Summary
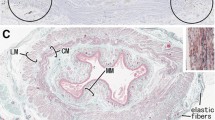
The morphological and topographical features of the intramural enteric nervous system in the small intestine of the pig has been studied on whole mounts by means of neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and S-100 protein immu-nohistochemistry. A clear visualization of the myenteric plexus allows the recognition of its characteristic morphology, including the thin tertiary plexus coursing within the smooth muscle layers. In the tela submucosa two ganglionated plexuses, each with its own specific characteristics, can clearly be demonstrated: (1) the plexus submucosus externus (Schabadasch) located near the inner surface of the circular muscle layer at the abluminal side of the submucosal vascular arcades, and (2) the plexus submucosus internus (Meissner) close to the outer surface of the lamina muscularis mucosae at the luminal side of the submucosal vascular arcades. Due to the possibility to trace clearly the perivascular plexuses of these vascular arcades by use of immunohistochemical techniques with antibodies to NSE and S-100 protein, the two submucosal nerve plexuses can be demonstrated with exceptional clarity. This is the first report of an investigation of the intramural nerve plexuses of the small intestine of the pig using the NSE and S-100 immunostaining methods, which is sufficiently detailed to substantiate the characteristic topography and structure of the two submucosal plexuses and their relation to the smooth muscle layers and perivascular plexuses. The level of NSE immunoreactivity for enteric neurons displays great variation, a substantial proportion of the type-II neurons appearing strongly stained. Although little is known of the specific function of these enzymes, proposals are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop AE, Carlei F, Lee V, Trojanowski J, Marangos PJ, Dahl D, Polak JM (1985) Combined immunostaining of neurofilaments, neuron specific enolase, GFAP and S-100. A possible means for assessing the morphological and functional status of the enteric nervous system. Histochemistry 82:93–97
Bock E (1978) Nervous system specific proteins. J Neurochem 30:7–14
Bock E, Dissing J (1975) Demonstration of enolase activity connected to the brain specific protein 14–3–2. Scand J Immunol 4 (Suppl 2): 31–36
Cicero T, Cowan WM, Moore BW (1970) Changes in the concentration of two brain proteins S-100 and 14–3–2′ during the development of the avian optic tectum. Brain Res 24:1–10
Cocchia D, Michetti F (1981) S-100 antigen in satellite cells of the adrenal medulla and the superior cervical ganglion of the rat. Cell Tissue Res 215:103–112
Dogiel AS (1899) Über den Bau der Ganglien in den Geflechten des Darmes und der Gallenblase des Menschen und der Säugetiere. Arch Anat Physiol Anat Abt 1899:130–158
Ferri G-L, Probert L, Cocchia D, Michetti F, Marangos PJ, Polak JM (1982) Evidence for the presence of S-100 protein in the glial component of the human enteric nervous system. Nature 297:409–410
Fletcher L, Rider CC, Taylor CB (1976) Enolase isoenzymes. III. Chromatographic and immunological characteristics of rat brain enolase. Biochim Biophys Acta 452:245–252
Fujita T, Iwanaga T, Nakajima T (1983) Immunohistochemical detection of nervous system-specific proteins in normal and neoplastic paraneurons in the gut and pancreas. In: Miyoshi A (ed) Gut peptides and ulcer. Biomed Res Found, Tokyo, pp 81–88
Furness JB, Costa M (1980) Types of nerves in the enteric nervous system. Neuroscience 5:1–20
Furness JB, Costa M (1987) The Enteric Nervous System. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Gabella G (1976) Ganglia of the autonomic nervous system. In: Landon DN (ed) The peripheral nerve. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 355–395
Gabella G (1979) Innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Int Rev Cytol 59: 129–193
Gabella G, Halasy K (1987) On the nerve plexus of the chicken gizzard. Anat Embyrol 177:97–103
Gu J, Polak JM, Tapia FJ, Marangos PJ, Pearse AGE (1981) Neuron-specific enolase in the Merkel cells of mammalian skin. Am J Pathol 104:63–68
