Abstract
The pineal hormone melatonin has been shown to exert an inhibitory influence only on estrogen receptor (ER)-positive human breast tumor cell lines and to modulate ER expression, suggesting that melatonin’s actions may be linked to the cell’s estrogen response pathway. Two distinct melatonin receptors have recently been identified, a membrane-bound G protein-coupled receptor (Mella) and a nuclear orphan receptor (RZR/RORα) belonging to the retinoic acid receptor class. Melatonin’s antitumorigenic effects in MCF-7 cells have been shown to be mediated via the Mella receptor and appear to be serum-dependent. We investigated whether melatonin, alone or in conjunction with serum factors such as EGF and insulin, can modulate ER activity by affecting ER phosphorylation and transactivation. We found that melatonin alone decreased ER phosphorylation but did not transactivate the ER. However, a combined treatment with melatonin followed by either EGF or insulin stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activity and induced ER phosphorylation, leading to transactivation of the human ER. Taken together, these findings suggest the possibility of cross talk between the melatonin receptor pathway and the tyrosine kinase receptor pathways.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
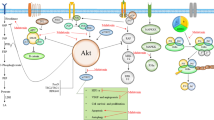
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acuna-Castroviejo D, Pablos MI, Menendez-Pelaez A, Reiter RJ (1993) Melatonin receptors in purified cell nuclei of liver. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol 82:253–256.
Ali S, Metzger D, Bornet J-M, Chambón P (1993) Modulation of transcriptional activation by ligand-dependent phosphorylation of the human oestrogen receptor A/B region. EMBO J 12:1153–1160.
Armstrong DK, Issacs JT, Ottaviano YL, Davidson NE (1992) Programmed cell death during regression of the MCF-7 human breast cancer following estrogen ablation. Cancer Res 51:3418–3424.
Arnold SF, Obourn JD, Yudt MR, Carter TH, Notides AC (1995) In vivo and in vitro phosphorylation of the human estrogen receptor. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 52:159–171.
Aronica SM, Katzenellenbogen BS (1993) Stimulation of estrogen receptor-mediated transcription and alteration in the phosphorylation state of the rat uterine estrogen receptor by estrogen, cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and insulin-like growth factor. Mol Endocrinol 7:743–752.
Bartsch C, Bartsch H, Jain AK, Laumas KR, Wetterberg L (1981) Urinary melatonin levels in human breast cancer patients. J Neural Transm 52:269–279.
Bates S, Davidson NE, Valverius EM, Freter CE, Dickson RB, Tam JP, Kudlow JE, Solomon DS, Lippman ME (1988) Expression of transforming growth factor alpha and its mRNA in human breast cancer: its regulation by estrogen and its possible functional significance. Mol Endocrinol 2:543–555.
Becker-André M, Wiesenberg I, Schaeren-Wiemers M, Saurat JH, Carlberg C (1994) Pineal gland hormone melatonin binds and activates an orphan of the nuclear receptor superfamilly. J Biol Chem 269:28531–28536.
Birnbaumer LG (1990) G-proteins in signal transduction. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 30:675–705.
Bittman EL, Weaver DL (1990) The distribution of melatonin binding sites in neuroendocrine tissue of the ewe. Biol Reprod 43:986–993.
Blask DE (1984) The pineal: An oncostatic gland? In: Reiter RJ (ed) The Pineal Gland. Raven Press, New York, pp 253–284.
Blask DE, Hill SM (1986) Effects of melatonin on cancer: studies on MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in culture. J Neural Transm 29:406–412.
Blask DE, Hill SM, Orstead KM, Massa JS (1986) Inhibitory effects of the pineal hormone melatonin and underfeeding during the promotional phase of 7,12-dimethylbenzanthracene (DMBA)-induced mammary tumorigenesis. J Neural Transm 67:125–138.
Blask DE, Pelletier DB, Hill SM, Lemus-Wilson A, Grosso DS, Wilson ST, Wise ME (1991) Pineal melatonin inhibition of tumor promotion in the N-nitroso-N-methylurea model of mammary carcinognesis: potential involvement of antiestrogenic mechanisms in vivo. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 117:526–532.
Brown AM, Jeltsch JM, Roberts M, Chambon P (1984) Activation of pS2 gene transcription is a primary response to estrogen in the human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Proc Natl Acad Sc. U.S.A. 81:6344–6388.
Burns DM, Cos CS, Blask D (1990) Demonstration and partial characterization of 2-iodomelatonin binding sites in experimental mammary carcinoma. Program of the 72nd Annual Meeting of the Endocrine Society, San Antonio, TX, p 62 (abstract).
Cavailles V, Augereau P, Garcia M, Rochefort H (1988) Estrogens and growth factors induce the mRNA of the 52K-pro-cathepsin-D secreted by breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1903–1919.
