Summary
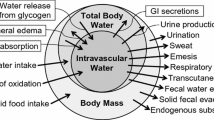
Plasma volume (PV), blood-borne substrate, and electrolyte responses to a warm weather (WBGT 15.5–24.5‡ C) marathon race were observed in four male and two female runners averaging 48 years of age. Additionally, continuous recordings were made of heart rate (HR) in three, and of rectal temperature (Tre) in two of the men. The race was finished by three of the men, with an average time of 3.61 h, a running pace estimated to require from 60–66% of the runner's \(\dot V_{O_2 }\) max. Near steady state levels for HR and Tre, ranging from 140–165 beats·min−1 and from 38.5–39.3‡ C, respectively, were reached early in the race. Total and percentage weight losses for the finishers were 2.52 kg and 3.9%, 2.18 kg and 3.4%, 4.77 kg and 6.7%, respectively; corresponding reductions in PV for these runners were 5.4%, 13.2%, and 27.4%. Pre-race control and immediate post-race serum glucose concentrations averaged 109 and 154 mg·dl−1 respectively. Final blood lactate values ranged from 11–42 mg·dl−1. Thus, it may be concluded that middle-aged runners who were successful in completing the marathon in a warm environment did so while maintaining steady state levels of HR and Tre. Although only water was ingested during the race, serum glucose for the finishing runners remained above, while serum [Na+] and [Cl−] remained within ±8% of, control values throughout the run. Complete data obtained from only one of the runners suggest that the initial exercise-induced reduction in PV is not augmented by subsequent cumulative dehydration provided water intake during the race is sufficient to limit weight loss to <4%.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altman PL (1961) Blood and other fluids. Biological handbooks. Fed Am Soc Exp Biol Washington DC, pp 200–201
Best CH, Partridge RC (1929) Observations on Olympic athletes. Proc R Soc B 105: 323–332
Costill DL (1970) Metabolic responses during distance running. J Appl Physiol 28: 251–255
Costill DL (1972) Physiology of marathon running. JAMA 221: 1024–1029
Costill DL, Fox EL (1969) Energetics of marathon running. Med Sci Sports 1: 81–86
Costill DL, Kammer WF, Fisher A (1970) Fluid ingestion during distance running. Arch Environ Health 21: 520–525
Costill DL, Fink WJ (1974) Plasma volume changes following exercise and thermal dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37: 521–525
Dancaster CP, Wherat SJ (1971) Fluid and electrolyte balance during the comrades marathon. S Afr Med J 45: 147–150
Dill DB (1965) Marathoner De Mar: physiological studies. J Natl Cancer Inst 35: 185–191
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volume of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37: 247–248
Gordon B, Kohn LA, Levine SA, Matton M, Scriver WM, Whiting WB (1925) Sugar content of the blood in runners following a marathon race. JAMA 85: 508–509
Hultman E, Nilsson LH (1971) Liver glycogen in man. Effect of different diets and muscular exercise. In: Pernow B, Saltin B (eds) Muscle metabolism during exercise. Plenum Press, New York, pp 143–151
Issekutz B Jr, Issekutz AC, Nash D (1970) Mobilization of energy sources in exercising dogs. J Appl Physiol 29: 691–697
Lavine SA, Gordon B, Derick CL (1924) Some changes in the chemical constituents of the blood following a marathon race. JAMA 82: 1778–1779
Magazanik A, Shapiro Y, Meytes D, Meytes I (1974) Enzyme blood levels and water balance during a marathon race. J Appl Physiol 36: 214–217
Margaria R, Cerretelli P, Aghema P, Sassi G (1963) Energy cost of running. J Appl Physiol 18: 367–370
Maron MB, Horvath SM, Wilkerson JE (1975) Acute blood biochemical alterations in response to marathon running. Eur J Appl Physiol 34: 173–182
Maron MB, Horvath SM, Wilkerson JE (1977) Blood biochemical alterations during recovery from competitive marathon running. Eur J Appl Physiol 36: 231–238
Maron MB, Horvath SM, Wilkerson JB, Gliner JA (1976) Oxygen uptake measurements during competitive marathon running. J Appl Physiol 40: 836–838
Myhre LG, Robinson S (1969) Immediate and delayed efforts of acute dehydration on plasma volume in man. Physiologist 12: 310
Olsson K-E, Saltin B (1970) Variation in total body water with muscle glycogen changes in man. Acta Physiol Scand 80: 11–18
Puckett HL, Wiley FH (1932) The relation of glycogen to water storage in the liver. J Biol Chem 96: 367–371
Pugh LGCE, Corbett J, Johnson RH (1967) Rectal temperatures, weight losses, and sweat rates in marathon running. J Appl Physiol 23: 347–352
Rowell LG, Kraning KK, Evans TO, Kennedy JW, Blackman JR, Kusumi F (1966) Splanchnic removal of lactate and pyruvate during prolonged exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 21: 1773–1783
Senay LC, Jr, Rogers G, Jooste P (1980) Changes in blood plasma during progressive treadmill and cycle exercise. J Appl Physiol: Respirat Environ Exercise Physiol 49: 59–65
Skinner NS, Jr, Costin JC, Saltin B, Vestagh G (1971) Glucose uptake in contracting isolated in situ dog skeletal muscle. In: Pernow B, Saltin B (eds) Muscle metabolism during exercise. Plenum Press, New York, pp 289–299
Wahren J (1977) Glucose turnover during exercise in man. Ann NY Acad Sci 301: 44–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Myhre, L.G., Hartung, G.H. & Tucker, D.M. Plasma volume and blood metabolites in middle-aged runners during a warm-weather marathon. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 48, 227–240 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422984
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422984