Abstract
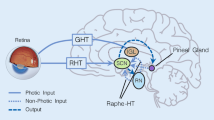
High affinity melatonin-binding sites have been described, by means of autoradiography with 2-125I-melatonin as the ligand, in more than 60 brain areas of about 20 mammalian species, with dramatic variations in the nature and number of labelled structures among the different species studied. As melatonin is involved in the synchronization of biological rhythms, we have tried to correlate the brain areas containing melatonin-binding sites with some rhythmic functions typical of give species. Therefore, we have studied the location of melatonin-binding sites in the complete brain of five long-day breeders with hibernation cycles, viz. one insectivore and four rodents. With the exception of the suprachiasmatic nuclei and the pars tuberalis of the pituitary, both of which contain binding sites in all five species, few reactive structures are common, even among species from the same family, e.g. the edible dormouse and the garden dormouse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong SM (1989) Melatonin and circadian control in mammals. Experientia 45:932–938
Bittman EL (1993) Melatonin binding sites in the central nervous system. Methods Neurosci 11:105–121
Bittman EL, Weaver DR (1990) The distribution of melatonin binding sites in neuroendocrine tissues of the ewe. Biol Reprod 43:986–993
Boissin-Agasse L, Barberis C, Audigier S, Roch G, Boissin J (1992) Localization of melatonin binding sites in the pars tuberalis of the mink at three times during the seasonal testicular cycle. Neurosci Lett 144:147–151
Bonnefond C, Mounerie R, Richard JP, Martinet L (1993) Melatonin and the circadian clock in mink. Effects of daily injections of melatonin on circadian rhythms of locomotor activity and autoradiographic localization of melatonin binding sites. J Neuroendocrinol 5:241–246
Brooks DS, Cassone VM (1992) Daily and circadian regulation of 2-(125I)iodomelatonin binding in chick brain. Endocrinology 131:1297–1304
Cassone VM (1991) Melatonin and suprachiasmatic nucleus function. In: Klein DC, Moore RY, Reppert SM (eds) Suprachiasmatic nucleus. The mind's clock. Oxford University Press, New York Oxford, pp 309–323
Cassone VM, Brooks DS (1991) Sites of melatonin action in the brain of the house sparrow, Passer domesticus. J Exp Zool 260:302–309
Cassone VM, Chesworth MJ, Armstrong S (1986a) Entrainment of rat circadian rhythms by daily injection of melatonin depends upon the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus. Physiol Behav 36:1111–1121
Cassone VM, Chesworth MJ, Armstrong SM (1986b) Dose-dependent entrainment of rat circadian rhythms by daily injection of melatonin. J Biol Rhythms 1:219–229
De Reviers MM, Ravault JP, Tillet Y, Pelletier J (1989) Melatonin binding sites in the pars tuberalis of the sheep. Neurosci Lett 100:89–93
De Reviers MM, Tillet Y, Pelletier J (1991) Melatonin binding sites in the brain of sheep exposed to light or pinealectomized. Neurosci Lett 121:17–20
Deveson S, Howarth JA, Arendt J, Forsyth JA (1992) In vitro autoradiographic localization of melatonin binding sites in the caprine brain. J Pineal Res 13:6–12
Devries MJ, Ferreira SA, Glass JD (1989) Evidence that short photoperiod-induced gonadal regression in the Mongolian gerbil is mediated by the action of melatonin in the medial hypothalamus. Brain Res 494:241–246
Duncan MJ, Mead RA (1992) Autoradiographic localization of binding sites for 2-[125]iodomelatonin in the pars tuberalis of the western spotted skunk (Spilogale putorius latifrons). Brain Res 569:152–155
Duncan MJ, Takahashi JS, Dubocovich ML (1989) Characteristics and autoradiographic localization of 2-[125]iodomelatonin binding sites in Djungarian hamster brain. Endocrinology 125:1011–1018
Duranti E, Stankov B, Spadoni G, Duranti A, Lucini V, Capsoni S, Biella G, Fraschini F (1992) 2-Bromomelatonin: synthesis and characterization of a potent melatonin agonist. Life Sci 51:479–485
Gauer F, Masson-Pévet M, Pévet P (1992 a) Effect of constant light, pinealectomy and guanosine triphosphate-gamma-S on the density of melatonin receptors in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus: a possible implication of melatonin action. J Neuroendocrinol 4:455–459
Gauer F, Masson-Pévet M, Pévet P (1992 b) Pinealectomy and constant illumination increase the density of melatonin binding sites in the pars tuberalis of rodents. Brain Res 575:32–38
Gauer F, Masson-Pévet M, Pévet P (1993 a) Melatonin receptor density is regulated in rat pars tuberalis and suprachiasmatic nuclei by melatonin itself. Brain Res 602:153–156
