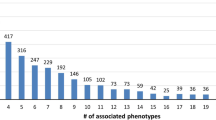
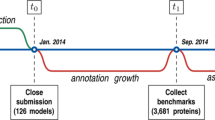
Abstract
Deciphering the relationship between human proteins (genes) and phenotypes is one of the fundamental tasks in phenomics research. The Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) builds upon a standardized logical vocabulary to describe the abnormal phenotypes encountered in human diseases and paves the way towards the computational analysis of their genetic causes. To date, many computational methods have been proposed to predict the HPO annotations of proteins. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive review of the existing approaches to predicting HPO annotations of novel proteins, identifying missing HPO annotations, and prioritizing candidate proteins with respect to a certain HPO term. For each topic, we first give the formalized description of the problem, and then systematically revisit the published literatures highlighting their advantages and disadvantages, followed by the discussion on the challenges and promising future directions. In addition, we point out several potential topics to be worthy of exploration including the selection of negative HPO annotations and detecting HPO misannotations. We believe that this review will provide insight to the researchers in the field of computational phenotype analyses in terms of comprehending and developing novel prediction algorithms.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The datasets analyzed in this review are available on the Human Phenotype Ontology website, “https://hpo.jax.org”.
References
Akhmetov I, Bubnov RV (2015) Assessing value of innovative molecular diagnostic tests in the concept of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine. EPMA J 6(1):19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13167-015-0041-3
Anbalagan M, Huderson B, Murphy L, Rowan BG (2012) Post-translational modifications of nuclear receptors and human disease. Nucl Recept Signal 10(1):nrs-1001
Ashburner M et al (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. Nat Genet 25(1):25–29. https://doi.org/10.1038/75556
Barbeira AN et al (2018) Exploring the phenotypic consequences of tissue specific gene expression variation inferred from GWAS summary statistics. Nat Commun 9(1):1–20
Bekker J, Davis J (2020) Learning from positive and unlabeled data: a survey. Mach Learn 109(4):719–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-020-05877-5
Bentz AB, Thomas GWC, Rusch DB, Rosvall KA (2019) Tissue-specific expression profiles and positive selection analysis in the tree swallow (Tachycineta bicolor) using a de novo transcriptome assembly. Sci Rep 9(1):1–12
Boycott KM, Vanstone MR, Bulman DE, MacKenzie AE (2013) Rare-disease genetics in the era of next-generation sequencing: discovery to translation. Nat Rev Genet 14(10):681–691. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3555
Bromberg Y (2013) Disease gene prioritization. PLoS Comput Biol 9(4):e1002902. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002902
Burges C (2010) From RankNet to LambdaRank to LambdaMART: an overview. Technical report, Microsoft Research
Bush WS, Moore JH (2012) Genome-wide association studies. PLoS Comput Biol 8(12):e1002822. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002822
Chapelle O, Schölkopf B, Zien A (eds) (2006) Semi-Supervised Learning. The MIT Press. https://doi.org/10.7551/mitpress/9780262033589.001.0001
Chen M, Wei Z, Huang Z, Ding B, Li Y (2020) Simple and deep graph convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 37th international conference on machine learning, ICML 2020, 13–18 July 2020, virtual event. Proceedings of machine learning research, vol 119, pp 1725–1735. PMLR
Cho H, Berger B, Peng J (2016) Compact integration of multi-network topology for functional analysis of genes. Cell Syst 3(6):540–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2016.10.017
Chong JX et al (2015) The genetic basis of Mendelian phenotypes: discoveries, challenges, and opportunities. Am J Hum Genet 97(2):199–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.06.009
Deans Andrew R et al (2015) Finding our way through phenotypes. PLoS Biol 13(1):e1002033. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002033
