Abstract
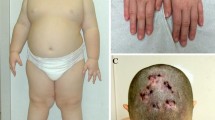
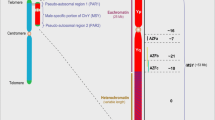
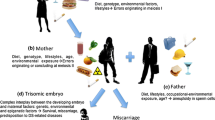
Although clinical features in Turner syndrome have been well defined, underlying genetic factors have not been clarified. To deduce the factors leading to the development of clinical features, we took the following four steps: (1) assessment of clinical features in classic 45,X Turner syndrome; (2) review of clinical features in various female sex chromosome aberrations (karyotype-phenotype correlations); (3) assessment of factors that could lead to Turner features; and (4) correlation of the clinical features with the effects of specific factors. The results indicate that the clinical features in 45,X and in other female sex chromosome aberrations may primarily be determined by: (1) degree of global non-specific developmental defects caused by quantitative alteration of a euchromatic or noninactivated region; (2) dosage effect of a pseudoautosomal growth gene(s), a Y-specific growth gene(s), and an Xp-Yp homologous lymphogenic gene(s); and (3) degree of chromosome pairing failure in meiocytes that are destined to develop as oocytes in the absence of SRY.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allanson JE (1987) Noonan syndrome. J Med Gent 24:9–13
Ashworth A, Rastan S, Lovell-Badge R, Kay G (1991) X-chromosome inactivation may explain the difference in viability of XO humans and mice. Nature 351:406–408
Ballabio A, Willard HF (1992) Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation and the XIST gene. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2:439–447
Ballard RA (1991) Hydrops fetalis. In: Taeusch HW, Ballard RA, Avery ME (eds) Diseases of the newborn, 6th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 833–836
Boue J, Boue A, Lazar P (1975) Retrospective and prospective epidemiological studies of 1500 karyotyped spontaneous human abortions. Teratology 12:11–26
Brook CGD, Murset G, Zachmann M, Prader A (1974) Growth in children with 45,XO Turner's syndrome. Arch Dis Child 49:789–795
Brook CGD, Gasser T, Werder EA, Prader A, Vanderschueren-Lodewykx MA (1977) Height correlations between parents and mature offspring in normal subjects and in subjects with Turner's and Klinefelter's and other syndromes. Ann Hum Biol 4:17–22
Burgoyne PS, Baker TG (1984) Meiotic pairing and gametogenic failure. In: Evans CW, Dickinson (eds) Controlling events in meiosis. Company of Biologists, Cambridge, pp 349–362
Burgoyne PS, Baker TG (1985) Perinatal oocyte loss in XO mice and its implications for the aetiology of gonadal dysgenesis in XO women. J Reprod Fertil 75:633–645
Cattanach BM (1961) XXY mice. Genet Res 2:156–160
Cattanach BM (1962) XO mice. Genet Res 3:487–490
Chandley AC (1986) A model for effective pairing and recombination at meiosis based on early replication sites (R-bands) along chromosomes. Hum Genet 72:50–57
Chandley AC, Speed RM, McBeath S, Hargreave TB (1986) A human 9;20 reciprocal translocation associated with male infertility analyzed at prophase and metaphase I of meiosis. Cytogenet Cell Genet 41:145–153
Chervenak FA, Isaacson G, Blakemore KJ, Breg WR, Hobbins JC, Berkovitz RL, Tortora M, Mayden K, Mahponey MJ (1983) Fetal cystic hygroma: cause and natural history. N Engl J Med 309:822–825
Chitayat D, Kalousek DK, Bamforth JS (1989) Lymphatic abnormalities in fetuses with posterior cervical cystic hygroma. Am J Med Genet 33:352–356
Clark EB (1984) Neck web and congenital heart defects: a pathogenic association in 45 X-O Turner syndrome? Teratology 29:355–361
Court Brown WM, Harnden DG, Jacobs PA, Maclean N, Mantle DJ (1964) Abnormalities of the sex chromosome complement in man. (Medical Research Council, Special Report Series No. 305) John Blackburn, Leeds
Cunniff C, Jones KL, Benirschke K (1991) Ovarian dysgenesis in individuals with chromosome abnormalities. Hum Genet 86:552–556
Cuttler L, Vliet GV, Conte FA, Kaplan SL, Grumbach MM (1985) Somatomedin-C levels in children and adolescents with gonadal dysgensis: differences from age-matched normal females and effect of chronic estrogen replacement therapy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 60:1087–1092
Daniel A (1979) Structural differences in reciprocal translocations: potential for a model of risk in Rcp. Hum Genet 51:171–182
