparison study of methodologies for pulse wave velocity estimation. J Hum Hypertens 22:669–677
Butlin M, Qasem A (2017) Large artery stiffness assessment using SphygmoCor technology. Pulse 4:180–192
Van Bortel L.M., Laurent S., Boutouyrie P., Chowienczyk P., Cruickshank J.K., De Backer T., Filipovsky J., Huybrechts S., Mattace-Raso F.U.S., Protogerou A.D., Schillaci G., Segers P., Vermeersch S., Weber T., Artery Society, European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Vascular Structure and Function, European Network for Noninvasive Investigation of Large Arteries (2012) Expert consensus document on the measurement of aortic stiffness in daily practice using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity. J. Hypertens 30:445–448
Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Agabiti RE, Azizi M, Burnier M, Clement D, Coca A, De Simone G, Dominiczak A, Kahan T, Mahfoud F, Redon J, Ruilope L, Zanchetti A, Kerins M, Kjeldsen S, Kreutz R, Laurent S, Lip GYH, McManus R, Narkiewicz K, Ruschitzka F, Schmieder R, Shlyakhto E, Tsioufis K, Aboyans V, Desormais I (2018) Practice guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension of the European society of hypertension (ESH) and the European society of cardiology (ESC). Blood Press 27:314–340
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) « Mini-mental state ». A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Zuliani G, Polastri M, Romagnoli T, Marabini L, Seripa D, Cervellati C, Zurlo A, Passaro A, Brombo G (2020) Clinical and demographic parameters predict the progression from mild cognitive impairment to dementia in elderly patients. Aging Clin Exp Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-020-01697-8
Yesavage JA, Brink TL, Rose TL, Lum O, Huang V, Adey M, Leirer VO (1982) Development and validation of a geriatric depression screening scale: a preliminary report. J Psychiatr Res 17(1):37–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3956(82)90033-4
Katz S, Ford AB, Moskowitz RW, Jackson BA, Jaffe MW (1963) Studies of illness in the aged. The index of ADL: a standardized measure of biological and psychological function. JAMA 185:914–919. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1963.03060120024016
Kuo HK, Lipsitz LA (2004) Cerebral white matter changes and geriatric syndromes: is there a link? J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 59(8):818–826. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/59.8.m818
Lion A, Spada RS, Bosser G, Gauchard GC, Anello G, Bosco P et al (2013) Biological determinants of postural disorders in elderly women. Int J Neurosci 123(1):24–30. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2012.722570
Perrin P, Jeandel C, Perrin CA, Béné MC (1997) Influence of visual control, conduction, and central integration on static and dynamic balance in healthy older adults. Gerontology 43(4):223–231. https://doi.org/10.1159/000213854
Bizzo G, Guillet N, Patat A, Gagey PM (1985) Specifications for building a vertical force platform designed for clinical stabilometry. Med Biol Eng Comput 23:474–476. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02448937
Lion A, Spada RS, Bosser G, Gauchard GG, Anello G, Bosco P, Calabrese S, Iero A, Stella G, Elia M, Perrin P (2014) “Postural first” principle when balance is challenged in elderly people. Int J Neurosci 124(8):558–566. https://doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2013.864288
Peultier-Celli L, Audouin M, Beyaert C, Perrin P (2020) Postural control in lyric singers. J Voice 23:S0892-1997(20)30154–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2020.04.019
Maire R, Mallinson A, Ceyte H, Caudron S, Van Nechel C, Bisdorff A, Magnusson M, Petersen H, Kingma H, Perrin P (2017) Discussion about visual dependence in balance control: European society for clinical evaluation of balance disorders. J Int Adv Otol 13(3):404–406. https://doi.org/10.5152/iao.2017.4344
Brooke-Wavell K, Perrett LK, Howarth PA, Haslam RA (2002) Influence of the visual environment on the postural stability in healthy older women. Gerontology 48(5):293–297. https://doi.org/10.1159/000065252
Perrin P, Gauchard GC, Perrot C, Jeandel C (1999) Effects of physical and sporting activities on balance control in elderly people. Br J Sports Med 33(2):121–126
Cromwell RL, Newton RA, Forrest G (2002) Influence of vision on head stabilization strategies in older adults during walking. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 57(7):M442-448
Brodoehl S, Klinger C, Witte OW (2016) Age-dependant modulation of the somatosensory network upon eye closure. Behav Brain Res 298:52–56
Watson NL, Sutton-Tyrell K, Youk AO, Boudreau RM, Mackey RH, Simonsick EM, Rosano C, Hardy SE, Windham BG, Harris TB, Najjar SS, Lakatta EG, Atkinson HH, Johnson KC, Bauer DC, Newman AB (2011) Arterial stiffness and gait speed in older adults with and without peripheral arterial disease. Am J Hypertens 24(1):90–95
Wong AK, Lord SR, Trollor JN, Sturnieks DL, Delbaere K, Menant J, Brodaty H, Sachdev PS, Close JC (2004) Hight arterial pulse wave velocity is a risk factors for falls in community-dwelling older people. J Am Geriatr Soc 62(8):1534–1539
Li Y, Hanssen H, Cordes M, Rossmeissl A, Endes S, Schmidt-Trucksäss A (2015) Aerobic, resistance and combined exercise training on arterial stiffness in normotensive and hypertensive adults: a review. Eur J Sport Sci 15(5):443–457. https://doi.org/10.1080/17461391.2014.955129
Otsuki T, Namatame H, Yoshikawa T, Zempo-Miyaki A (2020) Combined aerobic and low-intensity resistance exercise training increases basal nitric oxide production and decreases arterial stiffness in healthy older adults. J Clin Biochem Nutr 66(1):62–66. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.19-81
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Dr. Art Mallinson (Vancouver, British Columbia, CA) for his helpful advice in the final read-through of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was promoted by the Nancy University Hospital, France, which, as promoter, according to the law, paid for the study’s insurance coverage.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors contribute to the study concept and design. LP-C, AL and SB realized the posturography recordings. GW and AB realized the cardiovascular investigations determining the assignment in a given group. Statistical analyses were made under the supervision of RG, statistician. PhP is principal investigator of the study. All the authors contribute to the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the French Medical Ethical Committee (Comité de Protection des Personnes Est III de Lorraine) and by the National Agency for Medicines and Health Products Safety.
Informed consent
All the participants gave their written informed consent prior to the study.
Consent for publication
All the authors consent for publication.
Availability of data and material
The Direction for Research of the Nancy University Hospital, as study Promoter (which is not Investigator of the study), is the owner of the data and may allow their transmission according to the terms of an agreement.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peultier-Celli, L., Lion, A., Buatois, S. et al. Relation of arterial stiffness with postural control in older people. Eur Geriatr Med 12, 871–879 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-021-00468-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-021-00468-6