Deegan JI, Dimmer EC, Mungall CJ (2010) Formalization of taxon-based constraints to detect inconsistencies in annotation and ontology development. BMC Bioinform 11:530. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-530
Defferrard M, Bresson X, Vandergheynst P (2016) Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In: Advances in neural information processing systems 29: annual conference on neural information processing systems 2016, December 5–10, 2016, Barcelona, Spain, pp 3837–3845
Doğan T (2018) HPO2GO: prediction of human phenotype ontology term associations for proteins using cross ontology annotation co-occurrences. PeerJ 6:e5298. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.5298
Dolinski K, Botstein D (2007) Orthology and functional conservation in eukaryotes. Annu Rev Genet 41:465–507. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.40.110405.090439
Firth HV et al (2009) DECIPHER: database of chromosomal imbalance and phenotype in humans using ensembl resources. Am J Hum Genet 84(4):524–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.03.010
Forster DT, Boone C, Bader GD, Wang B (2021) BIONIC: biological network integration using convolutions. bioRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.15.435515
Fu G, Wang J, Yang B, Yu G (2016a) NegGOA: negative GO annotations selection using ontology structure. Bioinformatics 32(19):2996–3004. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw366
Fu G, Yu G, Wang J, Guo M (2016b) Protein function prediction using positive and negative examples (in Chinese). J Comput Res Dev 53(8):1753–1765. https://doi.org/10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20160196
Gao J, Yao S, Mamitsuka H, Zhu S (2018) AiProAnnotator: low-rank approximation with network side information for high-performance, large-scale human protein abnormality annotator. In: IEEE international conference on bioinformatics and biomedicine, BIBM 2018, Madrid, Spain, December 3–6, 2018, pp 13–20. IEEE Computer Society. https://doi.org/10.1109/BIBM.2018.8621517
Gao J, Liu L, Yao S, Mamitsuka H, Zhu S (2019) HPOAnnotator: improving large-scale prediction of HPO annotations by low-rank approximation with HPO semantic similarities and multiple PPI networks. BMC Med Genom 12(10):187. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12920-019-0625-1
Gligorijevic V, Barot M, Bonneau R (2018) deepNF: deep network fusion for protein function prediction. Bioinformatics 34(22):3873–3881. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty440
Goh K, Cusick ME, Valle D, Childs B, Vidal M, Barabási A (2007) The human disease network. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(21):8685–8690. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0701361104
Groza T et al (2015) The human phenotype ontology: semantic unification of common and rare disease. Am J Hum Genet 97(1):111–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.05.020
Guan Y et al (2012) Tissue-specific functional networks for prioritizing phenotype and disease genes. PLoS Comput Biol 8(9):e1002694
Hamosh A, Scott AF, Amberger JS, Bocchini CA, McKusick VA (2002) Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), a knowledgebase of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res 30(1):52–55. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki033
Han P, Yang P, Zhao P, Shang S, Liu Y, Zhou J, Gao X, Kalnis P (2019) GCN-MF: disease-gene association identification by graph convolutional networks and matrix factorization. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, KDD 2019, Anchorage, AK, USA, August 4–8, 2019, pp 705–713. ACM. https://doi.org/10.1145/3292500.3330912
Hekselman I, Yeger-Lotem E (2020) Mechanisms of tissue and cell-type specificity in heritable traits and diseases. Nat Rev Genet 21(3):137–150
Hoehndorf R, Schofield PN, Gkoutos GV (2011) PhenomeNET: a whole-phenome approach to disease gene discovery. Nucleic Acids Res 39(18):e119. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr538
Horton Jay D, Cohen Jonathan C, Hobbs Helen H (2007) Molecular biology of PCSK9: its role in LDL metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 32(2):71–77
Hu Y, Koren Y, Volinsky C (2008) Collaborative filtering for implicit feedback datasets. In: Proceedings of the 8th IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM 2008), December 15–19, 2008, Pisa, Italy, pp 263–272. IEEE Computer Society. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2008.22
