Summary
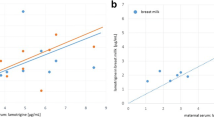
Diazepam plasma binding was determined in 17 matched pairs of maternal and foetal plasma, collected at delivery. Diazepam % free was higher (p<0.001) in maternal (mean 3.24%) than in either umbilical venous (mean 1.50%) or umbilical arterial (mean 1.24%) plasma. The data from in vitro dialysis studies were consistent with the reported higher diazepam concentrations in infants than in mothers at delivery. Plasma nonesterified fatty acids (NEFA) concentrations were higher (p<0.001) in maternal (x = 643 μM) than in matched umbilical venous plasma (x = 211 μM) and there was a significant correlation (p<0.01) between diazepam % free and corresponding plasma NEFA concentration for pooled data (r=0.871, n=34). Multiple and partial regression analysis indicates that transplacental differences in albumin, bilirubin and total protein concentrations made a minimal contribution to diazepam binding differences between mother and foetus and that approximately 76% of the variability in diazepam % free was accounted for by plasma NEFA concentration. The binding of diazepam to human serum albumin (HSA) was markedly perturbed by the presence of NEFA but not by bilirubin and there was no apparent cooperativity between bilirubin and NEFA on diazepam-HSA binding. Moreover, our findings provide further evidence that substantial differences in binding affinities exist between foetal and maternal plasma albumins.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mandelli M, Morselli PL, Nordio S, Pardi G, Principi P, Sereni F, Tognoni G (1975) Placental transfer of diazepam and its disposition in the newborn. Clin Pharmacol Ther 17: 564–572
Cree JE, Meyer J, Hailey DM (1973) Diazepam in labour: Its metabolism and effect on the clinical condition and thermogenesis of the newborn. Br Med J 4: 251–255
Moore RG, McBride WG (1978) The disposition of diazepam in pregnant women at parturition. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 13: 275–284
McAllister CB (1980) Placental transfer and neonatal effects of diazepam when administered to women just before delivery. Br J Anaesth 52: 423–427
Kanto J, Erkkola R, Sellman R (1973) Accumulation of diazepam and N-demethyldiazepam in the fetal blood during the labour. Ann Clin Res 5: 375–379
Erkkola R, Kangas L, Pekkarinen A (1973) The transfer of diazepam across the placenta during labour. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 52: 167–170
Rowlatt RJ (1978) Effect of maternal diazepam on the newborn. Br Med J 1 [6118]: 985
Levy G, Hayton WL (1973) Pharmacokinetic aspects of placental drug transfer. In: Boreus L (ed) Fetal pharmacology. Raven Press, New York
Hamar, C, Levy G (1980) Serum protein binding of drugs and bilirubin in newborn infants and their mothers. Clin. Pharmacol Ther 28: 58–63
Guerre-Millo M, Rey E, Challier J-C, Turquais J-M, d'Athis Ph, Olive G (1979) Transfer in vitro of three benzodiazepines across the human placenta. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 15: 171–173
Wood M, Wood AJJ (1981) Changes in plasma drug binding and α1-acid glycoprotein in mother and newborn infant. Clin Pharmacol Ther 29: 522–526
Colburn WA, Gibaldi M (1978) Plasma protein binding of diazepam after a single dose of sodium oleate. J Pharm Sci 67: 891–892
Wong GB, Sellers EM (1979) Intravascular factors affecting diazepam binding to human serum albumin. Biochem Pharmacol 28: 3265–3270
Ridd MJ, Brown KF, Moore RG, McBride WG, Nation RL (1982) Diazepam plasma binding in the perinatal period: Influence of nonesterified fatty acids. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 22: 153–160
Ridd MJ, Brwon KF, Moore RG, Nation RL (1982) Drug plasma binding and nonesterified fatty acids: Methodologic considerations. Int J Pharm 11: 11–20
Ridd MJ, Brown KF, Nation RL (1982) Plasma nonesterified fatty acids and pH: Potential artefacts in equilibrium dialysis studies with non-heparinized subjects. Clin Chem (submitted)
Spector AA, Hoak JC (1969) An improved method for the addition of long-chain free fatty acid to protein solutions. Anal Biochem 32: 297–302
Freund JE (1974) Modern Elementary statistics. Prentice-Hall International, London
Krasner J, Giacoia GP, Yaffe SJ (1973) Drug-protein binding in the newborn infant. Ann. NY Acad Sci 226: 101–114
Green TP, O'Dea RF, Mirkin BL (1979) Determinants of drug disposition and effect in the fetus. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 19: 285–322
Kober A, Jenner A, Sjoholm I, Borga O, Odar-Gederlöf I (1978) Differentiated effects of liver cirrhosis on the albumin binding sites for diazepam, salicylic acid and warfarin. Biochem Pharmacol 27: 2729–2735
Jacobsen J (1969) Binding of bilirubin to albumin-determination of the dissociation constants. FEBS Lett 5: 112
Gugler R, Shoeman DW, Azarnoff DL (1974) Effect of in vivo elevation of free fatty acids on protein binding of drugs. Pharmacology 12: 160–165
Miyoshi K, Saijo K, Kotani Y, Kashiwagi T, Kawai H (1966) Characteristic properties of fetal human albumin (Alb F) in isomerization equilibrium. Tokushima J Exp Med 13: 121–128
Wallace S (1977) Altered plasma albumin in the newborn infant. Br J Clin Pharmacol 14: 82–85
Friedman LA, Lewis PJ (1980) The effect of semisynthetic penicillins on the binding of bilirubin by neonatal serum. Br J Clin Pharmacol 9: 61–65
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ridd, M.J., Brown, K.F., Nation, R.L. et al. Differential transplacental binding of diazepam: Causes and implications. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24, 595–601 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542207
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00542207