Abstract
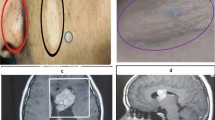
Six children with intraventricular tumors associated with tuberous sclerosis (TS) were treated at the Children's Health Center, Department of Pediatric Neurosurgery, in the period 1987–1992. The age of the patients ranged from 7 to 15 years. TS was diagnosed according to Gomez diagnostic criteria. Computer tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging showed intraventricular tumors associated with ventricular enlargement and multiple subependymal nodules commonly observed in cases of TS. All tumors were removed totally through frontal transcortical approach, with uneventful postoperative recovery. One patient, with two parallel tumors in the two frontal horns, underwent one-stage surgery with successful total removal. Histopathological examination in all cases showed subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SGCA). The growth pattern of SGCA associated with TS, documented by sequential CT scans over several years, is described. The diagnosis and surgical treatment of the tumor are discussed, and periodic CT scanning, at least every 2 years, is recommended for patients with TS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braffman BH, Bilaniuk LT, Naidich TP, Altman NR, Post MJ, Quencer RM, Zimmerman RA (1992)MR imaging of tuberous sclerosis: pathogenesis of this phakomatosis, use of gadopentetate dimeglumine, and literature review. Radiology 183:227–238
Chow CW, Klug GL, Lewis EA (1988) Subependymal giant-cell astrocytoma in children. An unusual discrepancy between histological and clinical features. J Neurosurg 68:880–883
Conzen M, Oppel F (1990) Tuberous selerosis in neurosurgery. An analysis of 18 patients. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 106:106–109
Fujiwara S, Takaki T, Nishio S (1989) Subependymal giant-cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis. Do subependymal nodules grow? Child's Nerv Syst 5:43–44
Gomez MR (1988) Varietes of expression of tuberous sclerosis. Neurofibromatosis 1:330–338
Hahn JS, Bejar R, Gladson CL (1991) Neonatal subependymal giant cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous selerosis: MRI, CT, and ultrasound correlation. Neurology 41:124–128
Hirsch JF, Sainte-Rose C (1991) A new surgical approach to subcortical lesions: balloon inflation and cortical gluing. J Neurosurg 74:1014–1017
Jozwiak S (1992) Diagnostic value of clinical features and supplementary investigations in tuberous sclerosis in children. Acta Paediatr Hung 32:71–88
McLaurin RL, Towbin RB (1985–1986) Tuberous sclerosis: diagnostic and surgical considerations. Pediatr Neurosci 12:43–48
Menor F, Marti-Bonmati L, Mulas F, Poyatos C, Cortina H (1992) Neuroimaging in tuberous sclerosis: a clinicoradiological evaluation in pediatric patients. Pediatr Radiol 22:485–489
Morimoto K, Mogami H (1986) Sequential CT study of subependymal giant-cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis. J Neurosurg 65:874–877
Painter MJ, Pang D, Ahdab-Barmada M, Bergman I (1984) Connatal brain tumors in patients with tuberous sclerosis. Neurosurgery 14:570–573
Russell DS, Rubinstein LJ (1989) Pathology of tumors of the nervous system, 5th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 114–120
Schut I, Duhaime AC, Sutton LN (1989) Pflakomatoses: surgical considerations. In: American Association of Neurological Surgeons (eds) Pediatric neurosurgery: surgery of the developing nervous system. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 453–462
Shepherd CW, Gomez MR, Lie JT, Crowson CS (1991) Causes of death in patients with tuberous sclerosis. Mayo Clin Proc 66:792–796
Shitara N, Yoshida J, Kageyama N, Takakura K (1990) Clinical aspects of tuberous sclerosis and associated brain tumors. In: Ishibash Y, Hori Y (eds) Tuberous sclerosis and neurofibromatosis: epidemiology, pathophysiology, biology and management. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 323–330
Stefansson K (1991) Tuberous sclerosis (editorial) Mayo Clin Proc 66:868–872
Waga S, Yamamoto Y, Kojima T (1977) Massive hemorrhage in tumor of tuberous sclerosis. Surg Neurol 8:99–101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roszkowski, M., Drabik, K., Barszcz, S. et al. Surgical treatment of intraventricular tumors associated with tuberous sclerosis. Child's Nerv Syst 11, 335–339 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301665
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301665