Jiang Y et al (2016) An expanded evaluation of protein function prediction methods shows an improvement in accuracy. Genome Biol 17(1):184. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1037-6
Joshi B et al (2008) Phosphorylated caveolin-1 regulates Rho/ROCK-dependent focal adhesion dynamics and tumor cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res 68(20):8210–8220
Kahanda I, Funk C, Verspoor K, Ben-Hur A (2015) PHENOstruct: prediction of human phenotype ontology terms using heterogeneous data sources [version 1; peer review: 2 approved]. F1000Research 4:259. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.6670.1
Kipf TN, Welling M (2017) Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In: 5th International conference on learning representations, ICLR 2017, Toulon, France, April 24–26, 2017, conference track proceedings. OpenReview.net
Koonin EV (2005) Orthologs, paralogs, and evolutionary genomics. Annu Rev Genet 39:309–338. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.39.073003.114725
Kulmanov M, Hoehndorf R (2020) DeepPheno: predicting single gene loss-of-function phenotypes using an ontology-aware hierarchical classifier. PLoS Comput Biol 16(11):e1008453. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008453
Lee DD, Seung HS (2000) Algorithms for non-negative matrix factorization. In: Advances in neural information processing systems 13, Papers from Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) 2000, Denver, CO, USA, pp 556–562. MIT Press
Lee JS et al (2019) PCSK9 inhibition as a novel therapeutic target for alcoholic liver disease. Sci Rep 9(1):1–16
Li H (2011) A short introduction to learning to rank. IEICE Trans Inf Syst 94-D(10):1854–1862. https://doi.org/10.1587/TRANSINF.E94.D.1854
Li Q, Han Z, Wu X-M (2018) Deeper insights into graph convolutional networks for semi-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the thirty-second AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, (AAAI-18), the 30th innovative applications of artificial intelligence (IAAI-18), and the 8th AAAI symposium on educational advances in artificial intelligence (EAAI-18), New Orleans, Louisiana, USA, February 2–7, 2018, pp 3538–3545. AAAI Press
Li G, Müller M, Thabet AK, Ghanem B (2019) DeepGCNs: can GCNs go as deep as CNNs? In: 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, ICCV 2019, Seoul, Korea (South), October 27–November 2, 2019, pp 9266–9275. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00936
Lin D (1998) An information-theoretic definition of similarity. In: Shavlik JW (ed) Proceedings of the fifteenth international conference on machine learning (ICML 1998), Madison, Wisconsin, USA, July 24–27. Morgan Kaufmann, pp 296–304
Liu L, Huang X, Mamitsuka H, Zhu S (2020) HPOLabeler: improving prediction of human protein-phenotype associations by learning to rank. Bioinformatics 36(14):4180–4188. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa284
Lu C, Wang J, Zhang Z, Yang P, Yu G (2016) NoisyGOA: noisy GO annotations prediction using taxonomic and semantic similarity. Comput Biol Chem 65:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2016.09.005
Lu C, Chen X, Wang J, Yu G, Yu Z (2018) Identifying noisy functional annotations of proteins using sparse semantic similarity (in Chinese). Sci Sin Inform 48(8):1035–1050. https://doi.org/10.1360/N112017-00105
Mann M, Jensen ON (2003) Proteomic analysis of post-translational modifications. Nat Biotechnol 21(3):255–261
Martin L, Latypova X, Terro F (2011) Post-translational modifications of tau protein: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 58(4):458–471
Mostafavi S, Morris Q (2010) Fast integration of heterogeneous data sources for predicting gene function with limited annotation. Bioinformatics 26(14):1759–1765. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq262
Mostafavi S, Ray D, Warde-Farley D, Grouios C, Morris Q (2008) GeneMANIA: a real-time multiple association network integration algorithm for predicting gene function. Genome Biol 9(S1):S4. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2008-9-s1-s4
