Abstract
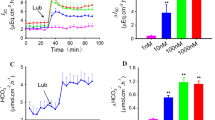
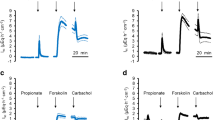
To further evaluate the mechanisms of oxalate (Ox2−) transport in the intestine the following studies were performed using isolated, short-circuited segments of the rabbit distal colon (DC). In control buffer, the DC absorbed Ox2− (net Ox2− flux, J OxNet =5.4±0.7 pmol · cm−2 · h−1). Replacement of Na+ with N-methyl-d-glucamine (NMDG+) abolished Ox2− absorption by decreasing mucosal to serosal Ox2− flux (J Oxms ), without affecting Cl− transport, while gluconate substitution for Cl− did not affect J OxNet or net Na+ flux (J NaNet ). Addition of Na+ to the serosal side of tissues bathed by NMDG+ buffer increased J Oxms 40% without altering mucosal to serosal Cl− flux (J Clms ). Serosal amiloride or dimethyl amiloride (10−3 M) abolished J OxNet by decreasing J Oxms , it increased serosal to muscosal Cl− flux (J Clsm ) and it gradually inhibited short-circuit current (I sc). Mucosal amiloride (10−4 M) abolished I sc but had no effect on Ox2− or Cl− fluxes. Serosal 4,4′-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid (DIDS, 10−6 M) reduced J Oxms by 20% and J OxNet by 43% without affecting J Clms or J ClNet . Dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate (dB-cAMP, 5×10−4 M, both sides) stimulated Ox2− secretion (J OxNet = −12.6±3.3 pmol · cm−2 · h−1). The dB-cAMP-induced secretion of Ox2− and Cl− were fully abolished by serosal furosemide (10−4 M) and partially inhibited (35%) by 5×10−4 M mucosal NPPB [5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)-benzoic acid], a putative Cl− channel blocker. It is proposed that: (1) basal absorption of Ox2−, but not Cl−, is dependent upon a previously undescribed basolateral Na+-H+ exchanger that may be coupled to a DIDS-sensitive, basolateral anion exchange system that mediates Ox2− flux; (2) the DC secretes Ox2− in response to dB-cAMP by a mechanism that is indistinguishable from the pathway for Cl− secretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benos DJ (1982) Amiloride: a molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells. Am J Physiol 242:C131-C145
Binder HJ (1974) Intestinal oxalate absorption. Gastroenterology 67:441–446
Bridges RJ, Worrell RT, Frizzel RA, Benos DJ (1989) Stilbene disulfonate blockade of colonic secretory Cl− channels in planar lipid bilayers. Am J Physiol 256:C902-C912
Diener M, Rummel W (1989) Actions of the Cl− channel blocker NPPB on absorptive and secretory transport processes of Na+ and Cl− in rat descending colon. Acta Physiol Scand 137:215–222
Dobbins JW, Binder HJ (1977) Importance of the colon in enteric hyperoxaluria. N Engl J Med 296:298–301
Dreinhofer J, Gogelein H, Greger R (1988) Blocking kinetics of Cl− channels in colonic carcinoma cells (HT29) as revealed by 5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)benzoic acid (NNPB). Biochim Biophys Acta 946:135–142
Dudeja PK, Foster ES, Brasitus TA (1989) Na+-H+ antiporter of rat colonic basolateral membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol 257:G624-G632
Earnest DL (1974) Enteric hyperoxaluria. Adv Intern Med 24:407–427
Finlayson B (1977) In: David DS (ed) Calcium metabolism in renal failure and nephrolithiasis. Wiley, New York, pp 354–357
Freel RW (1987) Dihydroxy bile salt-induced secretion of rubidium ion across the rabbit distal colon. Am J Physiol 252:G554-G561
Freel RW, Hatch M, Earnest DL, Goldner AM (1980) Oxalate transport across the isolated rat colon. A re-examination. Biochim Biophys Acta 600:838–843
Frizzel RA, Koch MJ, Schultz SG (1976) Ion transport by rabbit colon. I. Active and passive components. J Membr Biol 27:297–316
Halm DR, Frizzell RA (1986) Active K transport across rabbit distal colon: relation to Na absorption and Cl secretion. Am J Physiol 251:C252-C267
Hatch M, Vaziri ND (1991) Segmental differences in intestinal oxalate transport. FASEB J 5:A1138
Hatch M, Freel RW, Goldner AM, Earnest DL (1984) Oxalate and chloride absorption by the rabbit colon: sensitivity to metabolic and anion transport inhibitors. Gut 25:232–237
Heintze K, Stewart CP, Frizzell RA (1983) Sodium-dependent chloride secretion across rabbit descending colon. Am J Physiol 244:G357-G365
Keeling DJ, Taylor AG, Smith PL (1991) Effects of NPPB [5-nitro-2-(3-phenylpropylamino)benzoic acid] on chloride transport in intestinal tissues and the T84 cell line. Biochim Biophys Acta 1115:42–48
Kleyman R, Cragoe EJ (1990) Cation transport probes: the amiloride series. Methods Enzymol 191:739–755
Knickelbein RG, Dobbins JW (1990) Sulfate and oxalate exchange for bicarbonate across the basolateral membrane of rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol 259:G807-G813
Knickelbein RG, Aronson PS, Dobbins JW (1986) Oxalate transport by anion exchange across rabbit ileal brush border. J Clin Invest 77:170–175
McCabe RD, Smith PL (1985) Colonic potassium and chloride secretion: role of cAMP and calcium. Am J Physiol 248:G103-G109
O'Grady SM, Palfrey HC, Field M (1987) Characteristics and functions of Na-K-Cl cotransport in epithelial tissues. Am J Physiol 253:C177-C192
Rajendran V, Binder HJ (1993) Cl-HCO3 and Cl-OH exchanges mediate Cl uptake in apical membrane vesicles of rat distal colon. Am J Physiol 264:G874-G879
Rajendran VM, Oesterlin M, Binder HJ (1991) Sodium uptake across basolateral membrane of rat distal colon. Evidence for Na-H exchange and Na-anion cotransport. J Clin Invest 88:1379–1385
Reinach PS, Schoen HF (1990) NPPB inhibits the basolateral membrane K+ conductance in the isolated bullfrog cornea. Biochim Biophys Acta 1026:13–20
Seifter JL, Aronson PS (1986) Properties and physiologic roles of the plasma membrane sodium-hydrogen exchanger. J Clin Invest 78:859–864
Singh AK, Afink GB, Venglarik CJ, Wang RP, Bridges RJ (1991) Colonic Cl channel blockade by three classes of compounds. Am J Physiol 261:C51-C63
Smith PL, Sullivan SK, McCabe RD (1986) Concentration-dependent effects of disulfonic stilbenes on colonic chloride transport. Am J Physiol 250:G44-G49
Warnock DG, Pollack AS (1988) Na+/H+ exchange in epithelial cells. In: Grinstein S (ed) Na+/H+ exchange. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 77–90
Welsh MJ, Smith PL, Fromm M, Frizzell RA (1982) Crypts are the site of intestinal water and electrolyte secretion. Science 218:1219–1221
Wiener H, van Os C (1989) Rabbit distal colon epithelium. II. Characterization of (Na+,K+,Cl−)-cotransport and [3]H]-bumetanide binding. J Membr Biol 110:163–174
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatch, M., Freel, R.W. & Vaziri, N.D. Mechanisms of oxalate absorption and secretion across the rabbit distal colon. Pflugers Arch. 426, 101–109 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374677
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374677