Davis RM (1981) Localisation of male determining factors in man: a thorough review of structural anomalies of the Y chromosome. J Med Genet 18:161–195
Domar AD, Zuttermeister PC, Friedman R (1993) The psychological impact of infertility: a comparison with patients with other medial conditions. J Psychosom Obstet Gynaecol 14 [Suppl]:45–52
Dressler D, Potter H (1982) Molecular mechanisms of genetic recombination. Annu Rev Biochem 51:727–762
Ehrhardt AA, Meyer-Bahlburg HF (1975) Psychological correlates of abnormal pubertal development. Clin Endocrinol Metab 4:207–222
Epstein CJ (1990) Mechanisms leading to the phenotype of Turner syndrome. In: Rosenfeld RG, Grumbach ME (eds) Turner syndrome. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 13–28
Esterly NB (1992) The skin. In: Behrman RE (ed) Nelson textbook of pediatrics, 14th edn. WS Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1621–1688
Ferguson-Smith MA (1991) Genotype-phenotype correlations in individuals with disorders of sex determination and development including Turner's syndrome. Semin Dev Biol 2:265–276
Fisher EMC, Beer-Romero P, Brown LG, Ridley A, McNeil JA, Lawrence JB, Willard HF, Bieber FR, Page DC (1990) Homologous ribosomal protein genes on the human X and Y chromosomes: escape from X inactivation and possible implications for Turner syndrome. Cell 63:1205–1218
Frels W, Chapman VM (1979) Paternal X chromosome expression in extraembryonic membranes of XO mice. J Exp Zool 210:553–560
Gartler SM, Sparkes RS (1963) The Lyon-Beutler hypothesis and isochromosome X patients with the Turner syndrome. Lancet 1:411
Gartler SM, Liskay RM, Campbell BK, Sparkes R, Gant N (1972) Evidence for two functional X chromosomes in human oocytes. Cell Differ 1:215–218
Geerkens C, Just W, Vogel W (1994) Deletions of Xq and growth deficit: a review. Am J Med Genet 50:105–113
Gilbert EF, Opitz JM (1982) Developmental and other pathological changes in syndromes caused by chromosome abnormalities. Perspect Pediatr Pathol 7:1–63
Glenister TW (1956) Determination of sex in early human embryos. Nature 177:1135–1136
Goldman B, Polani PE, Daker MG, Angell RR (1982) Clinical and cytogenetic aspects of X-chromosome deletions. Clin Genet 21:36–52
Greenlee R, Hoyme H, Witte M, Crowe P, Witte C (1993) Developmental disorders of the lymphatic system. Lymphology 26:156–168
Grumbach MM, Conte FA (1992) Disorders of sexual differentiation. In: Wilson JD, Foster DW (eds) Williams textbook of endocrinology, 8th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 853–952
Harrison KB, Warburton D (1986) Preferential X-chromosome activity in human female placental tissues. Cytogenet Cell Genet 41:163–168
Hassold T, Benham F, Leppert M (1988) Cytogenetic and molecular analysis of sex-chromosome monosomy. Am J Hum Genet 42:534–541
Hemel JO van, Eussen B, Wesby-van Swaay E, Oostra BA (1992) Molecular detection of a translocation (Y;11)(q11.2;q24) in a 45,X male with signs of Jacobsen syndrome. Hum Genet 88:661–667
Hook EB, Warburton D (1983) The distribution of chromosomal genotypes associated with Turner's syndrome: livebirth prevalence rates and evidence for diminished fetal mortality and severity in genotypes associated with structural X abnormalities or mosaicism. Hum Genet 64:24–27
Hotta Y, Stern H (1981) Small nuclear RNA molecules that regulates nuclease accessibility in specific chromatin regions of meiotic cells. Cell 27:309–319
Hotta Y, Bennett MD, Toledo LA, Stern H (1979a) Regulation of R-protein and endonuclease activities in meiocytes by homologous chromosome pairing. Chromosoma 72:191–201
Hotta Y, Chandley AC, Stern H, Searle AG, Beechey CV (1979b) A disruption of pachytene DNA metabolism in male mice with chromosomally-derived sterility. Chromosoma 73:287–300
Jacobs PA, Betts PR, Cockwell AE, Crolla JA, Mackenzie MJ, Robinson DO, Youings SA (1990) A cytogenetic and molecular reappraisal of a series of patients with Turner's syndrome. Ann Hum Genet 54:209–223
Johnson R Jr, Rohrbaugh JW, Ross JL (1993) Altered brain development in Turner's syndrome: an event-related potential study. Neurology 43:801–808
Jones KL (1988) Smith's recognizable patterns of human malformation: genetic, embryonic and clinical aspects, 4th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