Carlberg C, Hooft van Huijsduijnen R, Staple JK, De Lamarter JF, Becker-Andre M (1994) RZRs, a new family of retinoid-related orphan receptors that function as both monomers and homodimers. Mol Endocrinol 8:757–770.
Carlson LL, Weaver DR, Reppert SM (1989) Melatonin signal transduction in hamster brain: inhibition of adenyl cyclase by pertusssis toxin-sensitive G protein. Endocrinology 125:2670–2676.
Chang N, Spaulding TS, Tseng MT (1985) Inhibitory effects of superior cervical ganglionectomy on dimethylbenzanthracene-induced mammary tumors in the rat. J Pineal Res 2:331–340.
Cos S, Blask DE, Lemus-Wilson A, Hill AB (1991) Effects of melatonin on the cell cycle kinetics and “estrogen-rescue” of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in culture. J Pineal Res 10:36–42.
Danforth DN, Tamarkin L, Lippman ME (1983 a) Melatonin increases oestrogen receptor binding activity of human breast cancer cells. Nature 305:323–325.
Danforth DN, Tamarkin L, Do R, Lippman ME (1983 b) Melatonin induced increase in cytoplasmic estrogen receptor activity in hamster uteri. Endocrinology 113:81–85.
Daniel PH, Prichard M L (1963) The response of experimentally induced mammary tumors in rats to ovariectomy. Br J Cancer 17:687–693.
Dickson RB, Lippman ME (1987) Estrogenic regulation of growth and polypeptide growth factor secretion in human breast carcinoma. Endocr Rev 8:29–43.
Dubocovich ML (1991) Pharmacological characterization of melatonin binding sites. Advances in Pineal Res 5:167–173.
Ebisawa T, Karne S, Lerner MR, Reppert SM (1994) Expression cloning of a high-affinity melatonin receptor from Xenopus dermal melanophores. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:6133–6137.
Eckert RL, Katzenellenbogen BS (1982) Effects of estrogens and antiestrogens on estrogen receptor dynamics and the induction of progesterone receptor in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 42:139–144.
Edwards DP, Chamness GC, McGuire WL (1979) Estrogen and progesterone receptor proteins in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Acta 5460:457–486.
Forman BM, Chen J, Blumberg B, Kliewer SA, Henshaw R, Ong ES, Evans RM (1994) Crosstalk among RORal and the Rev-erb family of orphan nuclear receptors. Mol Endocrinol 8: 1253–1261.
Godson C, Reppert SM (1997) The Mella melatonin receptor is coupled to parallel signal transduction pathways. Endocrinology 138:397–404.
Giguere V, Tini M, Flock G, Ong E, Evans RM, Otulakoski G (1994) Isoform-specific amino-terminal domains indicate DNA-binding properties of RORa, a novel family of orphan hormone nuclear receptors. Genes Dev 8:538–553.
Hafner F, Holler E, von Angerer E (1996) Effect of growth factors on estrogen receptor mediated gene expression. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 58:385–393.
Hazelrigg DG, Thompson M, Hastings MH, Morgan PJ (1996) Regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in the pars tuberalis of ovine pituitary: interactions between melatonin, insulinlike growth factor-1, and forskolin. Endocrinology 137:210–218.
Hill SM, Blask DE (1988) Effects of the pineal hormone melatonin on the proliferation and the morphological characteristics of human breast cancer cells (MCF-7) in culture. Cancer Res 48:6121–6126.
Hill SM, Spriggs LL, Simon MA, Muraoka H, Blask DE (1992) The growth inhibitory action of melatonin on human breast cancer cells is linked to the estrogen response system. Cancer Letters 64:249–256.
Horwitz KB, McGuire WL (1978) Estrogen control of progesterone receptor in human breast cancer: correlations with nuclear processing of estrogen receptors. J Biol Chem 253:2223–2228.
Kane CD, Means AR (1998) Ligand independent activation of orphan receptor mediated transcription by Ca++/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV. 80th Ann Mtg Endocrine Society, New Orleans, LA, Abstract # OR14–1, p 71.
Kato S, Endoh H, Masuhiro Y, Kitamoto T, Uchiyama S, Sasaki H, Masushige S, Gotch Y, Nishide E, Chambon P (1995) Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by the mitogen activated protein kinase. Science 270:1491–1494.
Katzenellenbogen BS (1980) Dynamics of steroid hormone receptor action. Ann Rev Physiol 42:17–35.
Klein-Hitpass L, Schorpp M, Wagner U, Ryffel GU (1986) An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5’-flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell 46:1053–1061.
