Abstract
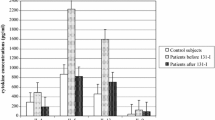
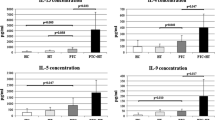
Long term interferon (IFN) therapy is frequently associated with side effects which affect the thyroid gland such as hypothyroidism and thyroiditis. We have therefore tested the ability of type I-IFNs to exert direct effects on primary cultures of human thyroid epithelial cells: (i) Type I-IFNs (IFN-α 2b and IFN-ω) inhibit cell proliferation as determined by [3H]thymidine incorporation with a half-maximal effect at ∼1 ng/ml (50 pM). Inhibition of cell growth is observed in cells derived from normal thyroid as well as neoplastic tissue (autonomous and non-secreting adenoma; follicular, papillary and anaplastic carcinoma). (ii) Over a similar concentration range, type I-IFNs suppressed thyroglobulin release by thyroid cells. (iii) IFN-α 2b stimulated surface expression of major histocompatibility class (MHC) I but not MHC II molecules, while IFN-γ enhanced the expression of both MHC I and MHC II molecules. This effect of IFN-γ, but not that of IFN-α 2b was antagonized by suramin. (iv) Incubation of thyroid cells with IFN-α 2b also resulted in increased cell surface levels of the intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1). These findings demonstrate that type I-IFNs directly affect thyroid function and explain related side effects of these cytokines. In addition, our results provide a rational basis for the possible use of type I-IFNs in the treatment of patients with advanced thyroid cancer for whom no therapeutic alternative exists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adolf GR (1987) Antigenic structure of human interferon-omega 1 (interferon alphaII1): Comparison with other human interferons. J Gen Virol 68:1669–1676
Borden EC (1992) Interferons: Pleiotropic cellular modulators. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 62:S18-S24
Burman P, Totterman TH, Oberg K, Karlsson FA (1986) Thyroid autoimmunity in patients on long term therapy with leukocyte-derived interferon. J Clin Endocrinol Metabolism 63:1086–1090
Clemens M, McNurlan M (1985) Regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation by interferons. Biochemical J 226:345–360
Coffey R, Leof F, Shipley G, Moses H (1987) Suramin inhibition of growth factor receptor binding and mitogenicity in AKR-2B cells. J Cell Physiol 132:143–148
Cordell JL, Falini B, Ether WN, Ghosh AK, Abdulaziz Z, Macdonald S, Pulford KAF, Stein H and Mason DJ (1984) Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP) complex. J Histochem 32:219–228
Dumont JE, Maenhaut C, Pirson-I, Baptist M, Roger-PP (1991) Growth factors controlling the thyroid gland. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab 5:727–754
Edwards BS, Merrit JA, Fuhlbrigge RC, Borden EC (1985) Low doses of interferon-alpha result in more effective clinical natural killer cell activation. J Clin Invest 75:1908–1913
Fauci AS, Rosenberg SA, Sherwin SA, Dinarello CA, Longo DL, Lane HC (1987) Immunomodulators in clinical medicine. Ann Intern Med 106:421–433
Fentiman IS, Thomas BS, Balquil FR, Rubens RD, Hayward JL (1985) Primary hypothyroidism associated with interferon therapy of breast cancer. Lancet I:1166–1167
Flores I, Mariano MT and Pestka S (1991) Human interferon omega binds to the alpha/beta receptor. J Biol Chem 266:19875–19877
Gisslinger H, Gilly B, Woloscuk W, Mayr WR, Havelec L, Linkesch W, Weissel M (1992) Thyroid autoimmunity and hypothyroidism during long-term treatment with recombinant interferon-alpha. Clin Exp Immunol 90:363–367
Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Londei M, Grenall C, Pirich K, Kassal H, Waldhusel W, Feldmann M (1988) Pathogenetic relevance of HLA class II expressing thyroid follicular cells in nontoxic goiter and in Graves' disease. J Clin Invest 81:1608–1614
Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Buchan G, Sadeghi R, Kissonerghis M, Londei M, Turner K, Pirich R, Roka B, Niederle H, Kassal H, Waldhäusel W, Feldmann M (1989) Transforming growth factor beta regulates thyroid growth. J Clin Invest 83:764–770
Hauptmann R, Swetly P (1985) A novel class of human type I interferons. Nucl Acids Res 13:4739–4749
Kaupilla A, Cantell K, Känne O, Kokko E, Vihko R (1982) Serum sex steroid and peptide hormone concentrations, and endometrial estrogen and progestin receptor levels during administration of human leukocyte interferon. Int J Cancer 29:291–294
Lok AS, Lai CL, Leung EK (1990) Interferon alpha antibodies may negate the antiviral effects of recombinant alpha-interferon treatment in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 12:1266–270