Just W, Geekens C, Held KR, Vogel W (1992) Expression of RPS4X in fibroblasts from patients with structural aberrations of the X chromosome. Hum Genet 89:240–242
Keats TE, Smith TH (1988) An atlas of normal developmental roentgen anatomy, 2nd edn. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago
Kennedy JF, Freeman MG, Benirschke KB (1977) Ovarian dysgenesis and chromosome abnormalities. Obstet Gynecol 50:13–20
Kirby ML, Waldo KL (1990) Role of neural crest in congenital heart disease. Circulation 82:332–340
Lacro RV, Jones KL, Benirschke K (1988) Coarctation of the aorta in Turner syndrome: a pathologic study of fetuses with nuchal cystic hygromas, hydrops fetalis, and female genitalia. Pediatrics 81:445–451
Lemli L, Smith DW (1963) The XO syndrome: a study of the differential phenotype in 25 patients. J Pediatr 63:577–588
Levilliers J, Quack B, Weissenbach J, Petit C (1989) Exchange of terminal portions of X- and Y-chromosomal short arms in human XY females. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2296–2300
Lippe BM (1990) Physical and anatomical abnormalities in Turner syndrome. In: Rosenfeld RG, Grumbach MM (eds) Turner syndrome. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 183–196
Lorda-Sanchez I, Binkert F, Maechler M, Shinzel A (1992) Molecular study of 45,X conceptuses: correlation with clinical findings. Am J Med Genet 42:487–490
Loughlin SAR, Redha A, McIver J, Boyd A, Carothers A, Connor JM (1991) Analysis of the origin of Turner's syndrome using polymorphic DNA probes. J Med Genet 28:156–158
Lubin MB, Gruber HE, Rimoin DL, Lachman RS (1990) Skeletal abnormalities in the Turner syndrome. In: Rosenfeld RG, Grumbach ME (eds) Turner syndrome. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 281–300
Madan K (1983) Balanced structural changes involving the human X: effect on sexual phenotype. Hum Genet 63:216–221
Marden PM, Smith DW, McDonald MJ (1964) Congenital anomalies in the newborn infant, including minor variations. J Pediatr 64:357–371
Mathur A, Stekol L, Schatz D, MacLaren NK, Scott ML, Lippe B (1991) The parental origin of the single X chromosome in Turner syndrome: lack of correlation with parental age or clinical phenotype. Am J Hum Genet 48:682–686
Mattei MG, Mattei JF, Giraud F (1982) X-autosome translocations: cytogenetic characteristics and their consequences. Hum Genet 61:295–309
Migeon BR, Jelalian K (1977) Evidence for two active X chromosomes in germ cells of female before meiotic entry. Nature 269:242–243
Mittwoch U (1971) Mongolism and sex: a common problem of cell proliferation? J Med Genet 9:92–95
Miyabara S, Sugihara H, Maehara N, Shouno H, Tasaki H, Yoshida K, Saito N, Kayama F, Ibara S, Suzumori K (1989) Significance of cardiovascular malformations in cystic hygroma: a new interpretation of the pathogenesis. Am J Med Genet 34:489–501
Moses MJ, Poorman PA (1981) Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements: II synaptic adjustment in a tandem duplication. Chromosoma 81:519–535
Moses MJ, Poorman PA, Roderick TH, Davisson MT (1982) Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements: IV synapsis and synaptic adjustment in two paracentric inversions. Chromosoma 84:457–474
Mostello DJ, Bofinger MK, Siddigi TA (1989) Spontaneous resolution of fetal cystic hygroma and hydrops in Turner syndrome. Obstet Gynecol 73:862–864
Murphy DG, DeCarli C, Daly E, Haxby JV, Allen G, White AB, McIntosh AR, Powell CM, Horwitz B, Rapoport SI, Schapiro MB (1993) X-chromosome effects on female brain: a magnetic resonance imaging study of Turner's syndrome. Lancet 342:1197–1200
Nielsen J (1990) Mental aspects of Turner syndrome and the importance of information and Turner contact groups. In: Rosenfeld RG, Grumbach MM (eds) Turner syndrome. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 451–461
Nora JJ (1989) Etiologic aspects of heart diseases. In: Adams FH, Emmanouilides GC, Riemenschneider TA (eds) Moss' heart disease in infants, children, and adolescents, 4th edn. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 15–23
Nurmi T, Uhari M, Linna S-L, Silvennoinen-Kassinen S, Koskela M, Kiuttu J, Tillikainen A (1982) Immune function in patients with chromosome deletions. Clin Exp Immunol 48:179–185
Ogata T, Matsuo N (1992) Comparison of adult height between patients with XX and XY gonadal dysgenesis: support for a Yspecific growth gene(s). J Med Genet 29:539–541
