Summary
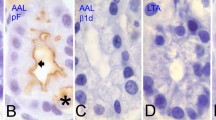
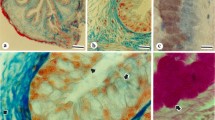
Glycoconjugates associated with the basal cell layer of various types of epithelia in the mouse and rat were examined histochemically with a battery of lectinhorseradish peroxidase (HRP) conjugates of differing sugar binding specificities. Basal cells in paraffin sections of composite tissue blocks stained with an isolectin from Griffonia simplicifolia (GSA I-B4) specific for terminal α-galactose residues but failed to react with the other lectins. Basal cells in epithelium lining striated and excretory ducts of salivary and lacrimal glands, tongue, esophagus, trachea, renal calyx, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, epididymis and vas deferens stained selectively and intensely for content of a glycoconjugate with terminal α-galactose. This galactoconjugate appeared associated with the plasmalemma of basal cells. Basal cells with a galactocalyx formed an intermittent to continuous layer generally increasing in prevalence distally in glandular duct systems. A minor population of pyramido-columnar cells with cytosolic GSA I-B4 reactivity occurred in striated ducts and appeared less numerous in intralobular excretory ducts and more prevalent in extraglandular ducts. In trachea and renal pelvis, the GSA I-B4 positive cell profiles ranged from low cuboidal to tall pyramidal in contour, but the latter appeared not to reach the lumen. In contrast, no GSA I-B4 positive basal cells were seen in any segment of the pancreatic or bile ducts or in the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract. These findings suggest that the basal cells found in similar sites in different epithelia and possessing in common a unique α-galactoconjugate may function in a manner common to all and not simply in providing progenitor cells for epithelial renewal. The location and distribution of GSA I-B4 reactive basal cells in diverse epithelia suggests that through their α-galactocalyx they serve in maintaining the established composition of luminal fluid perhaps by impeding the transepithelial movement of fluid and ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avrameas S (1969) Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry 6:43–52
Brabec RK, Peters BP, Bernstein IA, Gray RH, Goldstein IJ (1980) Differential lectin binding to cellular membranes in the epidermis of the newborn rat. Cell Biol 77:477–479
Burkett BN, Schulte BA, Spicer SS (1986) Histochemical evaluation of glycoconjugates in the male reproductive tract with lectin-horseradish peroxidase conjugates. I. Staining of principal cells and spermatozoa in the mouse. Am J Anat (in press)
Elias PM, Friend DS (1975) The permeability barrier in mammalian epidermis. J Cell Biol 65:180–191
Elias PM, McNutt NS, Friend DS (1977) Membrane alterations during cornification of mammalian squamous epithelia: a freeze-fracture, tracer, and thin-section study. Anat Rec 189:577–594
Hennigar RA, Schulte BA, Spicer SS (1985) Heterogeneous distribution of glycoconjugates in human kidney tubule. Anat Rec 211:376–390
Martinez-Palomo A, Erlij D, Bracho H (1971) Localization of permeability barriers in the frog skin epithelium. J Cell Biol 50:277–287
Nemanic MJ, Elias PM (1980) Skin barrier functions: do glycosidases play a role? J Cell Biol 87:20a (Abs 135)
Rehfield SJ, Lampe MA, Elias P (1980) Novel physiologic thermal transition due to lipids in mammalian keratinizing epithelium. J Cell Biol 87:20a (Abs 134)
Schulte BA, Spicer SS (1983a) Light microscopic detection of sugar residues in glycoconjugates of salivary glands and the pancreas with lectin-horseradish peroxidase conjugates. I. Mouse. Histochem J 15:1217–1238
Schulte BA, Spicer SS (1983b) Histochemical evaluation of mouse and rat kidneys with lectin-horseradish peroxidase conjugates. Am J Anat 168:345–362
Spicer SS, Warren L (1960) The histochemistry of sialic acid containing mucoproteins. J Histochem Cytochem 8:135–137
Stoward PJ, Spicer SS, Miller RL (1980) Histochemical reactivity of peanut lectin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate. J Histochem Cytochem 28:979–990
Virtanen I, Kariniemi AL, Holthofer H, Lehto VP (1985) Fluorochrome-coupled lectins reveal distinct cellular domains in human epidermis. J Histochem Cytochem 32:908 (Abs)
Yeh K-Y, Moog F (1984) Biosynthesis and transport of glycoproteins in the small intestinal epithelium of rats. Dev Biol 101:446–462
Zieske JD, Bernstein IA (1982) Modifiction of cell surface glycoprotein: addition of fucosyl residues during epidermal differentiation. J Cell Biol 95:626–631
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
In honour of Prof. P. van Duijn
This research was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants HL-29775 and AM-10956
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Flint, F.F., Schulte, B.A. & Spicer, S.S. Glycoconjugate with terminal α galactose. Histochemistry 84, 387–395 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00482968
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00482968