Abstract
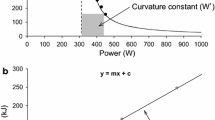
Eight highly trained male kayakers were studied in an attempt to examine whether critical power (CP), based upon four tests, could be determined from a combination of any two tests. The mean age of the subjects was 26.3 (SEM 3.8) years, mean height was 180.9 (SEM 5.1) cm, and mean body mass was 81.7 (SEM 8.3) kg. Four exercise sessions of 90 s, 240 s, 600 s, and 1200 s duration were used. For each subject the total work output was plotted against the duration of each test, the CP being obtained from the line of best fit. The CP obtained from this relationship was then compared to the CP derived from six combinations (90/240, 90/600, 90/1200, 240/600, 240/1200 and 600/1200 s) of various performance times. A repeated measures analysis of variance found a significant difference between the exercise intensity obtained from the line of best fit and that obtained for the combination of exercise times of 90/240s,F (7,1)=11.12 (P < 0.05). No other significant differences were found between the CP from the line of best fit and that from any of the other possible exercise combinations. This would suggest that any combination of time intervals except 90/240 s may be used to determine the CP of elite kayakers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bulbulian R, Wilcox AR, Darabos BL (1986) Anaerobic contribution to distance running performance of trained cross-country athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 18:107–113
De Vries HA, Moritani T, Nagata A, Magnussen K (1982) The relation between critical power and neuromuscular fatigue as estimated from EMG data. Ergonomics 25:783–791
De Vries HA, Tichy MW, Housh TJ, Smyth KD, Tichy A, Housh DJ (1987) A method for estimating physical working capacity at the fatigue threshold. Ergonomics 30:1195–1204
Ginn EM (1988) Physiological assessment of the kayak paddler. In: Draper J, Telford R (eds) Sport specific guidelines for the physiological assessment of the elite athlete. Australian Sports Commission, Canberra, Australia, pp 53–66
Housh DJ, Housh TJ, Bauge SM (1989) The accuracy of critical power test for predicting time to exhaustion during cycle ergometry. Ergonomics 32:997–1004
Housh DJ, Housh TJ, Bauge SM (1990) A methodological consideration for the determination of critical power and anaerobic work capacity. Res Q Exerc Sport 61:406–409
Housh TJ, Johnson GO, McDowell SL, Housh DJ, Pepper M (1991) Physiological responses at the fatigue threshold. Int J Sports Med 12:305–308
Jenkins DG, Quigley BM (1990) Blood lactate in trained cyclists during cycle ergometry at critical power. Eur J Appl Physiol 61:278–283
Jenkins DG, Quigley BM (1991) Critical power in the assessment of athletic ability. Sports Coach 14:18–22
Keppel G (1982) Design and analysis a researcher's handbook (2nd edn.). Prentice Hall,Englewood Cliffs, N. J., pp 185–270
Monod H, Scherrer J (1965) The work capacity of a synergic muscle group. Ergonomics 8:329–338
Moritani T, Nagata A, De Vries HA, Muro M (1981) Critical power as a measure of physical work capacity and anaerobic threshold. Ergonomics 24:339–350
Nagata A, Moritani T, Muro M (1983) Critical power as a measure of muscular fatigue threshold and anaerobic threshold. In: Matsui H, Kafayassi K (eds) Biomechanics IV A. Human Kinetics, Champagne, Ill., pp 86–93
Nebelsick-Gullet LJ, Housh TJ, Johnson GO, Bauge SM (1988) A comparison between methods of measuring anaerobic work capacity. Ergonomics 31:1413–1429
Poole DC (1986) Letter to the Editor-in-Chief. Med Sci Sports Exerc 18:703–704
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clingeleffer, A., Naughton, L.M. & Davoren, B. Critical power may be determined from two tests in elite kayakers. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 68, 36–40 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00599239
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00599239