Summary
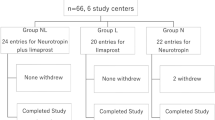
A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, crossover study in 40 lumbar spinal stenosis patients with a 1-year follow-up showed that calcitonin had beneficial effects on the patients' symptoms without producing any notable side effects. Calcitonin had a clear analgesic effect. The mean of walking distance increased, but the crossover trend was not as good as the analgesic effect. Side effects such as erythema and nausea were usually mild and transient. Calcitonin therapy can be used as a conservative treatment in selected cases of lumbar spinal stenosis. When rest pain was mild or the walking distance was under 200–300 m because of neurogenic claudication, the effect of calcitonin seemed to be poor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grabias S (1980) Current concepts review. The Treatment of spinal stenosis. J Bone Jt Surg 62-A:308–312
Getty CJM (1980) Lumbar spinal stenosis. J Bone Jt Surg 62-B:481–485
Johansson K-E, Uden A, Rosen I (1987) The effect of decompression on the neural course of spinal stenosis. SICOT XV 406:201
Herron LD, Mangelsdorf C (1991) Lumbar spinal stenosis: results of surgical treatment. J Spinal Disord 4:26–33
Porter RW, Hibbert C (1983) Calcitonin treatment for neurogenic claudication. Spine 5:90–93
Montagnani M, Gonnelli S, Francini G, Piolini M, Gennari C (1988) Analgesic effect of salmon calcitonin nasal spray in bone pain. Procgs Int Symp Calcitonin 88, Rome, pp 126–133
Fraioli F, Fabbri A, Gnessi L, Moretti C, Santoro C, Felici M (1982) Subarachnoid injection of salmon calcitonin induces analgesia in man. Eur J Pharmacol 78:381–382
Gennari C (1983) Clinical aspects of calcitonin in pain. Triangle 22:157–163
Eskola A, Alaranta H, Pohjolainen T, Soini J, Tallroth K, Slätis P (1989) Calcitonin treatment in lumbar spinal stenosis. Calcif Tissue Int 45:372–374
Bergquist-Ullman M, Larsson U (1977) Acute low back pain in industry (suppl 170) Acta Orthop Scand
Borg G (1972) Perceived exertion: a note on “history” and methods. Med Sci Sports 5:90–93
Porter RW, Miller CG (1988) Neurogenic claudication and root claudication treated with calcitonin. A double-blind trial. Spine 13:1061–1064
Streifler J, Hering R, Gadoth N (1989) Calcitonin for pseudoclaudication in lumbar spinal stenosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:543–544
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eskola, A., Pohjolainen, T., Alaranta, H. et al. Calcitonin treatment in lumbar spinal stenosis: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, cross-over study with one-year follow-up. Calcif Tissue Int 50, 400–403 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296769
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296769