Summary
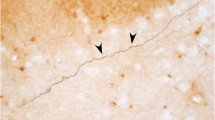
The interconnections between the amygdala and the hippocampal formation were investigated in the macaque monkey using anterograde tracers. The hippocampal inputs to the amygdala arose from the subicular and entorhinal cortices and passed through the angular bundle to terminate principally in the medial basal and lateral basal nuclei, with lighter termination in the lateral nucleus, the periamygdaloid cortex, and the cortical-transition area. The majority of these amygdaloid inputs arose from the rostral hippocampal formation although there was equivocal evidence of an additional projection from the caudal hippocampus to the central nucleus. Projections arose from many of the amygdaloid nuclei to terminate in the molecular layer of the amygdalo-hippocampal area and the adjacent stratum moleculare of the uncal portion of the hippocampus. The accessory basal, lateral basal, and medial basal nuclei also projected to the most rostral portions of the stratum moleculare of fields CA1–3, the heaviest termination occurring in field CA3. Additional projections from the basal nuclei terminated in the prosubiculum, presubiculum, and para-subiculum. The heaviest entorhinal inputs arose from the accessory basal and lateral nuclei and terminated in layers I, II, and III of areas 28b, 28i, and the prorhinal cortex. The major amygdaloid input to the perirhinal cortex arose from the lateral basal nucleus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adey WR, Meyer M (1952) Hippocampal and hypothalamic connexions of the temporal lobe of the monkey. Brain 75: 358–384
Aggleton JP, Burton MJ, Passingham RE (1980) Cortical and subcortical afferents to the amygdala of the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Brain Res 190: 347–368
Aggleton JP, Desimone R, Mishkin M (1986) The origin, course, and termination of the hippocampo-thalamic projections in the macaque. J Comp Neurol 243: 409–422
Aggleton JP, Mishkin M (1984) Projections of the amygdala to the thalamus in the cynomolgus monkey. J Comp Neurol 222: 56–68
Aggleton JP, Mishkin M (1985) Mamillary-body lesions and visual recognition in monkeys. Exp Brain Res 58: 190–197
Amaral DG, Cowan WM (1980) Subcortical afferents to the hippocampal formation in the monkey. J Comp Neurol 189: 573–591
Amaral DG, Veazey RB, Cowan WM (1982) Some observations on hypothalamo-amygdaloid connections in the monkey. Brain Res 252: 13–27
Bakst I, Amaral DG (1984) The distribution of acetylcholinesterase in the hippocampal formation of the monkey. J Comp Neurol 225: 344–372
Brierley JB (1977) Neuropathology of amnesic states. In: Whitty CWM, Zangwill OL (eds) Amnesia. Butterworths, London, pp 199–223
Brodman K (1909) Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Großhirnrinde in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund des Zellenbaues. Barth, Leipzig, pp 1–324
Crosby EC, Humphrey T (1941) Studies of the vertebrate telencephalon. II. The nuclear pattern of the anterior olfactory nucleus, tuberculum olfactorium and the amygdaloid complex in adult man. J Comp Neurol 74: 309–352
Hilpert P (1928) Der Mandelkern des Menschen. I. Cytoarchitektonik und Faserverbindungen. J Psychol Neurol 36: 44–74
Jimenez-Castellanos J (1949) The amygdaloid complex in the monkey studied by reconstructional methods. J Comp Neurol 91: 507–526
Johnston JB (1923) Further contributions to the study of the evolution of the forebrain. J Comp Neurol 35: 337–481
Krettek JE, Price JL (1977) Projections from the amygdaloid complex and adjacent olfactory structures to the entorhinal cortex and to the subiculum in the rat and cat. J Comp Neurol 172: 723–752
Lorente de Nó R (1934) Studies on the structure of the cerebral cortex. II. Continuation of the study of the ammonic system. J Psychol Neurol 46: 113–177
Mehler WR (1980) Subcortical afferent connections of the amygdala in the monkey. J Comp Neurol 190: 733–762
Mishkin M (1982) A memory system in the monkey. Philos Trans R Soc B298: 85–95
Morrison F, Poletti CE (1980) Hippocampal influence on amygdala unit activity in awake squirrel monkeys. Brain Res 192: 353–369
Murray EA, Mishkin M (1986) Visual recognition in monkeys following rhinal cortical ablations combined with either amygdalectomy or hippocampectomy. J Neurosci (in press)
Nauta WJM (1961) Fibre degeneration following lesions of the amygdaloid complex in the monkey. J Anat (Lond) 95: 515–530
Ottersen OP (1982) Connections of the amygdala in the rat. IV. Corticoamygdaloid and intramygdaloid connections as studied with axonal transport of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol 205: 30–48
Poletti CE, Creswell G (1977) Fornix system efferent projections in the squirrel monkey: an experimental degeneration study. J Comp Neurol 175: 101–128
Poletti CE, Sujatanond M (1980) Evidence for a second hippocampal efferent pathway to hypothalamus and basal forebrain comparable to fornix system: a unit study in the awake monkey. J Neurophysiol 44: 514–531
Rosene DL, Van Hoesen GW (1977) Hippocampal efferents reach widespread areas of cerebral cortex and amygdala in the rhesus monkey. Science 198: 315–317
Russchen FT (1982) Amygdalopetal projections in the cat. I. Cortical afferent connections. A study with retrograde and anterograde tracing techniques. J Comp Neurol 206: 159–179
Sarter M, Markowitsch HJ (1985) The amygdala's role in human mnemonic processing. Cortex 21: 7–24
Saunders RC, Rosene D (1986) A comparison of the amygdala and the hippocampal formation in the rhesus monkey. I. Convergence in the entorhinal, prorhinal and perirhinal cortices. J Comp Neurol (in press)
Valenstein ES, Nauta WJH (1957) A comparison of the distribution of the fornix system in the rat, guinea pig, cat and monkey. J Comp Neurol 113: 337–363
Van Hoesen GW, Pandya DN (1975) Some connections of the entorhinal (area 28) and perirhinal cortices of the rhesus monkey. III. Efferent connections. Brain Res 95: 39–59
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aggleton, J.P. A description of the amygdalo-hippocampal interconnections in the macaque monkey. Exp Brain Res 64, 515–526 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340489
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00340489