Gauer F, Masson-Pévet M, Pévet P (1993 b) Daily rhythms of melatonin binding sites in the rat pars tuberalis and suprachiasmatic nuclei; evidence for a regulation of melatonin receptors by melatonin itself. Neuroendocrinology 57:120–126
Gauer F, Masson-Pévet M, Saboureau M, George D, Pévet P (1993 c) Differential seasonal regulation of melatonin receptor density in the pars tuberalis and the suprachiasmatic nuclei: a study in the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus L.). J Neuroendocrinol 5:685–690
Goldman BD, Darrow JM (1983) The pineal gland and mammalian photoperiodism. Neuroendocrinology 37:386–396
Helliwell RJA, Williams LM (1992) Melatonin binding sites in the ovine brain and pituitary: characterization during the oestrous cycle. J Neuroendocrinol 4:287–294
Jennes L, Stumpf WE (1980) LHRH systems in the brain of the golden hamster. Cell Tissue Res 209:239–256
Karsch FJ, Bittman EI, Foster DL, Goodman RL, Legan SJ, Robinson JE (1984) Neuroendocrine basis of seasonal reproduction. Recent Prog Horm Res 40:185–232
Kirsch R, Belgnaoui S, Gourmelen S, Pévet P (1993) Free running Syrian and Siberian hamsters are entrained by daily infusions of melatonin. In: Wetterberg I (ed) Light and biological rhythms in man. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 107–120
Laitinen JT, Saavedra JM (1990) Characterization of melatonin receptors in the rat suprachiasmatic nuclei: modulation of affinity with cations and guanine nucleotides. Endocrinology 126:2110–2115
Laitinen JT, Flügge G, Saavedra JM (1990) Characterization of melatonin receptors in the rat area postrema: modulation of affinity with cations and guanine nucleotides. Neuroendocrinology 51:619–624
Lindroos OFC, Leinonen LM, Laasko ML (1992) Melatonin binding to the anteroventral and anterodorsal thalamic nuclei in the rat. Neurosci Lett 143:219–222
Martinoli MG, Williams LM, Kah O, Titchener LT, Pelletier G (1991) Distribution of central melatonin binding sites in the goldfish (Carassius auratus). Mol Cell Neurosci 2:78–85
Masson-Pévet M, George D, Gauer F, Pévet P (1993) Demonstration of melatonin binding sites in cyclohexylamine-formaldehyde-fixed brain tissue. Cell Tissue Res 274:207–209
Meijer JH, Rietveld WJ (1989) Neurophysiology of the suprachiasmatic circadian pacemaker in rodents. Physiol Rev 69:671–707
Morgan PJ, Williams LM, Davidson G, Lawson W, Howell HE (1989) Melatonin receptors on ovine pars tuberalis; characterization and autoradiographic localization. J Neuroendocrinol 1:1–4
Nakazawa K, Marubayashi U, McCann SM (1991) Mediation of the shortloop negative feedback of luteinizing release by melatonin-induced inhibition of LH release from the pars tuberalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 8:7576–7579
Nazarali AJ, Gutkind JS, Saavedra JM (1989) Calibration of 125I-polymer with 125I-brain paste standards for use in quantitative receptor autoradiography. J Neurosci Methods 30:247–253
Pelletier J, Castro B, Roblot G, Wylde R, De Reviers MM (1990) Characterization of melatonin receptors in the ram pars tuberalis: influence of light. Acta Endocrinol 123:557–562
Pévet P (1988) The role of the pineal gland in the photoperiodic control of reproduction in different hamster species. Reprod Nutr Dev 28:443–458
Ralph MR, Foster RG, Davis FC, Menaker M (1990) Transplanted suprachiasmatic nucleus determines circadian period. Science 247:975–978
Redman JR, Armstrong SM, Ng KT (1983) Free running activity rhythms in the rat entrainment by melatonin. Science 219:1089–1091
Reiter RJ (1991) Melatonin: that ubiquitously acting pineal hormone. News in Physiol Sci 6:223–227
Reppert SM, Weaver DR, Rivkees SA, Stopa EG (1988) Putative melatonin receptors in a human biological clock. Science 242:78–81
Rivkees SA, Cassone VM, Weaver DR (1989) Melatonin receptors in chick brain: characterization and localization. Endocrinology 125:363–368
Rollag MD, Niswender GD (1976) Radioimmunoassay of serum concentrations in sheep exposed to different lighting regimens. Endocrinology 98:482–489
Rusak B, Zucker I (1979) Neural regulation of circadian rhythms. Physiol Rev 59:449–526
Skene DJ, Masson-Pévet M, Pévet P (1992) Characterization of melatonin binding sites in the pars tuberalis of the European hamster. J Neuroendocrinol 4:189–192
Skene DJ, Masson-Pévet M, Pévet P (1993) Seasonal changes in melatonin binding sites in the pars tuberalis of male European hamsters and the effect of testosterone manipulation. Endocrinology 132:1682–1686
Stankov B, Fraschini F (1993) High affinity melatonin binding sites in the vertebrate brain. Neuroendocrinol Lett 15:149–164
