Summary
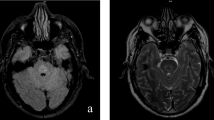
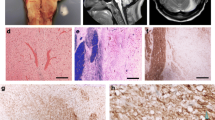
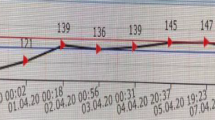
Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) evidently occurs more frequently than had been assumed up to now owing to the cases that have been substantiated solely on the basis of pathological anatomy. Its genesis is still unclarified. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance methods allow detection of the foci while the affected person is still alive. They are clearly capable of regression and are not automatically accompanied by a poor prognosis. Since an iatrogenic factor (forced compensation of hyponatremia) is increasingly under discussion as the cause of CPM, the condition also has substantial significance from a forensic point of view. On the basis of a prospective study on CPM confirmed in 100 brains of alcoholics, as well as 4 further cases from the forensic autopsy material, it is shown that hyponatremia is not likely to be the sole triggering factor. The course of the condition in the cases investigated shows that the capacity for action may be preserved up to death (which has occurred for other reasons) in not very pronounced CPM. In questionable violent and other unclear deaths, CPM must also be considered a possible cause of death. The various hypotheses on its etiology in the extensive literature are compared with the findings in our own cases and discussed.
Zusammenfassung
Die zentrale pontine Myelinolyse (ZPM) kommt offenkundig häufiger vor als bisher aufgrund der allein pathologisch-anatomisch gesicherten Fälle anzunehmen war, ihre Genese ist nach wie vor ungeklärt. Computer-Tomographie und Magnet-Resonanz-Verfahren lassen die Herde bereits zu Lebzeiten erkennen, die offenkundig rückbildungsfähig sind und nicht mit einer infausten Prognose einhergehen müssen. Da zunehmend ein iatrogener Faktor (forcierte Bilanzierung einer Hyponatriämie) als auslösende Ursache diskutiert wird, kommt der Erkrankung auch aus forensischer Sicht eine nicht zu unterschätzende Bedeutung zu. Anhand einer bei prospektiver Untersuchung von 100 Alkoholikergehirnen gesicherten ZPM sowie 4 weiteren Fällen aus dem forensischen Sektionsgut wird aufgezeigt, daß eine Hyponatriämie als alleiniger auslösender Faktor wohl nicht in Betracht kommt. Der Ablauf in den untersuchten Fällen zeigt, daß die Handlungsfähigkeit bei nicht sehr ausgeprägter ZPM bis zum (aus anderer Ursache erfolgten) Tod erhalten sein kann. Bei fraglichen gewaltsamen und anderen unklaren Todesfällen muß auch an eine zentrale pontine Myelinolyse als Todesursache gedacht werden. Aus der umfangreichen Literatur werden die verschiedenen Hypothesen zur Genese den Befunden in den eigenen Fällen gegenübergestellt und diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Adams RD, Victor M, Mancall LE (1959) Central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol Psych 81:154–172
Akai J, Hattcri T (1984) Alcoholic central pontine myelinolysis. Jap J Alc Drug Depend 19:167–172
Akai J, Arai M, Tagaki S (1986) Central pontine myelinolysis on alcoholism: Report of an autopsy case. Jap J Alc Drug Depend 20:72–78
Aleu FP, Terry RD (1963) Central pontine myelinolysis: A report of two cases. Arch Pathol 76:140–146
Anderson TL, Moore RA, Grinnel VS, Itabashi HH (1979) Computerized tomography in central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology (N.Y.) 29:1527–1530
Anderson RJ, Chung HM, Kluge R, Schrier RW (1985) Hyponatremia: A prospective analysis of its epidemiology and the pathogenetic role of vasopressin. Ann Intern Med 102:164–168
Arieff A (1981) Rapid correction of hyponatremia: Cause of pontine myelinolysis? Reply Am J Med 71:846–847
Arieff AI (1986) Hyponatremia, convulsions, respiratory arrest, and permanent brain damage after elective surgery in healthy women. N Engl J Med 314:1529–1542
Ayus CJ, Olivero JJ, Frommer PJ (1982) Rapid correction of severe hyponatremia intravenous hypertonic saline solution. Am J Med 78:43–47