Mills G, Zhang N, May C, Hill M, Chung A (1990) Suramin prevents binding of interleukin-2 to its cell surface receptor: a possible mechanism for immunosuppression. Cancer Res 50:3036–3042
Motoyasu S, Moriaty J, Toshiaki B, Kohn DL, Singer DS (1992) Hormonal regulation of major histocompatibility complex class I genes in rat thyroid FRTL-5 cells: Thyroid-stimulating hormone induces a cAMP-mediated decrease in class I expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:1944–1948
Öberg K, Alm GV, Magnuson A, Lundqvist G, Theodorsson E, Wide L, Wilander E (1989) Treatment of maligant carcinoid tumours with recombinant interferon alfa-2b: Development of neutralizing interferon antibodies and possible loss of antitumour activity. J Natl Cancer Inst 81:531–535
Pestka S, Langer JA, Zoon KC, Samuel CE (1987) Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem 56:727–777
Pichert G, Jost LM, Zobelli L, Obermatt B, Pedio G, Stahel RA (1990) Thyroiditis after treatment with interleukin-2 and interferonalpha-2a. Br J Cancer 62:100–104
Pollak M, Richard M (1990) Suramin blockade of insulinlike growth factor I stimulated proliferation of human osteosarcoma cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:1349–1352
Saji M, Moriarty J, Ban T, Singer DS, Kohn DL (1992) Major histocompatibility class I gene expression in rat thyroid cells is regulated by hormones, methimazole, and iodide as well as interferon. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 75:871–878
Scalzo S, Gengaro A, Boccoli I, Masciulli R, Gianella G, Salvo G, Marolla P, Carlini P, Massimini G, Holdener E, Testa U, Calabresi F, Peschle C (1990) Primary hypothyroidism associated with interleukin-2 and interferon alpha-2 therapy of melanoma and renal carcinoma. Eur J Cancer 26:1152–1156
Schultz M, Muller R, Von Zur Muhlen A, Brabant G (1989) Induction of hyperthyroidism by interferon-alpha. Lancet I:1452
Selzer E, Wilfing A, Schiferer A, Hermann M, Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Freissmuth M (1993) Stimulation of thyroid growth via the inhibitory G protein Gi: Constitutive expression of the G protein alpha-subunit Gi-alpha-l in autonomous adenoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1609–1613
Sen GC, Lengrel P (1992) The interferon system: a bird'seye view of its biochemistry. J Biol Chem 267:5017–5020
Springer TA (1990) Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature 346:425–434
Steis, RG, Smith JW, Urba WJ, Clark JW, Itri LM, Evans LM, Schoenberger C, Longo DL (1988) Resistance to interferon alfa-2a in hairy cell leukemia associated with neutralizing anti-interferon antibodies. N Engl J Med 318:1409–1413
Tanaka K, Yoshioka T, Bieberich C, Jay G (1988) Role of the major histocompatibility complex class I antigens in tumor growth and metastasis. Ann Rev Immunol 6:359–380
Trieb K, Dorfinger K,Neuhold N, Selzer E, Wilfing A, Czernin S, Hermann M, Niederle B, Gessl A, Vierhapper H, Freissmuth M, and Grubeck-Loebenstein B (1992) Suramin affects differentiated and undifferentiated human thyroid cells in vitro. J Endocrinol 134:505–511
Wiederman CJ, Vogel W, Tilg HWiedermann FJ, Herold M, Zilian U, Wohlfarter T, Gruber M, Braunsteiner H (1991) Suppression of thyroid function by interferon-alpha-2 in man. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343:665–668
Williams BRG (1991) Transcriptional regulation of interferon-stimulated genes. Eur J Biochem 200:1–11
Williams LT, Tremble PM, Lavin MF, Sunday AE (1984) Platelet derived growth factor receptors form a high-affinity state in membrane preparations: Kinetics and cross-linking studies. J Biol Chem 259:5287–5294
von Wussow P, Freund M, Block M, Diedrich B, Poliwoda H, Deicher H (1987) Clinical significance of anti-IFN-alpha-antibody titers during interferon therapy. Lancet II:635–636
von Wussow P, Hartmann F, Freund M, Poliwoda H, Deicher H (1988) Leukocyte-derived interferon-alpha in patients with antibodies to recombinant IFN-alpha 2b. Lancet I:882–883
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: M. Freissmuth at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selzer, E., Wilfing, A., Sexl, V. et al. Effects of type I-interferons on human thyroid epithelial cells derived from normal and tumour tissue. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 350, 322–328 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175039
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00175039