Laitinen JT, Saavedra JM (1990) Characterization of melatonin receptors in the rat suprachiasmatic nuclei: modulation of affinity with cations and guanine nucleotides. Endocrinology 126: 2210–2215.
Lawson NO, Wee B, Blask DE, Castles C, Spriggs LL, Hill SM (1992) Modulation of hypothalamic estrogen receptors by melatonin in female LSH/SsLak golden hamsters. J Biol Reprod 47:1082–1090.
Le Goff P, Montano MM., Shodin DJ, Katzenellenbogen BS (1994) Phosphorylation of the human estrogen receptor. J Biol Chem 269:4458–4466.
Lerner AB, Case JD, Heinzelman RV (1959) Structure of melatonin. J Am Chem Soc 81:6084–6085.
Lippman ME, Bolan G, Huff K (1976) The effects of estrogen and antiestrogen on hormone-responsive human breast cancer in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res 36:4595–4601.
Luttrell LM, Della Rocca GJ, van Biesen T, Lattrell DK, Lefkowitz RJ (1997) Gßy subunits mediate Src-dependent phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. A scaffold for G protein- coupled receptor-mediated Ras activity. J Biol Chem 272:4637–4644.
McNulty S, Morgan PJ, Thompson M, Davidson G, Lawson W, Hastings MH (1994) Phospholipases and melatonin signal transduction in the ovine pars tuberalis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 99:73–79.
McNulty S, Ross AW, Barrett P, Hastings MH, Morgan PJ (1994) Melatonin regulates the phosphorylation of CREB in ovine pars tuberalis. J Neuroendocrinol 6:523–532.
Menendez-Pelaez A, Reiter RJ (1993) Distribution of melatonin in mammalian tissues: the relative importance of nuclear versus cytoplasmic localization. J Pineal Res 15:59–69.
Molis TM, Spriggs LL, Hill SM (1994) Modulation of estrogen receptor mRNA expression by melatonin in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol 8:1681–1690.
Molis TM, Spriggs LL, Jupiter Y, Hill SM (1995) Melatonin modulation of estrogen-regulated proteins, growth factors, and proto-oncogenes in human breast cancer. J Pineal Res 18:93–103.
Molis TM, Walters MR, Hill SM (1993) Melatonin modulation of estrogen receptor expression in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol 3:687–694.
Morgan PJ, Lawson W, Davidson G, Howell HE (1989) Guanine nucleotides regulate the affinity of melatonin receptors in the ovine pars tuberalis. Neuroendocrinology 50:359–362.
Morgan PJ, Perry B, Edward HH, Helliwell R, Sugden D (1994) Melatonin receptors, localization, molecular pharmacology and physiological significance. Neurochem Int 24:101–146.
Murphy LC, Sutherland RL (1985) Differential effects of tamoxifen and analogs with non-basic side chains on cell proliferation in vitro. Endocrinology 116:1071–1078.
Pace AM, Faure M, Bourne HR (1995) Gil-mediated activation of the MAP kinase cascade. Mol Biol Cell 6:1685–1695.
Pearson WR (1990) Rapid ans sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Methods Enzymol 183:63–98.
Ram PR, Hill SM (1995) Melatonin’s inhibition of breast cancer cell proliferation is mediated through the RORa receptor pathway. Seventh Int. Congress on Hormones and Cancer, Quebec, Canada, p 62.
Ram PT, Kiefer T, Silverman M, Song Y, Brown GM, Hill SM (1998) Estrogen receptor transactivation in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by melatonin and growth factors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 141:53–64.
Reiter RJ (1980) The pineal and its hormones in the control of reproduction in mammals. Endocr Rev 1:109–131.
Reiter RJ (1987) The melatonin message: duration versus coincidence hypothesis. Life Science 40: 2119–2124.
Reiter RJ (1988) Neuroendocrinology of melatonin. In: Miles A, Philbrick DR, Thompson C (eds) Melatonin, Clinical Perspectives. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 1–42.
Reiter RJ (1991) Melatonin: That ubiquitously acting pineal hormone. Psychological Science 6: 223–228.
Reppert SM, Weaver DR, Ebisawa T (1994) Cloning and characterization of a melatonin receptor that mediates reproductive and circadian responses. Neuron 13:1177–1185.
Rivkees SA, Carlson LL, Reppert SM (1989) Guanine nucleotide binding protein regulation of melatonin receptors in lizard brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:11543–11546.
Rothenberg PL, Kahn CR (1988) Insulin inhibits pertussis toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of G-proteins. Evidence for a novel interaction between insulin receptors and G-proteins. J Biol Chem 263:15546–15552.
Saceda M, Lippman ME, Chambón P, Lindsey RL, Ponglikitmongkol M, Puente M, Martin MB (1988) Regulation of estrogen receptor in MCF-7 cells by estradiol. Mol Endocrinol 2:1157–1162.