Ayus CJ, Krothapalli RR, Arieff A (1985a) Changing concepts in treatment of severe symptomatic hyponatremia. Rapid correction and possible relation to central pontine myelinolysis. Am J Med 78:897–902
Ayus CJ, Krothapalli RK, Armstrong DL (1985b) Rapid correction of severe hyponatremia in the rat: Histopathological changes in the brain. Am J Physiol 248:711–719
Bailey OT, Bruno MS, Ober WE (1960) Central pontine myelinolysis. Am J Med 29:902–906
Behar A, Bentral E, Aviram A (1964) Central pontine myelinolysis (A case report). Acta Neuropathol 3:343–350
Berlit P (1986) Die zentrale pontine Myelinolyse. Nervenarzt 57:624–633
Berry K, Olszewski J (1963) Central pontine myelinolysis. A case report. Neurology 13:531–537
Bhagavan BS, Wagner JA, Juanteguy J (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis and medullary myelinolysis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 100:246–252
Burcar PJ, Norenberg MD, Yarnell PR (1977) Hyponatremia and central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology 27:223–226
Cadman TE, Rorke LB (1969) Central pontine myelinolysis in childhood and adolescence. Arch Dis Child 44:342–350
Cambier J, Masson M, Dairou R, Gray F, Henin D, Laurent D (1977) Myélinolyse centropontine associée à des lésions plus diffuses de la substance blanche. Troubles hydroélectriques en relation avec un traitment diuretique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 133:89–99
Chason JL, Landers JW, Gonzalez JE (1964) Central pontine myelinolysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat 27:317–325
Chercover DJ, Norman MG (1984) Central pontine myelinolysis in a 6-month old infant with rapidly corrected hyponatremia. Ann Neurol 16:261–262
Chou SM, Lorente L, Nugent RG (1975) Hypertrophic astroglia with arrested mitosis in central pontine myelinolysis (CPM). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 34, zit. bei Berlit (1986)
Cole M, Richardson EP jr, Segarre JM (1964) Central pontine myelinolysis. Further evidence relating the lesion to malnutrition. Neurology 14:165–170
Colmant HJ (1965) „Die Pontocerebellaren Dystrophien“; über sogenannte zentrale pontine Myelinolyse und verwandte Prozesse. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 206:612–629
Conger JD, McIntyre JA, Jacobi WJ (1969) Central pontine myelinolysis associated with inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion. Am J Med 47:813–817
Covey CM, Arieff AI (1978) Disorders of sodium and water metabolism and their effects on the nervous system. In: Brenner BM, Stein JH (Eds) Contemporary issues in nephrology. Churchill Livingstone, N.Y., Edinburgh-London, S. 213–241
Demanet JC, Bonnyns M, Beiberg H, et al (1971) Coma due to water intoxication in beer drinkers. Lancet 2:1115–1117
De Witt LD, Buananno FS, Kistler JP, Zeffiro T, De La Paz RL, et al (1984) Central pontine myelinolysis: Demonstration by nuclear magnetic resonance. Neurology (Clevel.) 34:570–576
Dubois GD, Arieff AI (1984) Treatment of hyponatremia: the case for rapid correction. In: Narins RG (Ed) Controversies in nephrology and hypertension. Churchill Livingstone, New York, S. 393–407
Endo Y, Oda M, Hara H (1981) Central pontine myelinolysis: A study of 37 cases in 1000 consecutive autopsies. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 53:145–153
Feigin I, Budzilovich GN (1980) The influence of the ground substance on the extracellular water of normal and edematous human brain: focal edema and the demyelinating diseases, including multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 39:13–29
Finlayson MH, Snider S, Oliva LA, Gault MH (1973) Cerebral and pontine myelinolysis: Two cases with fluid and electrolyte imbalance and hypotension. J Neurol Sci 18:399–409
Gerber O, Geller M, Stiller J, Yang W (1983) Central pontine myelinolysis: Resolution shown by computed tomography. Arch Neurol 40:116–118
Ghatak NR, Hadfield MG, Rosenblum WI (1978) Association of central pontine myelinolysis and Marchiafava-Bignami Disease. Neurology 28:1295–1298
Goebel HH, Herman-Ben Zur P (1972) Central pontine myelinolysis — a clinical and pathological study of 10 cases. Brain 95:495–504
Goebel HH, Herman-Ben Zur P (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. In: Vinken PJ, Broyn GW (Eds) Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 28. North Holland Publ. Amsterdam, S. 285–316
Goldman JE, Horoupian DS (1981) Demyelination of the lateral geniculate nucleus in the central pontine myelinolysis. Ann Neurol 9:185–189
Haan J, Deppe A (1986) Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse bei Alkoholismus. Klinik, Neurophysiologie, Computertomographie und Kernspintomographie bei einem Patienten, der überlebte. Nervenarzt 57:609–612
Haibach H, Ansbacher LE, Dix JD (1987) Central pontine myelinolysis: A complication of hyponatremia or of therapeutic intervention. J Forens Sci 32:444–451
Harper C (1979) Wernicke's encephalopathy: A more common disease then realised. A neuropathological study of 51 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 42:226–231
Hazaratji SMA, Kim RC, Lee SH, Marasigan AV (1983) Evolution of pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. J Comp Assist Tomogr 7:356–361
Iannacone PM, Wright AW, Cornwall CC (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. N.Y. Stat J Med 3:421–424
Ibrahim NBN (1981) Central pontine myelinolysis. Postgrad Med J 57:178–180
Ingram DA, Traub M, Kopelman PG, Summers BA, Swash M (1986) Brain-stem auditory evoked responses in diagnosis of central pontine myelinolysis. J Neurol 233:23–24
Jacob H, Spalke G (1971) Klinik und Neuropathologie zentral nervöser Komplikationen nach akuten Elektrolyt- und Wasserhaushaltsstörungen und besonderer Berücksichtigung der zentralen pontinen Myelinolyse. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr 39:169–191
Jellinger K (1977) Pathology and pathogenesis of apallic syndromes following closed head injuries. In: „The Apallic Syndrome“. Dalle OG, Gerstenbrand F, Lücking CH, Peters G, Peters UH (eds) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg NY, S. 88–102
Jellinger K, Grisold W (1982) Neuropathologie der posttraumatischen Encephalopathie. In: Frydl W (Hrsg) Neuropathologisches Symposion im Bezirkskrankenhaus Haar
Kalnins RM, Berkovic SF, Bladin PFC (1984) Central pontine myelinolysis with wide spread extrapontine lesions: A report of two cases. Clin Exp Nur 20:189–202
Kandt RS, Heldrich FJ, Moser HW (1983) Recovery from propable central pontine myelinolysis associated with Addison's Disease. Arch Neurol 40:118–119
Kepes JJ, Reece CA, Oxley DK (1965) Central pontine myelinolysis in a 7-year old boy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 28:39–47
Klavins JV (1963) Central pontine myelinolysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 22:302–317
Kleinschmidt-De Masters BK, Norenberg MD (1981) Rapid correction of hyponatremia causes demyelination. Relation to central pontine myelinolysis. Science 211:1068–1070
Kleinschmidt-De Masters BK, Norenberg MD (1982) Neuropathologic observations in electrolyte-induced myelinolysis in the rat. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 41:67–80
Kold A (1986) Hyponatremia: Cerebral symptoms and role in central pontine myelinolysis. Acta Neurol Scand 73:200–202
Kold A, Johansen O, Reintoft I, Reske-Nielsen E (1986) Central pontine myelinolysis. A case report with typical neuropathological findings. Acta Neurol Scand 73:260–263
Kosaka K, Kobayashi H, Iwase S (1970) A case of chronic alcoholism with central pontine myelinolysis. Brain Nerve (Tokyo) 22:1179–1185
Landers JW, Chason JL, Samuel VN (1965) Central pontine myelinolysis. A pathogenetic hypothesis. Neurology (Minneap.) 15:968–971
Larrue V, Barrere M (1984) Myélinolyse centro-pontine d'evolution regressive avec traduction tomodensitometrique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 140:576–579
