Abstract
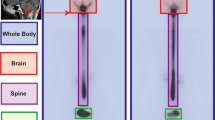
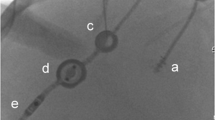
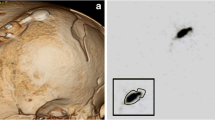
The increasing numbers and survival of children with shunt-treated hydrocephalus make it mandatory to refine the methods for cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shunt function evaluation. Radionuclide shuntography with 99mTc-DTPA, which has proved to be a safe and effective method, was performed in eight children with suspected CSF-shunt dysfunction. Characteristic shuntography patterns were found for proximal and distal CSF-shunt catheter obstruction as well as for overdrainage and normal CSF-shunt function. Shuntography contributed to the explanation of suspected CSF-shunt dysfunction in all children investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson H (1966) Craniosynostosis as a complication after operation for hydrocephalus. Acta Paediatr Scand 55: 192–196
Fernell E, Hagberg B, Hagberg G, Wendt L von (1986) Epidemiology of infantile hydrocephalus. I. Birth prevalence and general data. Acta Paediatr Scand 75: 975–981
Foltz EL, Blanks J (1988) Symptomatic low intracranial pressure in shunted hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 68: 401–408
Foltz EL, Shurtloff DB (1963) Five-year comparative study of hydrocephalus in children with and without operation (113 cases). J Neurosurg 20: 1064–1079
Gruber R (1980) The problem of chronic overdrainage of the ventricolo-peritoneal shunt in congenital hydrocephalus. Z Kinderchir 31: 362–369
Harbert J (1977) Radionuclide techniques in the evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid shunts. CRC Crit Rev Diagn Imaging 9: 207
Harbert J, Haddad D, McCullough D (1974) Quantitation of cerebrospinal fluid shunt flow. Radiology 112: 379–387
Jonson R, Ahlberg J, Mattsson S, Wikkelsö C, Lundberg S (1988) Patient exposure when using 99Tc-DTPA for evolution of cerebrospinal fluid shunt patency. Acta Radiol 29: 378–380
Oi S, Matsumoto S (1987) Infantile hydrocephalus and the slit ventricle syndrome in early infancy. Child's Nerv Syst 3: 145–150
Rudd TG, Shurtleff DB, Loeser JD, Nelp WB (1973) Radionuclide assessment of cerebrospinal fluid shunt function in children. J Nucl Med 14: 683–686
Serlo W, Heikkinen E, Saukkonen AL, Wendt L von (1985) Classification and management of the slit ventricle syndrome. Child's Nerv Syst 1: 94–99
Treves ST, Welch K, Kuruc A (1985) Cerebrospinal fluid. In: Treves ST (ed) Pediatric nuclear medicine. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 223–231
Wikkelsö C, Andersson H, Lindberg A, Blomstrand C (1983) ‘Shuntography’. A radionuclide scanning method for evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid shunt patency. Nucl Med Commun 4: 88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uvebrant, P., Sixt, R., Bjure, J. et al. Evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid shunt function in hydrocephalic children using 99mTc-DTPA. Child's Nerv Syst 8, 76–80 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298444
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00298444