Abstract
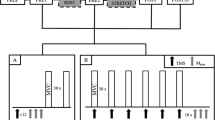
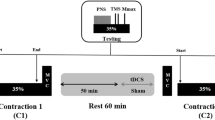
Motor evoked potentials (MEPs) elicited by transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and transcranial electrical stimulation (TES) of the motor cortex were recorded in separate sessions to assess changes in motor cortex excitability after a fatiguing isometric maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) of the right ankle dorsal flexor muscles. Five healthy male subjects, aged 37.4±4.2 years (mean±SE), were seated in a chair equipped with a load cell to measure dorsiflexion force. TMS or TES was delivered over the scalp vertex before and after a fatiguing MVC, which was maintained until force decreased by 50%. MEPs were recorded by surface electrodes placed over quadriceps, hamstrings, tibialis anterior (TA), and soleus muscles bilaterally. M-waves were elicited from the exercised TA by supramaximal electrical stimulation of the peroneal nerve. H-reflex and MVC recovery after fatiguing, sustained MVC were also studied independently in additional sessions. TMS-induced MEPs were significantly reduced for 20 min following MVC, but only in the exercised TA muscle. Comparing TMS and TES mean MEP amplitudes, we found that, over the first 5 min following the fatiguing MVC, they were decreased by about 55% for each. M-wave responses were unchanged. H-reflex amplitude and MVC force recovered within the 1st min following the fatiguing MVC. When neuromuscular fatigue was induced by tetanic motor point stimulation of the TA, TMS-induced MEP amplitudes remained unchanged. These findings suggest that the observed decrease in MEP amplitude represents a focal reduction of cortical excitability following a fatiguing motor task and may be caused by intracortical and/or subcortical inhibitory mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker SN, Olivier E, Lemon RN (1994) Recording an identified pyramidal volley evoked by transcranial magnetic stimulation in a conscious macaque monkey. Exp Brain Res 99:529–532
Barker AT, Freeston IL, Jalinous R, Merton PA, Morton HB (1985) Magnetic stimulation of the human brain. J Physiol (Lond) 369:3P
Bigland-Ritchie B, Woods JJ (1984) Changes in muscle contractile properties and neural control during human muscular fatigue. Muscle Nerve 7:691–699
Bigland-Ritchie B, Jones DA, Hosking GP, Edwards RHT (1978) Central and peripheral fatigue in sustained maximum voluntary contractions of human quadriceps muscle. Clin Sci Mol Med 54:609–614
Brasil-Neto JP, Pascual-Leone A, Valls-Sole J, Cammaro TA, Cohen LG, Hallett M (1993) Postexercise depression of motor evoked potentials:a measure of central nervous system fatigue. Exp Brain Res 93:181–184
Brasil-Neto JP, Cohen LG, Hallett M (1994) Central fatigue as revealed by postexercise decrement of motor evoked potentials. Muscle Nerve 17:713–719
Chisholm RC, Karrer R (1988) Movement related potentials and control of associated movements. Int J Neurosci 42:131–148
Day BL, Dressler D, Maertens de Noordhout A, Marsden CD, Nakashima K, Rothwell JC, Thompson PD (1989) Electrical and magnetic human motor cortex:surface EMG and single motor unit responses. J Physiol (Lond) 412:449–473
Dimitrijevic MR, McKay WB, Sarjanovic I, Sherwood AM, Svirtlih L, Vrbova G (1992) Co-activation of ipsi- and contralateral muscle groups during contraction of ankle dorsiflexors. J Neurol Sci 109:49–5
Edgley SA, Eyre JA, Lemon RN, Miller S (1990) Excitation of corticospinal tract by electromagnetic and electrical stimulation of the scalp in macaque monkey. J Physiol (Lond) 425: 301–320
Edwards RHT (1981) Human muscle function and fatigue. In: Porter R, Whelan J (eds) Human muscle fatigue: physiological mechanisms. Pitman, London, pp 1–18
Edwards RHT, Hill DK, Jones JA, Merton PA (1977) Fatigue of long duration in human skeletal muscle after exercise. J Physiol (Lond) 272:769–778
Freude G, Ullsperger P (1987) Changes in Bereitschaftspotential during fatiguing and nonfatiguing hand movements. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:105–108
Garland SJ, McComas AJ (1990) Reflex inhibition of human soleus muscle during fatigue. J Physiol (Lond) 429:17–27
Godt RE, Nosek TM (1989) Changes of intracellular milieu with fatigue or hypoxia depress contraction of skinned rabbit skeletal and cardiac muscle. J Physiol (Lond) 412:155–180
Grimby L, Hannerz J, Ranlund T (1974) Disturbances in the voluntary recruitment order of tibialis anterior motor units in spastic paraparesis upon fatigue. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 37:40–46
Hicks A, Fenton J, Garner S, McComas AJ (1989) M-wave potentiation during and after muscle activity. J Appl Physiol 66(6): 2606–20
Jones DA, Bigland-Ritchie B, Edwards RHT (1979) Excitation frequency and muscle fatigue: mechanical responses during voluntary and stimulated contractions. Exp Neurol 64:401–413
Kniffki K-D, Mense S, Schmidt RF (1978) Responses of group IV afferent units from skeletal muscle to stretch, contraction and chemical stimulation. Exp Brain Res 31:511–522
Leonard CT, Kane J, Perdaems J, Frank C, Graetzer DG, Moritani T (1994) Neural modulation of muscle contractile properties during fatigue: afferent feedback dependence. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 93:209–217
Macefield VG, Gandevia SC, Bigland-Ritchie B, Gorman RB, Burke D (1993) The firing rates of human motoneurones voluntarily activated in the absence of muscle afferent feedback. J Physiol (Lond) 471:429–443
Magleby KL (1987) Short-term changes in synaptic efficacy, In: Edleman GM, Gall WE, Cowan WM (eds) Synaptic function. Wiley, New York, pp 21–56
Marsh E, Sale D, McComas A, Quinlan J (1981) Influence of joint position on ankle dorsiflexion. J Appl Physiol 51:160–167
McKay WB, Tuel SM, Sherwood AM, Dimitrijevic MR (1993) Motor cortex responsiveness following performance of a fatiguing motor task. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19(2):1205
McKenzie DK, Bigland-Ritchie B, Gorman RB, Gandevia SC (1992) Central and peripheral fatigue of human diaphragm and limb muscles assessed by twitch interpolation. J Physiol (Lond) 454:643–656
Mense S, Stahnke M (1983) Responses in muscle afferent fibers of slow conduction velocity to contractions and ischemia in the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 342:383–397
Miller RG, Boska MD, Moussavi RC, Carson PJ, Weiner MW (1988) 31P nuclear magnetic resonance studies of high-energy phosphates and pH in human muscle fatigue. J Clin Invest 81: 1190–1196
Olyaei GR, Baxendale RH (1994) The effects of fatiguing voluntary activity on the H reflex excitability of the anterior tibial muscles in man (abstract). J Physiol (Lond) 477:58
Priori A, Bertolasi L, Dressler D, Rothwell JC, Day BL, Thompson PD, Marsden CD (1993) Transcranial electrical and magnetic stimulation of the leg area of the human motor cortex: single motor unit and surface EMG responses in the tibialis anterior muscle. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 89:131–137
Reid MB, Grubwieser GJ, Stokić DS, Koch SM, Leis AA (1993) Development and reversal of fatigue in human tibialis anterior. Muscle Nerve 16:1239–1245
Westerblad H, Lee JA, Lannergren J, Allen DG (1991) Cellular mechanisms of fatigue in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol 261: C195-C209
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McKay, W.B., Tuel, S.M., Sherwood, A.M. et al. Focal depression of cortical excitability induced by fatiguing muscle contraction: a transcranial magnetic stimulation study. Exp Brain Res 105, 276–282 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00240963
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00240963