Sanchez-Barcelo EJ, Corral SC, Mediavilla MD (1988) Influence of pineal gland function on the initiation and growth of hormone-dependent breast tumors. Possible mechanisms. In: Gupta D, Attanasio A, Reiter RJ (eds) The Pineal Gland and Cancer. Brain Res. Promotion, Tübingen, Germany, pp 221–232.
Shafie SM, Gibson SL, Hilf R (1977) Effects of insulin and estrogen on hormone binding in the R3230 AC mammary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 37:4641–4649.
Song Y, Chan CWY, Brown GM, Pang SF, Silverman M (1997) Studies of the renal actions of melatonin: evidence that the effects are mediated by 37 kD receptors of the Mella subtype localized primarily to the basolateral membrane of the proximal tubule. FASEB J 11:93–100.
Stankov B, Lucini V, Scaglione F (1991) 2-[125]iodomelatonin binding in normal and neoplastic tissues: In: Fraschini F, Reiter RJ (eds) Role of Melatonin and Pineals Peptides in Neuroimmuno- modulation. Plenum, New York, pp 117–125.
Steinhilber D, Brungs M, Werz O, Wiesenberg I, Danielsson C, Kahlen JP, Nayeri S, Schrader M, Carlberg C (1995) The nuclear receptor for melatonin represses 5-lipoxygenase gene expression in human B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 270:7037–7040.
Sutherland RL, Green MD, Hall RE, Reddle RR, Taylor IW (1983) Tamoxifen induces accumulation of MCF-7 human mammary carcinoma cells in G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 19:615–621.
Tamarkin L, Danforth D, Lichter A, DeMoss E, Cohen M, Chabner B, Lippman ME (1982) Decreased nocturnal plasma melatonin peak in patients with estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Science 216:1003–1005.
Tapp E (1982) The pineal gland in malignancy. In: Reiter RJ (ed) The Pineal Gland, Vol. 3, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 171–188.
Thompson EW, Katz D, Shima TB, Wakeling AE, Lippman ME, Dickson RB (1989) ICI 164,384, a pure antagonist of estrogen-stimulated MCF-7 cell proliferation and invasiveness. Cancer Res 49:6929–6934.
Tini M, Fraser A, Giguere V (1995) Functional interactions between retinoic acid receptors, related orphan receptor (RORa) and the retinoic acid receptors in the regulation of the µF-crytalline promoter. J Biol Chem 270:20156–20162.
Tzukerman MT, Esty A, Santiso-Mere D, Danielian P, Parker MG, Stein RB, Pike JW, McDonnell DP (1994) Human estrogen receptor transcriptional capacity is determined by both cellular and promoter context and mediated by two functionally distinct intramolecular regions. Mol Endocrinol 9:21–30.
Vanecek J, Pavlik A, Illnerova H (1987) Hypothalamic receptor sites revealed by autoradiography. Brain Res 435:359–363.
Vanecek J (1995) Melatonin inhibits increase of intracellular calcium and cyclic AMP in neonatal rat pituitary via independent pathways. Mol Cell Endocrinol 107:149–153.
Weaver DR, Namboordiri MAA, Reppert SM (1988) Iodinated melatonin mimics melatonin action and reveals discrete binding sites in fetal brain. FEBS Lett 228:123–127.
Weisz A, Breciani F (1988) Estrogen induces expression of c-fos and c-myc protooncogenes in rat uterus. Mol Endocrinol 2:816–824.
Welsch CW, Nagasawa H (1977) Prolactin and murine mammary tumorigenesis: a review. Cancer Res 37:951–963.
Wiesenberg I, Missbach M, Kahlen JP, Schrader M, Carlberg C (1995) Transcriptional activation of the nuclear receptor RZRa by the pineal gland hormone melatonin and identification of CGP 52608 as a synthetic ligand. Nucleic Acid Res 23:327–333.
Williams LM, Morgan PJ, Hastings MH, Lawson W, Davidson G, Howell HE (1989) Melatonin receptor sites in the Syrian hamster brain and pituitary: localization and characterization using [125I]iodinated melatonin. J Neuroendocrinol 1:315–329.
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2001 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hill, S.M., Kiefer, T., Teplitzky, S., Spriggs, L.L., Ram, P. (2001). Modulation of the Estrogen Response Pathway in Human Breast Cancer Cells by Melatonin. In: Bartsch, C., Bartsch, H., Blask, D.E., Cardinali, D.P., Hrushesky, W.J.M., Mecke, D. (eds) The Pineal Gland and Cancer. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-59512-7_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-59512-7_16
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-64003-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-59512-7
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive