Summary
The thermoregulatory responses to 1 h exercise of 14 male (age range 18–65 year) and 7 female (age range 18–46 year) athletes and 4 (3♂ and 1 ♀) non-athletic subjects have been investigated in a moderate environment (T db=21‡ C, T wb=15‡ C and rh<50%) and analysed in relation to age, sex, and maximum aerobic power output (VO2 max).
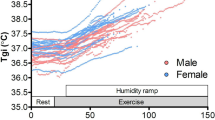
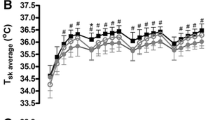
The maximal sweat loss (M sw max) under the given conditions was closely related (r=+0.90) to VO2 max and for a given relative work load (%VO2 max), rectal (T re) and mean skin (¯T sk) temperatures was the same in all subjects.
Sweat loss (004d sw) was linearly related to total heat production (H) and to peripheral tissue heat conductance (K) and if expressed in relative terms (%M sw max) was linearly related to T re. For a given T re relative sweat rate was identical in the groups studied. From these results it would seem that during exercise T re rises to meet the requirements of heat dissipation by establishing a thermal gradient from core to skin and stimulating sweating in proportion to maximal capacity of the system. Thus provided the thermal responses to work were standardised using the appropriate physiological variables, there was no evidence to be found for differences in thermoregulatory function which could be ascribed to sex or age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
åstrand, I.: Aerobic work capacity in men and women with special reference to age. Acta Physiol. Scand. [Suppl.] 169 (1960)
Bittel, J., Henane, R.: Comparison of thermal exchanges in men and women under neutral and hot conditions. J. Physiol. 250, 475–489 (1975)
Brouha, L., Smith, P. E., De Lanne, R., Maxfield, M. E.: Physiological reactions of men and women during muscular activity and recovery in various environments. J. Appl. Physiol. 16, 133–140 (1960)
Collins, K. J., Crockford, G. W., Weiner, J. S.: The local training effect of secretory activity on the response of eccrine sweat glands. J. Physiol. 184, 203–214 (1966)
Davies, C. T. M.: Limitations to the prediction of maximum oxygen intake from cardiac frequency measurements. J. Appl. Physiol. 24, 700–706 (1968)
Davies, C. T. M.: The influence of skin temperature on sweat regulation and aerobic performance during severe work. J. Appl. Physiol. (in press) (1979)
Davies, C. T. M., Brotherhood, J., ZeidiFard, E.: Temperature regulation during severe exercise with some observations on effects of skin wetting. J. Appl. Physiol. 41, 772–776 (1976)
Dill, C. B., Yousef, K., Nelson, J. D.: Reponses of men and women to two-hour walks in desert heat. J. Appl. Physiol. 35, 231–235 (1973)
Drinkwater, B. L., Denton, J. E., Kupprat, I. C., Talag, T. S., Horvath, S. M.: Aerobic power as a factor in women's response to work in hot environments. J. Appl. Physiol. 41, 815–821 (1976)
Ellis, F. P., Exton-Smith, A. N., Foster, K. G., Weiner, J. S.: Eccrine sweating and mortality during heat waves in very young and very old persons. Isr. J. Med. Sci. 12, 815–817 (1976)
Fox, R. H., Lofstedt, B. E., Woodward, Patricia, M., Eriksson, E., Wekstrom, B.: Comparison of thermoregulatory function on men and women. J. Appl. Physiol. 26, 444–463 (1969)
Hardy, J. D., Dubois, E. F.: The technique of measuring radiation and convection. J. Nutr. 15, 461–475 (1938)
Haslag, W. M., Hertzman, A. B.: Temperature regulation in young women. J. Appl. Physiol. 20, 1283–1288 (1965)
Hertig, B. A., Belding, H. S., Kraning, K. K., Batterton, D. L., Smith, C. R., Sargent, F.: Artifical acclimatization of women to heart. J. Appl. Physiol. 18, 383–386 (1963)
Kerslake, D. McK.: The stress of hot environments. Monographs of the physiological society, No. 29, New York: Cambridge University Press 1972
Nielsen, B.: Thermoregulation at rest and exercise. Acta Physiol. Scand. [Suppl.] 323 (1969)
Piwonka, R. W., Robinson, S.: Acclimatization of highly trained men to work in severe heat. J. Appl. Physiol. 22, 9–12 (1967)
Robinson, R.: Experimental studies of physical fitness in relation to age. Arbeitsphysiologie 10, 251 (1938)
Rowell, L. B.: Human cardiovascular adjustments to exercise and thermal stress. Physiol. Rev. 54, 75–159 (1974)
Saltin, B., Hermanson, L.: Eosophageal, rectal and muscle temperature during exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 21, 1757–1762 (1966)
Weinman, K. P., Slabochova, Z., Bernauer, E. M., Morimoto, T., Sargent, F.: Reactions of men and women to repeated exposure to humid heat. J. Appl. Physiol. 22, 533–538 (1967)
Wyndham, C.: Role of skin and core temperature in man's temperature regulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 20, 31–36 (1965)
Wyndham, C. H., Morrison, J. F., Williams, C. G.: Heat reactions of male and female Caucasians. J. Appl. Physiol. 20, 357–364 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davies, C.T.M. Thermoregulation during exercise in relation to sex and age. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 42, 71–79 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421907
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421907