Stankov B, Cozzi B, Lucini V, Capsoni S, Fauteck J, Fumagalli P, Fraschini F (1991 a) Localization and characterization of melatonin binding sites in the brain of the rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) by autoradiography and in vitro ligand-receptor binding. Neurosci Lett 133:68–72
Stankov B, Fraschini F, Reiter RJ (1991 b) Melatonin binding sites in the central nervous system. Brain Res Rev 16:245–256
Stankov B, Fraschini F, Reiter RJ (1993) The melatonin receptor: distribution, biochemistry, and pharmacology. In: Yu Hs, Reiter RJ (eds) Melatonin: biosynthesis, physiological effects, and clinical applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton Ann Arbor London, pp 155–186
Stankov B, Capsoni S, Lucini V, Fauteck J, Gatti S, Gridelli B, Biella G, Cozzi B, Fraschini F (1993) Autoradiographic localization of putative melatonin receptors in the brain of two old world primates: Cercopithecus aethiops and Papio ursinus. Neuroscience 52:459–468
Stanton TL, Siuciak JA, Dubocovich ML, Krause DN (1991) The area of 2-125I-melatonin binding in the pars tuberalis of the ground squirrel is decreasing during hibernation. Brain Res 557:285–288
Stehle J (1990) Melatonin binding sites in brain of the 2-day-old chicken: an autoradiographic localization. J Neural Transm 81:83–89
Stehle J, Vanecek J, Vollrath L (1989) Effects of melatonin on spontaneous electrical activity of neurons in rat suprachiasmatic nuclei: an in vitro iontophoretic study. J Neural Transm 78:173–177
Tamarkin L, Baird CJ, Almeida OFX (1985) Melatonin: a coordinating signal for mammalian reproduction Science 227:714–720
Vakkuri O, Leppaluoto J, Vuolteenaho C (1984) Development and validation of a melatonin radioimmunoassay using radioiodinated melatonin as tracer. Acta Endocrinol 106:152–157
Vanecek J, Jansky L (1989) Short days induce changes in specific melatonin binding in hamster median eminence and anterior pituitary. Brain Res 477:387–390
Vanecek J, Pavlik A, Illnerova H (1987) Hypothalamic melatonin receptor sites revealed by autoradiography. Brain Res 435:359–362
Weaver DR, Reppert SM (1990) Melatonin receptors are present in the ferret pars tuberalis and pars distalis, but not in the brain. Endocrinology 127:2607–2609
Weaver DR, Rivkees SA, Reppert SM (1989) Localization and characterization of melatonin receptor in rodent brain by in vitro autoradiography. J Neurosci 9:2581–2590
Weaver DR, Carlson LL, Reppert SM (1990) Melatonin receptors and signal transduction in melatonin-sensitive and melatonininsensitive populations of white-footed mice (Peromyscus leucopus). Brain Res 506:353–357
Weaver DR, Rivkees SA, Carlson LL, Reppert SM (1991) Localization of melatonin receptors in mammalian brain. In: Klein DC, Moore RY, Reppert SM (eds) Suprachiasmatic nucleus. The mind's clock. Oxford University Press, New York Oxford, pp 289–308
Weaver DR, Stehle JH, Stopa EG, Reppert SM (1993) Melatonin receptors in human hypothalamus and pituitary. Implications for circadian and reproductive responses to melatonin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 76:295–301
Wiechmann AF, Wirsig-Wiechmann CR (1992) Asymmetric distribution of melatonin receptors in the brain of the lizard Anolis carolinensis. Brain Res 593:281–286
Wiechmann AF, Wirsig-Wiechmann CR (1993) Distribution of melatonin receptors in the brain of the frog Rana pipiens as revealed by in vitro autoradiography. Neuroscience 52:459–468
Williams LM (1989) Melatonin binding sites in the rat brain and pituitary mapped by in vitro autoradiography. J Mol Endocrinol 3:71–75
Williams LM, Morgan PJ (1988) Demonstration of melatonin-binding sites on the pars tuberalis of the rat. J Endocrinol 119:R1-R3
Williams LM, Morgan PJ, Hastings MH, Lawson W, Davidson G, Howell HE (1989) Melatonin receptor sites in the Syrian hamster brain and pituitary. Localization and characterization using [125]iodomelatonin. J Neuroendocrinol 1:315–320
Yous S, Andrieux J, Howell HE, Morgan PJ, Renard P, Pfeiffer B, Lesieur D, Guardiola-Lemaître B (1992) Novel naphthalencic ligands with high affinity for the melatonin receptor. J Med Chem 35:1484–1486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masson-Pévet, M., George, D., Kalsbeek, A. et al. An attempt to correlate brain areas containing melatonin-binding sites with rhythmic functions: a study in five hibernator species. Cell Tissue Res 278, 97–106 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305781
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305781