Gunn M (1968) Histological and histochemical observations on the myenteric and submucous plexuses of mammals. J Anat 102:223–239
Haimoto H, Takahashi Y, Koshikawa T, Nagura H, Kalo K (1985) Immunohistochemical localization of γ-enolase in normal human tissues other than nervous and neuroendocrine tissues. Lab Invest 52:257–263
Isobe T, Ishioka N, Okuyama T (1981) Structural relation of two S-100 proteins in bovine brain; subunit composition of S-100a protein. Eur J Biochem 115:469–474
Isobe T, Takahashi K, Okuyama T (1984) S100a0 (αα) protein is present in neurons of the central and peripheral nervous system. J Neurochem 43:1494–1496
Kato K, Suzuki F, Umeda Y (1981a) Highly sensitive immunoassays for three forms of rat brain enolase. J Neurochem 36:793–797
Kato K, Suzuki F, Semba R (1981b) Determination of brain enolase isozymes with an enzyme immunoassay at the level of single neurons. J Neurochem 37:998–1005
Kobayashi S, Suzuki M, Endo T, Tsuji S, Daniel EE (1986) Framework of the enteric nerve plexuses: an immunocytochemical study in the guinea pig jejunum using an antiserum to S-100 protein. Arch Histol Jpn 49:159–188
Kondo H, Iwanaga T, Nakajima T (1983) An immunocytochemical study on the localization of S-100 protein in the retina of rats. Cell Tissue Res 231:527–532
Marangos PJ, Schmechel D (1980) The neurobiology of the brain enolases. In: Youdim MBH, Lovenberg W, Sharman DF, Lagnado JR (eds) Essays in neurochemistry and neuropharmacology, Vol 4. Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 211–247
Marangos PJ, Zomzely-Neurath C, York C (1976) Determination and characterization of neuron specific protein (NSP) associated enolase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 68:1309–1316
Marangos PJ, Zis AP, Clark RL, Goodwin FK (1978a) Neuronal, non-neuronal and hybrid forms of enolase in brain: structural, immunological and functional comparisons. Brain Res 150:117–133
Marangos PJ, Goodwin FK, Parma A, Lauter C, Trams E (1978b) Neuron specific protein (NSP) in neuroblastoma cells: relation to differentiation. Brain Res 145:49–58
Marangos PJ, Parma AM, Goodwin FK (1978c) Functional properties of neuronal and glial isoenzymes of brain enolase. J Neurochem 31:727–732
Marangos PJ, Schmechel D, Parma AM, Clark RL, Goodwin FK (1979) Measurement of neuron-specific (NSE) and non-neuronal (NNE) isoenzymes of enolase in rat, monkey and human nervous tissue. J Neurochem 33:319–329
Marangos PJ, Schmechel DE, Parma AM, Goodwin FK (1980) Developmental profile of neuron-specific (NSE) and non-neuronal (NNE) enolase. Brain Res 190:185–193
Marangos PJ, Schmechel DE, Oertel WH (1981) Neuron-specific enolase: a functional marker for the diffuse neuro-endocrine system. In: Bloom SR, Polak JM (eds) Gut hormones. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 101–106
Matus A, Mughal S (1975) Immunohistochemical localization of S-100 protein in brain. Nature 258:746–748
Nada O, Kawana T (1988) Immunohistochemcial identification of supportive cell types in the enteric nervous system of the rat colon and rectum. Cell Tissue Res 251:523–529
Nakajima T, Kameya T, Watanabe S, Hirata T, Shimosato Y, Isobe T (1984) S-100 protein distribution in normal and neoplastic tissues. In: DeLellis RA (ed) Advances in immunohisto-chemistry. Masson Publishing Inc, New York, pp 141–158
Perez VJ, Olney JW, Cicero TJ, Moore BW, Bahn BA (1970) Wallerian degeneration in rabbit optic nerve: cellular localization in the central nervous system of the S-100 and 14–3–2 proteins. J Neurochem 17:511–519
Pickel VM, Reis DJ, Marangos PJ, Zomzely-Neurath C (1976) Immunocytochemical localization of nervous system specific protein (NSP-R) in rat brain. Brain Res 105:184–187
Rider CC, Taylor CB (1974) Enolase isoenzymes in rat tissues. Electrophoretic, chromatographic, immunological and kinetic properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 365:285–300
Rintoul JR (1960) The comparative morphology of the enteric nerve plexuses. MD thesis, University of St. Andrews, Scotland
Schabadasch A (1930) Intramurale Nervengeflechte des Darmrohrs. Z Zellforsch 10:320–385