Laureno R (1981a) Pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis following rapid correction of experimental hyponatremia. Trans Am Neurol Assoc 106:98–101
Laureno R (1981b) Rapid correction of hyponatremia: Cause of pontine myelinolysis? Am J Med 71:846
Laureno R (1983) Central pontine myelinolysis following rapid correction of hyponatremia. Ann Neurol 13:232–242
Leslie KO, Robertson AS, Norenberg MD (1980) Central pontine myelinolysis: An osmotic gradient pathogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 39:370
Levitt RO, Shenker DM (1979) Central pontine myelinolysis. Alcoholism (N.Y.) 3:83–85
Lindboe CF (1981) Myelin wird aufgelöst. Ugeskr Laeger 143:631
Lipsmeyer E, Ackerman GL (1966) Irreversible brain damage after water intoxication. J Am Assoc 196:286–287
Lüthy F (1931) Über die hepato-lentikuläre Degeneration. Dtsch Z Nervenheilk 123:101–181
Monteiro L (1971) La myélinolyse du centre du pons dans le cadre d'un nouveau syndrome histopathologique de topographie systmatisée. A propos d'un cas anatomoclinique. J Neurol Sci 13:293–314
Marra TR (1984) Hemiparesis apparently due to central pontine myelinolysis following hyponatremia. Ann Neurol 14:687–688
Mathews T, Moossy J (1975) Central pontine myelinolysis. Lesion evolution and pathogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 34:77–85
Mathieson G, Olszewski J (1960) Central pontine myelinolysis with other cerebral changes: A report of two cases. Neurology 10:345–354
Matsuoka T, Miyoshi K, Saka K, Hayashi S, Kageyama N (1965) Central pontine myelinolysis. Acta Neuropathol 5:117–132
McCormick WF, Danneel CM (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Intern Med 119:444–478
Mehraein P (1986) Persönliche Mitteilung
Messert B, Orrison WW, Hawkins MJ, Quaglieri CE (1979) Central pontine myelinolysis: Considerations on etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Neurology (Minneap.) 29:147–160
Minauf M, Krepler P (1969) Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse bei einem Kind mit Leukämie. Neurology (Minneap.) 29:55–65
Minauf M, Jellinger K (1970) Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse bei einem Kind mit protrahiertem posttraumatischem Koma. Neuropädiatrie 2:107–111
Nakada T, Knight R (1984) Alcohol and the central nervous system. Med Clin North Am 68:121–131
Neumann K (1987) Zur Bedeutung der zentralen pontinen Myelinolyse (Untersuchungen an 100 Gehirnen chronischer Alkoholiker im forensischen Obduktionsgut). Inaug. Diss. Ludwig-Maximilians-Univ. München
Neundörfer B, Niemöller K (1981) Neurologische Störungen bei Alkoholikern. Therapiewoche 31:4317–4328
Nichtweiß M, Wiegand Ch, Prawitz RH, Kühnert A (1986) Zur Kenntnis der zentralen pontinen Myelinolyse. Anästh Intensivther Notfallmed 21:343–345
Norenberg MD, Leslie KO, Robertson AS (1982) Association between rise in the serum sodium and central pontine myelinolyse. Ann Neurol 11:128–138
Norenberg MD (1983) A hypothesis of osmotic endothelial injury. A pathogenetic mechanism in central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol 40:66–69
Norenberg MD (1984) Treatment of hyponatremia: The case for a more conservative approach. In: Narins RG (Ed) Controversies in nephrology and hypertension. Churchill Livingstone New York, S. 379–391
Norenberg MD, Papendick RE (1984) Chronicity of hyponatremia as a factor in experimental myelinolysis. Ann Neurol 15:544–547
Oda Y, Okada Y, Nakanishi I, Kajikawa K et al. (1984) Central pontine myelinolysis with extra-pontine lesions. Acta Pathol Jpn 34:403–410
Okeda R (1974) Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse: pathogenetische Aspekte aufgrund morphometrischer Untersuchungen des Brückenfußes. Acta Neuropathol 27:233–246
Oppenheimer DR (1976) Demyelinating diseases. In: Blackwood W, Corsellis Jan (Eds) Greenfield's Neuropathology, Edward Arnold London, S. 470–499
Paguirigan A, Lefken EB (1969) Central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology (Minneap.) 19:1007–1011 (1969)
