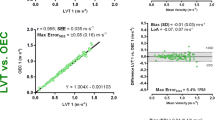
Summary
The validity and accuracy of the Biodex dynamometer was investigated under static and dynamic conditions. Static torque and angular position output correlated well with externally derived data (r=0.998 andr>0.999, respectively). Three subjects performed maximal voluntary knee extensions and flexions at angular velocities from 60 to 450° · s−1. Using linear accelerometry, high speed filming and Biodex software, data were collected for lever arm angular velocity and linear accelerations, and subject generated torque. Analysis of synchronized angular position and velocity changes revealed the dynamometer controlled angular velocity of the lever arm to within 3.5% of the preset value. Small transient velocity overshoots were apparent on reaching the set velocity. High frequency torque artefacts were observed at all test velocities, but most noticeably at the faster speeds, and were associated with lever arm accelerations accompanying directional changes, application of resistive torques by the dynamometer, and limb instability. Isokinematic torques collected from ten subjects (240, 300 and 400° · s−1) identified possible errors associated with reporting knee extension torques at 30° of flexion. As a result of tissue and padding compliance, leg extension angular velocity exceeded lever arm angular velocity over most of the range of motion, while during flexion this compliance meant that knee and lever arm angles were not always identical, particularly at the start of motion. Nevertheless, the Biodex dynamometer was found to be both a valid and an accurate research tool; however, caution must be expercised when interpreting and ascribing torques and angular velocities to the limb producing motion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farrell M, Richards JG (1986) Analysis of the reliability and validity of the Kinetics Communicator exercise device. Med Sci Sports Exerc 18:44–49
Gransberg L, Knutsson E (1983) Determination of dynamic muscle strength in man with acceleration controlled isokinetic movements. Acta Physiol Scand 119:317–320
Perrine JJ, Edgerton VR (1978) Muscle force-velocity and power-velocity relationships under isokinetic loading. Med Sci Sports 10:159–166
Sapega AA, Nicholas JA, Sokolow D, Saraniti A (1982) The nature of torque “overshoot” in Cybex isokinetic dynamometry. Med Sci Sports Exerc 14:368–375
Seger JY, Westing SH, Hanson M, Karlson E, Ekblom B (1988) A new dynamometer measuring concentric and eccentric muscle strength in accelerated, decelerated, or isokinetic movements. Eur J Appl Physiol 57:526–530
Smith SL, Dillman CJ, Rosenhoover SG (1988) Validation of an automatic video analysis system. Med Sci Sports Exerc 20:S75
Taylor NAS, Cotter JD, Stanley SN, Marshall RN (1989) Muscle torque and velocity relationships in elite power and endurance athletes. In: Gregor RJ, Zernicke RF, Whiting WC (eds) Proceedings of the XII International Congress of Biomechanics, Los Angeles, USA. Abstract no. 185, pp 370–371
Taylor NAS, Cotter JD, Gartner PW, Silver DT, Stanley SN, Marshall RN (1990) The inter-relationship of torque and velocity in leg extension of normal and elite athletes. Commonwealth and International Conference on Physical Education, Sport, Health, Dance, Recreation and Leisure. Auckland, New Zealand
Winter DA, Wells RP, Orr GW (1981) Errors in the use of isokinetic dynamometers. Eur J Appl Physiol 46:397–408
Wyman J (1926) Studies on the relation of work and heat in tortoise muscle. J Physiol 61:337–352
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, N.A.S., Sanders, R.H., Howick, E.I. et al. Static and dynamic assessment of the Biodex dynamometer. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 62, 180–188 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00643739
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00643739