Scheuermann DW, Stach W (1984) Fluorescence microscopic study of the architecture and structure of an adrenergic network in the plexus myentericus (Auerbach), plexus submucosus externus (Schabadasch) and plexus submucosus internus (Meissner) of the porcine small intestine. Acta Anat 119:49–59
Scheuermann DW, Stach W, De Groodt-Lasseel MHA, Timmermans J-P (1987a) Calcitonin gene-related peptide in morphologically well-defined type II neurons of the enteric nervous system in the porcine small intestine. Acta Anat 129:325–328
Scheuermann DW, Stach W, Timmermans J-P (1987b) Topography, architecture and structure of the plexus submucosus internus (Meissner) of the porcine small intestine in scanning electron microscopy. Acta Anat 129:96–104
Scheuermann DW, Stach W, Timmermans J-P (1987c) Topography, architecture and structure of the plexus submucosus externus (Schabadasch) of the porcine small intestine in scanning electron microscopy. Acta Anat 129:105–115
Scheuermann DW, Stach W, Timmermans J-P (1988a) Serotonin-immunoreactivity in the wall of the porcine small intestine. Verh Anat Ges (in press)
Scheuermann DW, Stach W, Timmermans J-P (1988b) Immunohistochemistry provides evidence for the existence of two functionally different submucosal plexuses in the small intestine of the pig. Anat Anz (in press)
Schmechel D, Marangos PJ, Zis AP, Brightman M, Goodwin FK (1978a) Brain enolases as specific markers of neuronal and glial cells. Science 199:313–315
Schmechel D, Marangos PJ, Brightman M (1978b) Neurone-specific enolase is a molecular marker for peripheral and central neuroendocrine cells. Nature 276:834–836
Schmechel DE, Brightman MW, Barker JL (1980a) Localization of neuron-specific enolase in mouse spinal neurons grown in tissue culture. Brain Res 181:391–400
Schmechel DE, Brightman MW, Marangos PJ (1980b) Neurons switch from non-neuronal enolase to neuron-specific enolase during differentiation. Brain Res 190:195–214
Schnitzer J (1987) Immunocytochemical localization of S-100 protein in astrocytes and Müller cells in the rabbit retina. Cell Tissue Res 248:55–61
Shimizu A, Suzuki F, Kato K (1983) Characterization of αα, ββ, γγ and αγ human enolase isoenzymes and preparation of hybrid enolases (αγ, βγ and αβ) from homodimeric forms. Biochem Biophys Acta 748:278–284
Stach W (1969) Neurohistologische Untersuchungen an den Ner-vengeflechten der Dickdarmwand. Ein Beitrag zur Innervation des Magen-Darmkanals. MD thesis, Wilhelm Pieck University, Rostock, German Democratic Republic
Stach W (1977a) Der Plexus submucosus externus (Schabadasch) im Dünndarm des Schweins. I. Form, Struktur und Verbindungen der Ganglien und Nervenzellen. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 91:737–755
Stach W (1977b) Neuronenstruktur und -architektur im Plexus submucosus externus (Schabadasch) des Duodenums. Verh Anat Ges 71:867–871
Stach W (1981) Zur neuronalen Organisation des Plexus myentericus (Auerbach) im Schweinedünndarm. II. Typ II-Neurone. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch 95:161–182
Stach W, Scheuermann DW, Timmermans J-P (1987) Licht- und Rasterelektronenmikroskopie der submukösen Nervengeflechte des Darmwandnervensystems. Verh Anat Ges 81:729–730
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry. J Wiley, New York
Vinores SA, Herman MM, Rubinstein LJ, Marangos PJ (1984) Electron microscopic localization of neuron-specific enolase in rat and mouse brain. J Histochem Cytochem 32:1295–1302
Wharton J, Polak JM, Cole GA, Marangos PJ, Pearse AGE (1981) Neuron-specific enolase as an immunocytochemical marker for the diffuse neuroendocrine system in human fetal lung. J Histochem Cytochem 29:1359–1364
Wilson AJ (1981) Ultrastructural and cytochemical studies on the submucous plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. PhD thesis, Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheuermann, D.W., Stach, W., Timmermans, JP. et al. Neuron-specific enolase and S-100 protein immunohistochemistry for defining the structure and topographical relationship of the different enteric nerve plexuses in the small intestine of the pig. Cell Tissue Res. 256, 65–75 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224719
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224719