Ogata T, Matsuo N (1993) Sex chromosome aberrations and stature: deduction of the principal factors involved in the determination of adult height. Hum Genet 91:551–562
Ogata T, Tyler-Smith C, Purvis-Smith S, Turner G (1993) Chromosomal localisation of a gene(s) for Turner stigmata on Yp. J Med Genet 30:918–922
Omoe K, Endo A (1993) Growth and development of 39,X mouse embryos at mid-gestation. Cytogenet Cell Genet 63:50–53
Opitz JM, Gilbert EF (1982) CNS anomalies and the midline as a “developmental field”. Am J Med Genet 12:443–455
Park WW (1957) The occurrence of sex chromatin in early human and macaque embryos. J Anat 91:369–373
Polani PE, Angel R, Giannelli F, Chapelle A de la, Race RR, Sanger R (1970) Evidence that the Xg locus is inactivated in structurally abnormal X chromosome. Nature 227:613–616
Prader A, Largo RH, Molinari L, Issler C (1989) Physical growth of Swiss children from birth to 20 years of age: first Zurich longitudinal study of growth and development. Helv Paediatr Acta 52 [Suppl]:1–125
Putte SCJ van der (1977) Lymphatic malformation in human fetuses: a study of fetuses with Turner's syndrome or status Bonnevie-Ullrich. Virchows Arch [A] 376:233–246
Ratcliffe SG, Butler GE, Jones M (1991) Edinburgh study of growth and development of children with sex chromosome abnormalities. IV. Birth defects 26:1–44
Ropers HH, Migl B, Zimmer J, Fraccaro M, Maraschio PP, Westerveld A (1981) Activity of steroid sulfatase in fibroblasts with numerical and structural X chromosome aberrations. Hum Genet 57:354–356
Rosenfeld RG (1989) Turner syndrome: a guide for physicians. The Turner Syndrome Society, Wayzala
Rosenfeld RG, Luzzatti L, Hintz RL, Miller OL, Koo GC, Wachtel SS (1979) Sexual and somatic determinants of the human Y chromosome: studies in a 46,XYp-phenotypic female. Am J Hum Genet 31:458–468
Ross JL, Long LM, Loriaux DL, Cutler GB Jr (1985) Growth hormone secretory dynamics in Turner syndrome. J Pediatr 106:202–206
Rovet JF (1993) The psychoeducational characteristics of children with Turner syndrome. J Learn Disabil 26:333–341
Rubin KR (1990) Osteoporosis in Turner syndrome. In: Rosenfeld RG, Grumbach MM (eds) Turner syndrome. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 301–317
Santesson B, Book JA, Kjessler B (1973) The mortality of human XO embryos. J Reprod Fertil 34:51–55
Sarto GE, Therman E, Patau K (1973) X inactivation in man: a woman with t(Xq-;12q+). Am J Hum Genet 25:262–270
Schmidt M, Du Sart D (1992) Functional disomies of the X chromosome influence the cell selection and hence the X inactivation pattern in females with balanced X-autosome translocations: a review of 122 cases. Am J Med Genet 42:161–169
Setterfield LA, Mahadevaiah S, Mittwoch U (1988a) Pachytene pairing in relation to sperm and oocyte numbers in a male-fertile reciprocal translocation in the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 49:293–299
Setterfield LA, Mahadevaiah S, Mittwoch U (1988b) Chromosome pairing and germ cell loss in male and female mice carrying a reciprocal translocation. J Reprod Fertil 82:363–379
Shapiro BL (1983) Down syndrome: a disruption of homeostasis. Am J Med Genet 14:241–269
Shepard TH, Fantel AG (1986) Pathogenesis of congenital defects associated with Turner's syndrome: the role of hypoalbuminemia and edema. Acta Endocrinol [Suppl] 279:440–447
Sheridan R, Llerena J Jr, Matkins S, Debenham P, Cawood A, Bobrow M (1989) Fertility in a male with trisomy 21. J Med Genet 26:294–298
Siegel PT, Clopper R, Stabler B (1991) Psychological impact of significantly short stature. Acta Paediatr Scand 377 [Suppl]:14–18
Simpson JL (1990) Localizing ovarian determinants through phenotypic-karyotypic deductions. In: Rosenfeld RG, Grumbach ME (eds) Turner syndrome. Marcel Dekker. New York, pp 65–77
Simpson JL, Lebeau MM (1981) Gonadal and statural determinants of the X chromosome and their relationship to in vitro studies showing prolonged cell cycles in 45. X; 46,X,del(X) (p11); 46,X,del(X)(q13); and 46,X,del(X)(q22) fibroblasts. Am J Obstet Gynecol 141:930–938
Simpson JL, Christakos AC, Horwith M, Silverman FS (1971) Gonadal dysgenesis in individuals with apparently normal chromosomal complements: tabulation of cases and compilation of genetic data. Birth Defects 7:215–228
