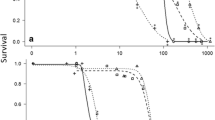
The fate and effects of two pyrethroid insecticides (lambda-cyhalothrin and cypermethrin) were investigated in replicated 25 m3 pond mesocosms. Three pesticide treatments which simulated spray drift deposition were examined: 0.7 g a.i. ha-1 cypermethrin and 0.17 and 1.7 g a.i. ha-1 lambda-cyhalothrin. Based on the use rate and pesticidal activity of the chemicals, the cypermethrin and lower lambda-cyhalothrin rates were approximately equivalent. After applications, pyrethroid residues in the water column declined rapidly. Treatment-related effects were observed on some macroinvertebrate taxa, most notably the Asellidae and Gammaridae. Surfacedwelling insects also suffered initial knock-down, particularly in the 1.7 g a.i. ha-1 lambda-cyhalothrin treatment, but there was recovery after the spray period. No adverse effects occurred on algae, macrophytes or zooplankton, but there were occasional enhancements (e.g. algal biomass and abundances of copepod nauplii and Rotifera) which may have been indirect effects. An overall comparison of the treatments indicated that the higher lambda-cyhalothrin rate had the greatest effects, whilst the cypermethrin application had a somewhat greater impact than the lower lambda-cyhalothrin treatment rate (due to effects on peracarid crustaceans). The study indicated that should spray drift occur at the levels expected for either pyrethroid's normal use patterns, potential impacts on natural aquatic ecosystems would be minor and transient.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon (1979) Biological Methods for the Surveillance of River Water Quality. University of Aston Report, DOE. Contract No. DER/480/100.
Eberhardt, L.L. (1978) Appraising variability in population studies. J. Wildl. Manag. 42, 207–38.
Gaarder, T. and Gran, M.M. (1927) Investigations of the production of plankton in Oslo Fjord. Rapp. Process-Verbaux. Reunions. Cons. Perma. Int. Explor. Mer. 42.
Ganzelmeier, M., Koepp, H., Spangenberg, R. and Streloke, M. (1993) Wann Pflanzenschutzmittel Abstandsauflagen erhalten. Pflanzenschutz-Praxis 3/1993, 14–15.
Hadfield, S.T., Sadler, J.K., Bolygo, E. and Hill, I.R. (1992) Development and validation of residue methods for the determination of the pyrethroids lambda-cyhalothrin and cypermethrin in natural waters. Pestic. Sci. 34, 207–13.
Hamer, M.J., Maund, S.J. and Hill, I.R. (1992) Laboratory methods for evaluating the impact of pesticides on water/sediment organisms. Brighton Crop Protect. Conf.-Pests Dis. 2, 487–96.
Heimbach, F., Pflüger, W. and Ratte, H.-T. (1992) Use of small artificial ponds for assessments of hazards to aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 11, 27–34.
Heinis, L.J. and Knuth, M.L. (1992) The mixing, distribution and persistence of esfenvalerate within littoral enclosures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 11, 11–25.
Hill, I.R. (1985) Effects on non-target organisms in terrestrial and aquatic environments. In Leahey, J.P. ed. The pyrethroid insecticides, pp. 151–262. London: Taylor & Francis.
Hill, I.R. (1989) Aquatic organisms and pyrethroids. Pestic. Sci. 27, 429–65.
Hill, I.R., Shaw, J.L. and Maund, S.J. (1994a) Review of aquatic field tests with pyrethroid insecticides. In Hill, I.R., Heimbach, F., Leeuwangh, P. and Matthiessen, P. eds. Freshwater field tests for hazard assessment of chemicals, pp. 249–71. Michigan: Lewis Publishers.
Hill, I.R., Travis, K.Z. and Ekoniak, P. (1994b) Spray-drift and run-off of foliar applied pyrethroids to aquatic mesocosms: rates, frequencies and methods. In: Graney, R.L., Kennedy, J.H. and Rodgers, J.H. eds. Aquatic mesocosm studies in ecological risk assessment, pp. 201–40. Special Publication, Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. Michigan: Lewis Publishers.
Hurlbert, S.H. (1984) Pseudoreplication and the design of field experiments. Ecol. Monogr. 54, 187–211.
Lind, O.T. (1979) Handbook of Common Methods in Limnology. St Louis, Toronto, London: The C.V. Mosby Co.
Lozano, S.J., Brazner, J.C., Knuth, M.L., Heinis, L.J., Sargent, K.W., Tanner, D.K., Anderson, L.E., O'Halloran, S.L., Bertelsen, S.L., Jensen, D.A., Kline, E.R., Balcer, M.D., Stay, F.S. and Siefert, R.E. (1989) Effects, Persistence and Distribution of Esfenvelerate in Littoral Enclosures. US EPA Duluth and University of Wisconsin-Superior, Report DU E104/PPA 06/7592 A.
Lozano, S.J., O'Halloran, S.L., Sargent, K.W. and Brazner, J.C. (1992) Effects of esfenvalerate on aquatic organisms in littoral enclosures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 11, 35–47.
Miller, T.A. and Salgado, V.L. (1985) The mode of action of pyrethroids on insects. In Leahey, J.P. ed. The pyrethroid insecticides, pp. 151–262. London: Taylor & Francis.
Muir, D.C.G., Rawn, G.P. and Grift, N.P. (1985) Fate of the pyrethroid insecticide deltamethrin in small ponds: a mass balance study. J. Agricult. Food Chem. 33, 603–9.
Shaw, J.L., Moore, M., Kennedy, J.H. and Hill, I.R. (1994) Design and statistical analysis of field aquatic mesocosm studies. In Graney, R.L., Kennedy, J.H. and Rodgers, J.H. eds. Aquatic mesocosm studies in ecological risk assessment, pp. 85–104. Special Publication, Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry. Michigan: Lewis Publishers.
Sokal, R.R. and Rohlf, F.J. (1981) Biometry, 2nd edition. New York: W.H. Freeman.
Stephenson, R.R. (1982) Aquatic toxicology of cypermethrin. 1. Acute toxicity to some freshwater fish and invertebrates in laboratory tests. Aquatic Toxicol. 2, 175–85.
Tooby, T.E., Thompson, A.N., Rycroft, R.J., Black, I.A. and Hewson, R.T. (1981) A Pond Study to Investigate the Effects of Fish and Aquatic Invertebrates of Deltamethrin Applied Directly onto Water. UK MAFF Report PRD 1276.
Wetzel, R.G. (1983) Limnology, 2nd edition. Saunders College Publishing.
Yasuno, M., Hanazato, T., Iwakuma, T., Takamura, K., Ueno, R. and Takamura, N. (1988) Effects of permethrin on phytoplankton and zooplankton in an enclosure ecosystem in a pond. Hydrobiologia 159, 247–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farmer, D., Hill, I.R. & Maund, S.J. A comparison of the fate and effects of two pyrethroid insecticides (lambda-cyhalothrin and cypermethrin) in pond mesocosms. Ecotoxicology 4, 219–244 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116342
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116342