Abstract
Orthostatic hypotension, the clinically most important side effect in treatment with tricyclic antidepressants, was investigated in a double-blind study with clomipramine and the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram given for 5 weeks. All patients were initially given placebo for 1 week.
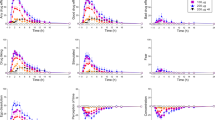
In the clomipramine group (n=17) a significant orthostatic drop in the systolic blood pressure was observed during treatment; this remained significant over the whole investigational period. A curvilinear correlation was demonstrated between the orthostatic drop in systolic blood pressure and the plasma levels of clomipramine and desmethylclomipramine. The most pronounced orthostatic reaction was thus seen in 1–2 weeks, at plasma levels of 25–75 μg/l (clomipramine). The correlation between the subjective symptoms and the measured orthostatic drop was poor, as was the correlation between the subjective symptoms and the plasma levels of the two active compounds. The change in orthostatic heart rate during clomipramine treatment was insignificant.
In the citalopram group (n=15) no significant changes in orthostatic blood pressure or heart rate were demonstrated during treatment and these patients had no orthostatic complaints.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åsberg M, Cronholm B, Sjöqvist F, Tuck D (1970) Correlation of subjective side effects with plasma concentrations of nortriptyline. Br Med J 4:18–21
Christensen P, Thomsen HY, Pedersen OL, Thayssen P, Oxhøj H, Kragh-Sørensen P, Gram LF. Cardiovascular effects of amitriptyline in the treatment of elderly depressed patients. Psychopharmacology in press
Fennimore DC, Meyer CJ, Davis CM, Hsu F, Zlatkis A (1977) High-performance thin-layer chromatographic determination of psychopharmacologic agents in blood serum. J Chromatogr 142:399–409
Glassman AH, Bigger JT, Giardina EV, Kantor SJ, Perel JM, Davies M (1979) Clinical characteristics of imipramine-induced orthostatic hypotension. Lancet I:468–472
Gurney C, Roth M, Garside RF, Kerr TA, Schapira K (1972) Studies in the classification of affective disorders. The relationship between anxiety states and depressive illnesses. J Psychiatr 121:162–166
Hall H, Ogren S-O (1981) Effects of antidepressant drugs on different receptors in the brain. Eur J Pharmacol 70:393–407
Hamilton M (1967) Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. J Soc Clin Psychol 6:278–296
Hayes JR, Born GF, Rosenbaum AH (1977) Incidence of orthostatic hypotension in patients with primary affective disorders treated with tricyclic antidepressants. Mayo Clin Proc 52:509–512
Hyttel J (1982) Citalopram-pharmacological profile of a specific serotonin uptake inhibitor with antidepressant activity. Progr Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 6:277–295
Kantor SJ, Glassman AH, Bigger JT, Perel JM, Giardina EV (1978) The cardiac effects of therapeutic plasma concentrations of imipramine. Am J Psychiatr 135:534–538
Møller M, Thayssen P, Kragh-Sørensen P, Pedersen OL, Kristensen CB, Bjerre M, Benjaminsen S, Gram LF (1983) Mianserin: Cardiovascular effects in elderly patients. Psychopharmacology 80:174–177
Nagy A, Treiber L (1973) Quantitative determination of imipramine and desipramine in human blood by direct densiometry of thin-layer chromatograms. J Pharm Pharmacol 25:599–603
Nielsen JR, Johansen T, Arentoft A, Gram LF (1983) Effects of imipramine on the orthostatic changes in blood pressure, heart rate and catecholamines. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 10:497–504
Tang SW, Seeman P (1980) Effect of antidepressant drugs on serotonergic and adrenergic receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 311:255–261
Thayssen P, Bjerre M, Kragh-Sørensen P, Møller M, Pedersen OL, Kristensen CB, Gram LF (1981) Cardiovascular effects of imipramine and nortriptyline in elderly patients. Psychopharmacology 74:360–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christensen, P., Thomsen, H.Y., Pedersen, O.L. et al. Orthostatic side effects of clomipramine and citalopram during treatment for depression. Psychopharmacology 86, 383–385 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427895
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00427895