Sinclair AH, Berta P, Palmer MS, Hawkins JR, Griffiths BL, Smith MJ, Foster JW, Frischauf A-M, Lovell-Badge R, Goodfellow PN (1990) A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature 346:240–244
Singh RP (1970) Hygroma of the neck in XO abortuses. Am J Clin Pathol 53:104–107
Singh RP, Carr DH (1966) The anatomy and histology of XO human embryos and fetuses. Anat Rec 155:369–383
Speed RM (1984) Meiotic configurations in female trisomy 21 foetuses. Hum Genet 66:176–180
Speed RM (1986a) Oocyte development in XO foetuses of man and mouse: the possible role of heterologous X-chromosome pairing in germ cell survival. Chromosoma 94:115–124
Speed RM (1986b) Prophase pairing in a mosaic 18p-;iso18q human female foetus studied by surface spreading. Hum Genet 72:256–259
Speed RM (1988) The possible role of meiotic pairing anomalies in the atresia of human fetal oocytes. Hum Genet 78:260–266
Speltz ML, Greenberg MT, Endriga MC, Galbreath H (1994) Developmental approach to the psychology of craniofacial anomalies. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 31:61–67
Tharapel AT, Anderson KP, Simpson JL, Martens PR, Wilroy RS Jr, Llerena JC Jr, Schwartz CE (1993) Deletion (X)(q26. 1→ q28) in a proband and her mother: molecular characterization and phenotypic-karyotypic deductions. Am J Hum Genet 52:463–471
Therman E, Susman B (1990) The similarity of phenotypic effects caused by Xp and Xq deletions in the human female: a hypothesis. Hum Genet 85:175–183
Therman E, Denniston C, Sarto GE, Ulber M (1980) X chromosome constitution and the human female phenotype. Hum Genet 54:133–143
Therman E, Laxova R, Susman B (1990) The critical region on the human Xq. Hum Genet 85:455–461
Underwood LE, Van Wyk JJ (1992) Normal and aberrant growth. In: Wilson JD, Foster DW (eds) Williams textbook of endocrinology, 8th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1079–1138
Verp MS, Rosinsky B, Beau MM Le, Martin AO, Kaplan R, Wallemark C-B, Otano L, Simpson JL (1988) Growth disadvantage of 45. X and 46,X,del(X)(p11) fibroblasts. Clin Genet 33:277–285
Vittay P, Bosze P, Gaal M, Laszlo J (1980) Lymph vessel defects in patients with ovarian dysgenesis. Clin Genet 18:387–391
Vogel F, Motulsky AG (1986) Human genetics: problems and approaches, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo
Wallace BMN, Hulten MA (1983) Triple chromosome synapsis in oocytes from a human foetus with trisomy 21. Ann Hum Genet 47:271–276
Wallace BMN, Hulten MA (1985) Meiotic chromosome pairing in the normal human female. Ann Hum Genet 49:215–226
Weil D, Portnoi M-F, Levilliers J, Wang I, Mathieu M, Taillemite J-L, Meiser M, Boudailliez B, Petit C (1993) A 45,X male with an X;Y translocation: implications for the mapping of the genes responsible for Turner syndrome and X-linked chondrodysplasia punctata. Hum Mol Genet 2:1853–1856
Weiss L (1971) Additional evidence of gradual loss of germ cells in the pathogenesis of streak ovaries in Turner's syndrome. J Med Genet 8:540–544
Witt DR, Hoyme HE, Zonana J, Manchester DK, Fryns JP, Stevenson JG, Curry CJR, Hall JG (1987) Lymphedema in Noonan syndrome: clues to pathogenesis and prenatal diagnosis and review of the literature. Am J Med Genet 27:841–856
Zarabi M, Mieckowski GC, Mazer J (1983) Cystic hygroma associated with Noonan's syndrome. J Clin Ultrasound 11:398–400
Appendix: References of karyotype-phenotype correlations
Court-Brown WM et al (1964) Abnormalities of the sex chromosome complement in man. (Medical Research Council, Special Report Series No. 305) John Blackburn, Leeds
Ferguson-Smith MA et al (1964) Cytogenetics 3:355–383
Engle E, Forbes AP (1965) Medicine 44:135–164
Kallio H (1973) Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand [Suppl] 24:1–78
Goldberg MB et al (1968) Am J Med 45:529–543
Jacobs PA et al (1961) Lancet 1:1183–1189
Maclean N et al (1961) Lancet 2:406–408
Stewart JSS (1960) Acta Endocrinol 33:89–102
Lemli L, Smith DW (1963) J Pediatr 63:577–587
Mattevi MS et al (1971) Humangenetik 13:126–143
Greenblatt RB et al (1967) Am J Obstet Gynecol 98:151–172
Chapelle A de la (1962) Acta Endocrinol 25 [Suppl 65]:1–122
Therman E et al (1961) Am J Hum Genet 13:193–204
Rigo S et al (1968) Med J Aust 1:515–519
Groll M, Cooper M (1976) Obstet Gynecol 47:225–226
King CR et al (1978) Obstet Gynecol 52:617–624
Bahner F et al (1960) Acta Endocrinol 35:397–404
Grace HJ et al (1973) Am J Obstet Gynecol 115:279–282