Notaro M, Schubach M, Frasca M, Mesiti M, Robinson PN, Valentini G (2017a) Ensembling descendant term classifiers to improve gene-abnormal phenotype predictions. In: International meeting on computational intelligence methods for bioinformatics and biostatistics, pp 70–80. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-14160-8_8
Notaro M, Schubach M, Robinson PN, Valentini G (2017b) Prediction of Human Phenotype Ontology terms by means of hierarchical ensemble methods. BMC Bioinform 18(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1854-y
Oti M, Snel B, Huynen MA, Brunner HG (2006) Predicting disease genes using protein–protein interactions. J Med Genet 43(8):691–698. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.2006.041376
Pavan S, Rommel K, Marquina MEM, Höhn S, Lanneau V, Rath A (2017) Clinical practice guidelines for rare diseases: the orphanet database. PLoS One 12(1):e0170365. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170365
Peng J, Xue H, Wei Z, Tuncali I, Hao J, Xuequn Shang (2021) Integrating multi-network topology for gene function prediction using deep neural networks. Brief Bioinform 22(2):2096–2105. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbaa036
Petegrosso R, Park S, Hwang TH, Kuang R (2017) Transfer learning across ontologies for phenome–genome association prediction. Bioinformatics 33(4):529–536. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw649
Peter RN (2012) Deep phenotyping for precision medicine. Hum Mutat 33(5):777–780. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.22080
Robinson PN, Köhler S, Bauer S, Seelow D, Horn D, Mundlos S (2008) The Human Phenotype Ontology: a tool for annotating and analyzing human hereditary disease. Am J Hum Genet 83(5):610–615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.09.017
Rousselet E, Marcinkiewicz J, Kriz J, Zhou A, Hatten ME, Annik Prat, Seidah NG (2011) PCSK9 reduces the protein levels of the LDL receptor in mouse brain during development and after ischemic stroke. J Lipid Res 52(7):1383–1391
Scheuermann RH, Ceusters W, Smith B (2009) Toward an ontological treatment of disease and diagnosis. Summit Transl Bioinform 2009:116–120
Schriml LM, Arze C, Nadendla S, Wayne Chang Y, Mazaitis M, Felix V, Feng G, Kibbe WA (2012) Disease ontology: a backbone for disease semantic integration. Nucleic Acids Res 40(D1):D940–D946. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr972
Seo J-W, Lee K-J (2004) Post-translational modifications and their biological functions: proteomic analysis and systematic approaches. BMB Rep 37(1):35–44
Smith B (2003) Ontology. In: Floridi L (ed) Blackwell Guide to the Philosophy of Computing and Information, Chapter 11. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 155–166
Smith CL, Goldsmith CW, Eppig JT (2005) The Mammalian Phenotype Ontology as a tool for annotating, analyzing and comparing phenotypic information. Genome Biol 6(1):R7. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2004-6-1-r7
Son JH et al (2018) Deep phenotyping on electronic health records facilitates genetic diagnosis by clinical exomes. Am J Hum Genet 103(1):58–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2018.05.010
Valentini G, Armano G, Frasca M, Lin J, Mesiti M, Matteo Re (2016) RANKS: a flexible tool for node label ranking and classification in biological networks. Bioinformatics 32(18):2872–2874. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw235
Vargas L et al (2002) Functional interaction of caveolin-1 with Bruton’s tyrosine kinase and Bmx. J Biol Chem 277(11):9351–9357
Wang P, Lai W, Li MJ, Xu F, Yalamanchili HK, Lovell-Badge R, Wang J (2013) Inference of gene-phenotype associations via protein–protein interaction and orthology. PLoS One 8(10):e77478. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077478
Wang Y-C, Peterson SE, Loring JF (2014) Protein post-translational modifications and regulation of pluripotency in human stem cells. Cell Res 24(2):143–160
Wang Z, Zhou M, Arnold CW (2020) Toward heterogeneous information fusion: bipartite graph convolutional networks for in silico drug repurposing. Bioinformatics 36(Supplement\_1):i525–i533, 07. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa437
Wei X, Zhang C, Freddolino PL, Zhang Y, Lu Z (2020) Detecting Gene Ontology misannotations using taxon-specific rate ratio comparisons. Bioinformatics 36(16):4383–4388. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa548
