Abstract
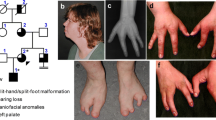
A large inbred kindred from Pakistan in which an isolated type of split-hand/split-foot anomaly is transmitted as an X-chromosomal trait has previously been described. An X/autosomal translocation and an X-chromosomal rearrangement have been excluded by cytogenetic studies. In order to map the gene responsible for this disorder, linkage analysis has been performed by using 14 highly polymorphic DNA markers distributed over the whole X chromosome. Two-point linkage analysis between the disease locus and X-chromosomal marker loci gives maximal lod scores at θ= 0.00 with the loci DXS294 (Z max= 5.13) and HPRT (Z max= 4.43), respectively, suggesting that the gene for the X-chromosomal split-hand/split-foot anomaly is localized at Xq26–q26.1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Abbas H, Haque S, Flatz G (1987) X-chromosomally inherited split hand/split foot anomaly in a Pakistani kindred. Hum Genet 75:169–173
Freire-Maia A (1971) A recessive form of ectrodactyly, and its implications for genetic counseling. J Hered 62:53
McKusick VA (1992) Mendelian inheritance in man, 10th edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore London, pp 1031 and 1963
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Ott J (1991) Analysis of human genetic linkage, 2nd revised edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Roberts SH, Hughes HE, Davies SJ, Meredith AL (1991) Bilateral split hand and split foot malformation in a boy with a de novo interstitial deletion of 7q21.3. J Med Genet 28:479–481
Van den Berghe H, Dequeker J, Fryns JP, David G (1978) Familial occurrence of severe ulnar hypoplasia and lobster claw feet: a new syndrome. Hum Genet 42:109–113
Verma IC, Joseph R, Bhargava S, Mehta S (1976) Split-hand and split-foot deformity inherited as an autosomal recessive trait. Clin Genet 9:8–14
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faiyaz ul Haque, M., Uhlhaas, S., Knapp, M. et al. Mapping of the gene for X-chromosomal split-hand/split-foot anomaly to Xq26–q26.1. Hum Genet 91, 17–19 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230215
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230215