Philip J, Sele V (1976) Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 55:283–286
Kohn G et al (1980) Am J Med Genet 5:339–343
Sholeir MHK (1978) Birth Defects 14:171–184
Nakashima I, Robinson A (1971) Pediatrics 47:770–773
Lajborek-Czyz I (1976) Clin Genet 9:113–116
Wray HL et al (1981) Fertil Steril 35:509–514
Baudier MM et al (1985) Obstet Gynecol 65 [Suppl]:60–63
Dewhurst J (1981) Br J Obstet Gynecol 88:944–949
German J (1970) Clin Genet 1:15–27
Lindsten J et al (1963) Nature 197:648–649
Carr DH, Barr ML (1963) J Pediatr 62:696–702
Hsu LYF et al (1978) J Med Genet 15:222–226
Summitt RL, Dobbins WT (1965) J Pediatr 67:76–83
Engel E, Forbes AP (1961) Lancet 2:1004–1005
Simpson JL (1975) Birth Defects 11:23–59
Sparkes RS, Motulsky AG (1963) Lancet 1:947
Ree MJ (1965) J Med Genet 2:205–211
Otto PG et al (1981) Hum Genet 57:159–164
Leisti J (1971) Ann Acad Sci Fenn 179:1–69
Priest JH et al (1975) J Med Genet 12:378–389
Senzer N et al (1973) Am J Dis Child 126:312–316
Fujita H et al (1977) Hum Genet 39:147–155
Hodgson S et al (1981) Hum Genet 58:176–178
Daniel A et al (1979) J Med Genet 16:278–284
Fryns JP et al (1983) Clin Genet 24:180–183
Barnabei VM et al (1983) South Med J 76:249–250
Latt SA et al (1976) Chromosoma 57:135–153
Ponzio G et al (1987) Clin Genet 32:20–23
Therman E et al (1974) Am J Hum Genet 26:83–92
Gordon H et al (1979) Videodensitometric analysis of normal and abnormal X chromosomes by computer. In: Vallet HL, Porter JH (eds) Genetic mechanisms of sexual development. Academic Press, New York, pp 331–364
Dewald G et al (1978) Am J Med Genet 1:445–460
Tegenkamp TR et al (1978) Am J Hum Genet 30 [Suppl]:69A
Rivera H et al (1987) Ann Genet 30:98–100
Robertson J et al (1982) J Med Genet 19:463–465
Sarto GE, Therman E (1980) Am J Obstet Gynecol 136:904–911
Disteche C et al (1972) Clin Genet 3:388–395
Ferraro M et al (1980) J Med Genet 17:457–463
Leal-Garza C et al (1986) Arch Invest Med 17:337–346
Smith A et al (1979) Ann Genet 22:143–147
Stoll C et al (1979) Eur J Pediatr 131:141–145
Yu CW et al (1982) Am J Med Genet 11:305–317
Schwanitz G et al (1977) Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma) 26:277–281
Fraisse J et al (1975) Ann Genet 18:243–245
Howell RT et al (1976) J Med Genet 13:496–500
Midro AT et al (1988) Clin Genet 34:153–160
Curry CJR et al (1984) N Engl J Med 311:1010–1015
Bick D et al (1989) Am J Med Genet 33:100–107
Meindl A et al (1993) J Med Genet 30:838–842
Bartsch-Sandhoff M et al (1976) Hum Genet 31:263–270
Petrinelli P et al (1978) Hum Genet 45:351–354
Giraud F et al (1974) Arch Fr Pediatr 31:717–724
Thayer BA et al (1987) Am J Hum Genet 41 [Suppl]:A143
Varela M et al (1987) Am J Hum Genet 41 [Suppl]:A144
Kaosaar M, Mikelsaar A-V (1980) Hum Genet 53:275–277
Conte W et al (1988) Am J Hum Genet 43 [Suppl]:A105
Fryns JP et al (1981) Hum Genet 57:385–387
Kalousek D et al (1979) J Pediatr 94:891–894
Massa G et al (1992) Eur J Pediatr 151:893–894
Golob E et al (1967) Dtsch Med Wochenschr 92:71–74
Weed JC (1972) Unusual ovarian development. In: Dougherty CM, Spencer R (eds) Female sex anomalies. Harper and Row, New York, pp 195–204
Kaiser P et al (1976) Hum Genet 32:86–100
Fraccaro M et al (1977) Hum Genet 39:283–292
Boczkowski K et al (1978) Clin Genet 13:409–414
Leichtman DA et al (1978) Ann Intern Med 89:473–476
Barakat BY et al (1979) Am J Obstet Gynecol 133:460–461
Salesses A et al (1981) Ann Endocrinol 42:147–151
Payne DG, Fayez JA (1982) NC Med J 43:287–288
Fitzgerald PH et al (1984) Clin Genet 25:301–309
Palmer CG, Reichmann A (1976) Hum Genet 35:35–49
Ishitobi K et al (1982) Jpn J Intern Med 71:1275–1282
Fujita H (1980) Sex chromosome abnormalities. In: Baba K, Kobayashi N (eds) (Pediatric Mook Series No 11) Congenital malformation syndromes. Kimbara Press, Tokyo, pp 158–165
Bjøro K (1965) Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 44 [Suppl 4]:1–126
Steinberger E et al (1966) J Med Genet 3:226–229
Tveteras E (1965) Acta Paediatr Scand [Suppl 159]:131–132
Aarskog D (1967) Acta Paediatr Scand [Suppl 177]:69–72
Frantz J, Noel B (1975) Rev Fr Endocrinol Clin 16:445–453
Dzenis IG, Antipina NN (1979) Hum Genet 52:275–279
Bachman R et al (1971) Am J Ment Defic 75:435–441
Anuman-Rajadhon Y, Unakul W (1983) J Med Assoc Thai 66:122–124
Therman E et al (1981) Hum Genet 57:104–107