Wiechen K et al (2001) Caveolin-1 is down-regulated in human ovarian carcinoma and acts as a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Am J Pathol 159(5):1635–1643
Wolpert DH (1992) Stacked generalization. Neural Netw 5(2):241–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0893-6080(05)80023-1
Xu X, Cui Y, Cao L, Zhang Y, Yin Y, Hu X (2017) PCSK9 regulates apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med 13(5):1993–1999
Xu H, Wang Y, Lin S, Deng W, Peng D, Cui Q, Yu X (2018) PTMD: a database of human disease-associated post-translational modifications. Genom Proteom Bioinform 16(4):244–251
Xue H, Peng J, Shang X (2019) Towards gene function prediction via multi-networks representation learning. In: The thirty-third AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, AAAI 2019, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, January 27–February 1, 2019, pp 10069–10070. AAAI Press. https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v33i01.330110069
Youngs N, Penfold-Brown D, Drew K, Shasha DE, Bonneau R (2013) Parametric Bayesian priors and better choice of negative examples improve protein function prediction. Bioinformatics 29(9):1190–1198. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt110
Youngs N, Penfold-Brown D, Bonneau R, Shasha DE (2014) Negative example selection for protein function prediction: the NoGO database. PLoS Comput Biol 10(6):e1003644. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003644
Yu H, Zhang VW (2015) Precision medicine for continuing phenotype expansion of human genetic diseases. BioMed Res Int 2015:745043. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/745043
Yu G, Fu G, Wang J, Guo M (2017a) Predicting irrelevant functions of proteins based on dimensionality reduction (in Chinese). Sci Sin Inf 47(10):1349–1368. https://doi.org/10.1360/N112017-00009
Yu G, Lu C, Wang J (2017b) NoGOA: predicting noisy GO annotations using evidences and sparse representation. BMC Bioinform 18(1):350. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1764-z
Zhao X-M, Wang Y, Chen L, Aihara K (2008) Gene function prediction using labeled and unlabeled data. BMC Bioinform 9:57. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-57
Zhou D, Bousquet O, Lal TN, Weston J, Schölkopf B (2003) Learning with local and global consistency. In: Advances in neural information processing systems 16 [Neural information processing systems, NIPS 2003, December 8–13, 2003, Vancouver and Whistler, British Columbia, Canada]. MIT Press, pp 321–328
Zhu C, Byrd RH, Lu P, Nocedal J (1997) Algorithm 778: L-BFGS-B: Fortran subroutines for large-scale bound-constrained optimization. ACM Trans Math Softw 23(4):550–560. https://doi.org/10.1145/279232.279236
Zhu X, Ghahramani Z, Lafferty JD (2003) Semi-supervised learning using Gaussian fields and harmonic functions. In: Machine learning, proceedings of the twentieth international conference (ICML 2003), August 21–24, 2003, Washington, DC, USA. AAAI Press, pp 912–919
Zitnik M, Leskovec J (2017) Predicting multicellular function through multi-layer tissue networks. Bioinformatics 33(14):i190–i198
Zitnik M, Agrawal M, Leskovec J (2018) Modeling polypharmacy side effects with graph convolutional networks. Bioinformatics 34(13):i457–i466. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty294
Funding
SZ has been supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 61872094), Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (no. 2018SHZDZX01), ZJ Lab, and Shanghai Center for Brain Science and Brain-Inspired Technology. LL has been supported by the 111 Project (no. B18015), Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project (no. 2017SHZDZX01) and Information Technology Facility, CAS-MPG Partner Institute for Computational Biology, Shanghai Institute for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Authors’ Contributions
SZ conceived and supervised the work. SZ and LL designed the study. LL drafted the paper. SZ modified the paper. SZ and LL finalized the paper.
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent to Publication
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Zhu, S. Computational Methods for Prediction of Human Protein-Phenotype Associations: A Review. Phenomics 1, 171–185 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-021-00019-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-021-00019-w