Peiffer J (1984a) Zur Neuropathologie der Nebenwirkungen nervenärztlicher Therapie. Aus: Sitzungsbericht der Heidelberger Akademie der Wissenschaften, mathematisch-naturwissenschaftliche Klasse, 4. Abhandlung. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, NY. S. 91–93
Peiffer J (1984b) Neuropathologie. Alkoholschäden. In: Remmele W (Hrsg.) Pathologie Bd. 4, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, S. 129–136
Peters G (1970) Klinische Neuropathologie. 2. Aufl., Thieme Stuttgart, S. 202
Pfister HW, Einhäupl KM, Brandt T (1985) Mild central pontine myelinolysis: A frequently undetected syndrome. Eur Arch Psychiatry Neurol Sci 235:134–139
Popoff N, Budzilovich G, Goodgold A, Feigin I (1965) Hepatocerebral degeneration. (Its occurence in the presence and the absence of normal copper metabolism). Neurology (Minneap.) 15:919–930
Poser CM (1973) Demyelination in the central nervous system in chronic alcoholism: (central pontine myelinolysis and Marchiafava-Bignami's Disease). Ann NY Acad Sci 215:373–381
Powers JM, McKeever PE (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. An ultrastructural and elemental study. J Neurol Sci 29:65–81
Raimondi EC (1983) Mielinolisis pontina central. Medicina (Buenos Aires) 43:67–72
Regardera JF, Enriquez R, Morales et al. (1984) Asociacion de la enfermedad de Marchiafava Bignami con la mielinolisis centropontica y la esclerosis laminar de Morel: presentacion de un caso. Med Clin (Barc) 82:117–120
Reuck de J, Vander Eecken H, Thiery E, Crevits L (1975) Central pontine myelinolysis and its arterial blood supply. Acta Neurol et Psychiatrica Belgica 75:193–205
Rosenbloom S, Buchholz D, Kumar AJ, Kaplan RA, Moses II, Rosenbaum AE (1984) Evolution of central pontine myelinolysis on CT. Am J Neurol 5:110–112
Rosman NP, Kakulas BA, Richardson EP Jr (1966) Central pontine myelinolysis in a child with leukemia. Arch Neurol 14:273–280
Schneck SA (1966) Neuropathological features of human organ-transplantation: II. Central pontine myelinolysis and neuroaxonal dystrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 25:18–39
Schneck SA (1988) Central pontine myelinolysis. In: Minckler J (ed) Pathology of nervous system. Vol. 1 McGraw Hill, New York, Toronto Sidney London, S 859–961
Schroth G (1984) Clinical and CT confirmed recovery from central pontine myelinolysis. Neuroradiology 26:149–151
Seitelberger F, Gross H (1969) Zur organischen Hirnschädigung des Alkoholkranken (zentrale pontine Myelinolyse). Wiener Med Akademie 109–138
Seitelberger F, Jonasch G (1970) Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse nach Schädeltrauma. Dtsch Z Nervenheilk 197:28–41
Seitelberger F (1973) Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse. Schweiz Arch Neurol Neurochir Psychiatr 112:285–297
Shiraki H, Itzuka R, Seitelberger F (1964) Six autopsy cases with central pontine myelinolysis. Adv Neurol Sci (Tokyo) 8:113–117
Shurtliff LF, Ajax ET, Englert E Jr, D'Agostino AN (1966) Central pontine myelinolysis and cirrhosis of the liver: A report of 4 cases. Am J Clin Pathol 46:239–244
Sima A, Bradvik B (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis: A case report. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 84:73–78
Stam J, van Oers MHJ, Verbeeten B Jr (1984) Recovery after central pontine myelinolysis. J Neurol 231:52–53
Stark E, Reusche E (1985) Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse: Bericht über vier Fälle bei verschiedenen Grunderkrankungen. In: Gänshirt H, Berlit P, Haack G (Hrsg). Verh Dtsch Ges Neurol. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, S. 463–466
Sterns RH, Riggs JE, Schochet SS (1986) Osmotic demyelination syndrome following correction of hyponatremia. New Engl J Med 314:1535–1542
Sterns R (1986) The prognosis of severe symptomatic hyponatremia. Abstract. Kidney Int 29:205A
Sterns R, Thomas D, Garell D (1986) Brain dehydration after rapid correction of hyponatremia. Abstract. 19th Ann Meeting Am Soc Nephrology