Lejeune J et al (1966) Ann Genet 9:132–133
Davies JR et al (1976) Clin Genet 10:202–207
Laszlo J, Gaal M (1977) Excerta Med Int Congr Ser 428:187–199
Chapelle A de la et al (1975) Hereditas 80:113–120
Goldman B et al (1982) Clin Genet 21:36–52
Grumbach MM, Conte FA (1992) Disorders of sex differentiation. In: Wilson JD, Foster DW (eds) Williams textbook of endocrinology, 8th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 853–952
Boczkowski K, Mikkelsen M (1973) J Med Genet 10:350–355
Jacobs PA et al (1960) Lancet 1:1213–1216
Baughman FA Jr et al (1968) Am J Obstet Gynecol 102:1065–1069
Weber FM et al (1970) Am J Obstet Gynecol 107:1092–1098
Bocian M et al (1971) J Med Genet 8:358–363
Jenkins MB, O'Rourke WJ (1974) Lancet 1:210
Sarto GE et al (1974) Clin Genet 6:289–293
Therman E et al (1979) Hum Genet 50:59–64
Baue G, Gilgenkrantz S (1976) Gynecologie 27:19–23
Stoll C et al (1973) Lancet 1:436
Wolf U et al (1980) Hum Genet 54:149–154
Srivastava PK et al (1979) South Med J 72:1461–1463
Oishi H et al (1974) Jpn J Hum Genet 19:91–92
Seki T et al (1981) Jpn J Hum Genet 26:307–312
Ishitobi K, Harada Y (1979) Proc Jpn Acad 55:10–14
Brankovic S et al (1979) Hum Genet 48:139–142
Re M et al (1988) Panminerva Med 30:262–265
Lippe BM, Brandall BF (1973) Am J Dis Child 126:222–224
Forabosco A, Dallapiccola B (1974) Lancet 2:403–404
Slater R, Ntuyabaliw WK (1974) Lancet 2:57–58
Skibsted L et al (1984) Hum Genet 67:1–5
Simpson JL, Le Beau MM (1981) Am J Obstet Gynecol 141:930–938
Berghe H van den et al (1973) Humangenetik 20:163–166
Hecht F et al (1970) J Med Genet 7:1–4
Wright EV, Scanion MF (1974) Lancet 1:933
Chapelle A de la, Schroder J (1975) Hereditas 80:137–140
Ruthner U et al (1979) Hum Genet 48:135–137
Wyss D et al (1982) Clin Genet 21:145–159
Mijin K et al (1982) J Med Genet 19:305–306
Kaiser P et al (1984) Clin Genet 26:433–439
Fryns JP et al (1982) Clin Genet 22:76–79
Naguib KK et al (1988) Fertil Steril 49:917–919
Grouchy J de et al (1961) Lancet 2:777–778
Fitch N et al (1982) Am J Obstet Gynecol 142:968–972
Taysi K (1983) Am J Med Genet 14:367–372
Trunca C et al (1984) Hum Genet 68:87–89
Palmer C et al (1973) Am J Hum Genet 25 [Suppl]:57A
Bates A, Howard PJ (1990) J Med Genet 27:722–723
Tharapel AT et al (1993) Am J Hum Genet 52:463–471
Herva R et al (1979) Am J Med Genet 3:43–58
Wilson MG et al (1983) Am J Med Genet 14:567–576
Wells S et al (1991) J Med Genet 28:163–166
Allderdice PW, Eales B (1981) Am J Hum Genet 33 [Suppl]:69A
Krauss CM et al (1987) N Engl J Med 317:125–131
Allderdice PW et al (1978) Am J Med Genet 2:233–240
Pallister PD, Opitz JM (1978) Birth Defects 14:133–146
Festa B et al (1984) Acta Med Auxol 16:205–209
Sarto GE et al (1973) Am J Hum Genet 25:262–270
Gilgenkrantz S et al (1975) Humangenetik 26:25–34
Phelan JP et al (1977) Am J Obstet Gynecol 129:607–613
Opitz JM et al (1978) Birth Defects 14:365–375
Forabosco A et al (1979) Ann Genet 22:11–16
Dorus E et al (1979) Clin Genet 16:253–259
Mijin K et al (1981) Clin Genet 20:403–406
Haseltine FP et al (1982) Am J Med Genet 13:115–123
Van Dyke DL et al (1977) Am J Hum Genet 29 [Suppl]:109A
Rudak E et al (1979) Clin Genet 25:199–200
Barnabei VM et al (1981) Am J Hum Genet 33:61–66
Filippi G et al (1983) J Med Genet 20:467–468
Markovic VD et al (1985) Am J Med Genet 20:87–96
Ji X-W et al (1988) Am J Med Genet 31:783–786
Madan K et al (1981) Hum Genet 59:290–296
Cann HM et al (1975) Am J Hum Genet 27 [Suppl]:23A
Cantu LM et al (1985) Am J Med Genet 20:677–684
Patel U et al (1989) Am J Hum Genet 45 [Suppl]:A86
Mariani R et al (1980) Ann Pediatr 27:129–132
Leddet-Chevallier I et al (1981) Ann Genet 24:162–164
Carpenter NJ et al (1980) J Med Genet 17:216–221
Mattei MG et al (1978) Hum Genet 41:251–257
Dutrillaux B et al (1974) Helv Paediatr Acta [Suppl 34]:19–31
Lucas M, Smithies A (1973) Ann Hum Genet 37:9–12
Yamamoto Y et al (1979) J Med Genet 16:395–399
Sauer F et al (1977) Obstet Gynecol 49:101–104
Pearson PL et al (1978) Cytogenet Cell Genet 22:534–537
Clarke G et al (1964) J Med Genet 1:27–34
Hagen van den CB, Molne K (1978) Clin Gent 13:118
Diedrich U, Hansmann I (1985) Hum Genet 70:281–283
Hodgson SV et al (1986) J Med Genet 23:477–478
Wegner R-D (1982) Hum Genet 61:79
Mann JD, Higgins J (1974) Am J Hum Genet 26:416
Mann JD et al (1965) Am J Hum Genet 17:377–383
Latt SA et al (1976) Chromosoma 57:135–153
