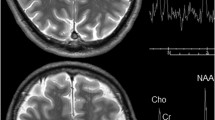
Abstract
We examined 13 patients with chronic carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); all of them had been in an explosion in a coal mine 25 years previously. Symmetrical globus pallidus lesions were observed in 12, as was degeneration of the white matter, with focal cortical atrophy. The temporal parietal and occipital lobes were usually affected, the parietooccipital region being the most frequently and extensively damaged. Of the 12 patients with white matter degeneration 7 had definitely asymmetrical cortical and subcortical lesions. There were 6 patients with dilated temporal horns, probably due to atrophy of the hippocampal gyri. A history of CO inhalation and an awareness of the typical distributions of lesions are important for recognition of the effects of CO poisoning, especially when patients are in the chronic stage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horowitz AL, Kaplan R, Sarpel G (1987) Carbon monoxide toxicity: MR imaging in the brain. Radiology 162:787–788
Vion-Dury J, Jiddane M, Van Bunnen Y, Rumeau C, Lavielle J (1987) Sequelae of carbon monoxide poisoning: an MRI study of two cases. J Neuroradiol 14:60–65
Vieregge P, Klostermann W, Blümm RG, Borgis KJ (1989) Carbon monoxide poisoning: clinical, neurophysiological, and brain imaging observations in acute disease and follow-up. J Neurol 236:478–481
Tuchman RF, Moser FG, Moshé SL (1990) Carbon monoxide poisoning: bilateral lesions in the thalamus on MR imaging of the brain. Pediatr Radiol 20:478–479
Sparr SA, Jay M, Drislane FW, Venna N (1991) A historic case of visual agnosia revisited after 40 years. Brain 114:789–800
Birbamer G, Aichner F, Felber S, Kampfl A, Berek K, Schmutzhard E, Gerstenbrand F (1991) MRI of cerebral hypoxia. Neuroradiology 33 [Suppl]: 53–55
Batnitzky S, Sherlock R, McMillan JH, Miller JDR, Rosenthal SJ, Nelson DL (1991) CT and MRI features of acute toxic encephalopathies. Neuroradiology 33 [Suppl]:653–655
Chang KH, Han MH, Kim HS, Wie BA, Han MC (1992) Delayed encephalopathy after acute carbon monoxide intoxication: MR imaging features and distribution of cerebral white matter lesions. Radiology 184:117–122
Lapresle J, Fardeau M (1967) The central nervous system and carbon monoxide poisoning. II. Anatomical study of brain lesion following intoxication with carbon monoxide (22 cases). Prog Brain Res 24:31–74
Kim KS, Weinberg PE, Suh JH, Ho SU (1980) Acute carbon monoxide poisoning: computed tomography of the brain. AJNR 1:399–402
Miura T, Mitomo M, Kawai R, Harada K (1985) CT of the brain in acute carbon monoxide intoxication: characteristic features and prognosis. AJNR 6:739–742
Kono E, Kono R, Shida K (1983) Computerized tomographies of 34 patients at the chronic stage of acute carbon monoxide poisoning. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 233:271–278
Taylor R, Holgate RC (1988) Carbon monoxide poisoning: asymmetric and unilateral changes on CT. AJNR 9:975–977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchino, A., Hasuo, K., Shida, K. et al. MRI of the brain in chronic carbon monoxide poisoning. Neuroradiology 36, 399–401 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00612127
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00612127