Stochdorph O (1986) Persönliche Mitteilung
Stockard JJ, Rossiter VS, Wiederholt W, Kobayashi RM (1976) Brainstem auditoryevoked responses in suspected central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol 33:726–728
Sztencel J, Baleriaux D, Borenstein S, Brunko E, Zeugers de Beyl D (1983) Central pontine myelinolysis: Correlation between CT and electrophysiological data. Am J Neuroradiol 4:529–530
Telfer RB, Miller EM (1979) Central pontine myelinolysis following hyponatremia, demonstrated by computerized tomography. Ann Neurol 6:455–456
Thofson DS, Hutton JT, Stears JC, Sung JH, Norenberg MD (1981) Computerized tomography in the diagnosis of central and extrapontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol 38:243–246
Thomas LA, Robin AM, Verity S et al. (1979) Computerized tomography in central pontine myelinolysis. Neurology (Minneap.) 29:1527–1530
Tomlinson BE, Pierides AM, Bradley WG (1976) Central pontine myelinolysis. Two cases with associated electrolyte disturbances. Q J Med (New Ser) 45:373–386
Torvic A, Lindboe CF, Rodge S (1982) Brain lesions in alcoholics. A neuro-pathological study with clinical correlations. J Neurol Sci 56:223–248
Ule G, Jakob H (1978) Chronische infantile zentrale pontine Myelinolyse vom multifokalen Typ mit sekundären Capillarcalcinosen und Hypoxieschäden. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 42:43–45
Valsamis MP, Peress NS, Wright LD (1971) Central pontine myelinolysis in childhood. Arch Neurol 25:307–312
Victor M, Laureno R (1978) Neurologic complications of alcohol abuse: Epidemiologic aspects. Advances in Neurology Vol. 19 Neuroepidemiology, ed. by Schoeberg B.S. N.Y., Raven press, S. 597–610
Vogel FS (1978) Conundrum of central pontine myelinolysis. Ann Part 1:29–39
Werder M, Ruppert RK, Bajc O, Truninger B (1982) Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse und Schwartz-Bartter-Syndrom. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 112:765–769
Wiederholt WC, Kobayashi RM, Stockard JJ, Rossiter VS (1977) Central pontine myelinolysis. A clinical reappraisal. Arch Neurol 34:220–223
Wilske J, Henn R (1983) Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse — Ursache unklarer Todesfälle. In: Barz J et al. (Hrsg) Fortschritte der Rechtsmedizin. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg N Y, S. 123–128
Witt De LD, Buonanno FS, Kistler JP, Zeffiro T et al. (1984) Central pontine myelinolysis. Demonstration by nuclear magnetic resonance. Neurology (Clevel.) 34:570–576
Wright DG, Laureno R, Victor M (1979) Pontine und extrapontine myelinolysis. Brain 102:361–385
Yeow YK, Tija TL (1984) Central pontine myelinolysis with computerized tomography confirmation: A case report. Singapore Med J 25:57–59
Yufe RS, Hyde ML, Terbrugge K (1980) Auditory evoked responses and computerized tomography in central pontine myelinolysis. Can J Neurol Sci 7:297–300
Zegers de Beyl D, Flament-Durand J, Borenstein S, Brunko E: Ocular bobbing and myoclonus in central pontine myelinolysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 46:564–565
Zegers de Beyl D (1985) CT follow-up in central pontine myelinolysis (Letter). Neurology (Minneap.) 35:444
Zeumer H (1987) Persönliche Mitteilung
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Professor Rainer Henn zum 60. Geburtstag gewidmet
Erweiterte Fassung eines Vortrages anläßlich der 65. Jahrestagung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Rechtsmedizin, St. Gallen, 9.–13.9.1986
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bratzke, H., Neumann, K. Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse Morphologie und forensische Bedeutung. Z Rechtsmed 102, 79–97 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200502
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00200502
Key words
- Central pontine myelinolysis, prospective investigation
- Alcoholics, central pontine myelinolysis
- Forensic autopsy