Sujansky E et al (1973) Pediatr Res 7:343
Powell CM et al (1993) Am J Hum Genet 53 [Suppl]:No 1215
Keitges EA, Palmer CG (1982) Am J Hum Genet 34 [Suppl]:131A
Pearson PL et al (1974) Birth Defects 10:136–142
Kleczkowska A et al (1985) Clin Genet 27:147–152
Hagemeijer A et al (1977) Cytogenet Cell Genet 18:333–348
Biemont MC et al (1978) Ann Genet 21:133–141
Buckton KE et al (1971) Ann Hum Genet 35:171–178
Garcia-Sagredo JM et al (1984) Clin Genet 26:117–124
Garcia JE et al (1977) J Hered 68:75–80
Thorrburn MJ et al (1970) J Med Genet 7:402–406
Leisti JT et al (1975) Am J Hum Genet 27:441–453
Gardner HA et al (1983) Am J Med Genet 14:647–656
Rivera H et al (1986) Clin Genet 29:425–428
Turleau C et al (1977) Hum Genet 37:97–104
Couturier J et al (1979) Hum Genet 49:319–326
Cervenka J et al (1976) Hum Genet 34:1–7
Summit RL et al (1974) J Pediatr 84:539–546
Francke U et al (1976) Somat Cell Genet 2:27–40
Patracchini P et al (1989) Hum Genet 83:264–266
Mashkova MV, Verlinskaya DK (1976) Tsitologiia 18:901–905
Buhler EM et al (1977) Nature 265:142–144
Waters JJ et al (1990) Am J Med Genet 36:310–312
Dutrillaux B et al (1972) CR Acad Sci III 274:3324–3327
Gaal M, Laszlo J (1977) Hum Hered 27:396–402
Nikolis J, Stolevic E (1978) Hum Genet 45:115–122
Kristensen H et al (1975) Humangenetik 26:133–138
Mohandas T et al (1986) Am J Hum Genet 39 [Suppl]:A126
McLaughlin CJ et al (1987) Am J Hum Genet 41 [Suppl]:A133
Shabtai F et al (1983) Clin Genet 23:234–235
Duckett DP, Young ID (1988) Hum Genet 79:251–254
Keitges EA et al (1982) Hum Genet 62:210–213
Buckton KE et al (1981) Ann Hum Genet 45:159–168
Soler A et al (1981) Clin Genet 20:234–235
Neu RL et al (1988) J Med Genet 25:52–60
Maeda T et al (1979) Clin Genet 15:259–266
Evans MI et al (1980) Clin Genet 18:30–33
Cerrillo M, Varela M (1986) Am J Hum Genet 39 [Suppl]:A108
Blagowidow N et al (1989) Am J Med Genet 34:159–162
Rosenfeld RG et al (1979) Am J Hum Genet 31:458–468
Magenis RE et al (1984) J Pediatr 105:916–919
Disteche CM et al (1986) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7841–7844
Cantrell MA et al (1989) Hum Genet 83:88–92
Levilliers J et al (1989) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2296–2300
Muller U et al (1992) Hum Genet 90:239–242
Ogata T et al (1993) J Med Genet 30:918–922
Rivera H et al (1988) Ann Genet 31:244–246
McElreavy K et al (1992) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:11016–11020
Muller J et al 81992) J Clin Endocrinol Metab 75:331–333
Zeng V et al (1993) J Med Genet 30:655–657
McElreavy K et al (1992) Genomics 13:838–840
Vilain E et al (1993) Differentiation 52:151–159
Affara N et al (1993) Hum Mol Genet 2:785–789
Vilain K et al (1992) Am J Hum Genet 50:1008–1011
Jager RJ et al (1990) Nature 348:452–454
Hawkins JR et al (1992) Hum Genet 88:471–474
Hawkins JR et al (1992) Am J Hum Genet 51:979–984
Jager RJ et al (1992) Hum Genet 90:350–355
Fraser JH et al (1960) Lancet 2:626–627
Carli de L et al (1960) Lancet 2:130–131
Jacobs PA et al (1959) Lancet 2:423–425
Stewart JSS, Sanderson AR (1960) Lancet 2:21–23
Sandberg AA et al (1960) JAMA 174:221–225
Harnden DG et al (1960) Lancet 1:1213–1216
Johnston AW et al (1961) BMJ 2:1046–1052
Maclean N et al (1962) Lancet 1:293–296
Close HG (1963) Lancet 2:1358–1359
Barr ML et al (1969) Can Med Assoc J 101:247–258
Newton MS et al (1972) Clin Genet 3:215–225
Singer J et al (1972) J Med Genet 9:238–239
Guzman-Toledano R et al (1976) J Med Genet 13:516–517
Fryns JP et al (1983) Clin Genet 23:341–349
Spear GS, Porto M (1988) Am J Med Genet 29:511–515
Hood OJ et al (1990) Am J Med Genet 36:73–75
Tanner JM et al (1966) Arch Dis Child 41:454–471 (part I) and 41:613–635 (part II)
Hamill PV et al (1977) Vital Health Stat [11] 165:1–74
Twisselmann F (1969) Development biometrique de l'enfant a l'adulte. Presses Universitaires de Bruxelles, Bruxelles
Sempe M et al (1979) Auxologie: methode et sequences. Theraplix, Paris
Prader A et al (1989) Helf Paediatr Acta 52 [Suppl]:1–125
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogata, T., Matsuo, N. Turner syndrome and female sex chromosome aberrations: deduction of the principal factors involved in the development of clinical features. Hum Genet 95, 607–629 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209476
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209476