Summary
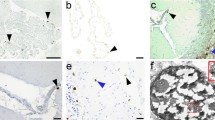
A 46-year-old female, with an 11 year history of malignant lymphoreticular disease, developed a neurological illness clinically manifested by a focal mass lesion in the left frontal lobe. In biopsied tissue, immunofluorescence study revealed the presence of JC antigen in the glial cells. Histologically, the lesion was characteristic of PML consisting of focal necrosis in the subcortical white matter, numerous fat laden macrophages and marked hypertrophy of oligodendrocytes and astrocytes. By electron microscopy, hypertrophic astrocytes contained intranuclear viral particles consistent with papova virions and aggregates of intracytoplasmic viral particles consisting of a single to several virions tightly surrounded by a single membrane. The membrane appeared to have been derived from that of the cellular vesicles. Fusion of the virus-associated membrane to the astroglial plasmalemma occurred when the virions appeared to shift towards extracellular space. The virioncontaining astrocytes showed cytoplasmic “fibrillar hypertrophy” similar to the characteristic gigantic astroglias of PML. This fact would provide an additional evidence that these gigantic cells, although lacking identifiable viral structures, were the result of anaplastic transformation by JC virus. Many virus-bearing sstroglias were noted to be in the early stage of cellular necrosis, or “edematous degeneration”. This further indicates that the JC virus is capable of inducing both lytic and abortive astroglial infections. Many oligodendroglias were hypertrophic due to the presence of intranuclear viral particles and markedly increased numbers of microtubules and free ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Membrane-bound intracytoplasmic viral particles were also noted in the oligodendroglias. Some fat laden macrophages contained large intracytoplasmic viral bodies, presumably orginating from phagocytized virus-bearing cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åström, K. E.: Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital (ed. B. Castleman). New Engl. J. Med.286, 1047–1054 (1972)
Åström, K. E., Mancall, E. L., Richardson, E. P. Jr.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: Hitherto unrecognized complication of chronic lymphatic leukemia and Hodgkin's disease. Brain81, 93–111 (1958)
Brun, A., Nordenfeldt, E., Kjellen, L.: Aspects on the variability of progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)24, 232–243 (1973)
Cancilla, P. A.: Neuroclinical-pathology conference. Progressive central nervous system disease in the course of chronic myelocytic leukemia. Bull. Los Angeles neurol. Soc.36, 93–102 (1971)
Castaigne, P., Escourolle, R., Derouesne, C. H., Cathala, F., Hauw, J. J., Duclos, H., Goust, J. M.: Un cas de leucoencephalopathie multifocale progressive. Etude anatomoclinique et immunologique Isolement à partir d'une biopsie cérébrale, d'une nouvelle souche de virus Papova. Rev. neurol.128, 85–94 (1973)
Castaigne, P., Rondot, P., Escourolle, R., Ribadeau, J. L., Dumas, F., Cathala, F., Hauw, J. J.: Leucoencéphalopathie multifocale progressive et «gliome» multiples. Rev. neurol.130, 379–392 (1974)
Chou, S. M., Oguchi, K., Holden, E. M., Tarsy, D.: Unusual ultrastructural findings in PML (Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy). J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.34, 81–82 (1975)
Dolman, C. L., Furesz, J., Mackay, B.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Two cases with electron microscopic and viral studies. Canad. med. Ass. J.97, 8–12 (1967)
Eckhart, W.: Cell transformation by polyoma virus and SV40. Nature (Lond.)224, 1069–1071 (1969)
Field, A. M., Gardener, S. D., Goodbody, R. A., Woodhouse, M. A.: Identity of a newly isolated human polyomavirus from a patient with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. clin. Path.27, 341–347 (1974)
Gambetti, P., Frulkar, S. E., Somlyo, A. P., Gonatas, N. K.: Calcium-containing structures in vertebrate glial cells. Ultrastructural and microprobe analysis. J. Cell Biol.64, 322–330 (1975)
Gaylord, W. H., Jr., Hsiung, G. D.: The vacuolating virus of monkeys. II. Virus morphology and intranuclear distribution with some histochemical observations. J. exp. Med.114, 987–996 (1961)
Howatson, A. F., Almeida, J. D.: An electron microscope study of polyoma virus in hamster kidney. J. Biophys. biochem. Cytol.7, 753–760 (1960)
Hadfield, M. G., Martinez, A. J., Gilmartin, R. C.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with paramyxovirus-like structures, Hirano bodies, and neurofibrillary tangles. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)27, 277–288 (1974)
Ikuta, F.: Particles of Papova virus group associated with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Clin. Neurol.6, 671 (1967)
Kanshepolsky, J., Beggs, J., Waggener, J. D.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: pathological and electron microscopic studies. Ariz. Med.28, 743–747 (1971)
Kepes, J. J., Chou, S. M., Price, L. W.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy with 10 year survival in a patient with non-tropical sprue: Report of a case with unusual light and electron microscopic features. Neurology (Minneap.)25, 1006–1012 (1975)
Knight, A., O'Brien, P., Osoba, D.: “Spontaneous” progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Ann. intern. Med.77, 229–233 (1972)
Krempien, B., Kokmann, F. W., Schiemer, H. G., Mayer, P.: Über die progressive multifokale Leukoencephalopathie. Beitrag zur Differential diagnose mit elektronenmikroskopischen und cytophotometrischen Untersuchungen. Virchows Arch. path. Anat.355, 158–178 (1972)
Lyon, L. W., McCormick, W. F., Schochet, S. S., Jr.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Arch. intern. Med.128, 420–426 (1971)
Manz, H. J., Dinsdale, H. B., Morrin, P. F.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a renal allograft recipient. Ann. intern. Med.75, 75–83 (1971)
Mathews, T., Wisotzkey, H., Moosey, J.: Multiple central nervous system infections in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurology (Minneap.)26, 9 (1976)
Mayor, H. D., Stinebaugh, S. E., Jamison, R. M., Jordan, L. E., Melnick, J. L.: Immunofluorescent, cytochemical and microcytological studies on the growth of the simian vacuolating virus (SV40) in tissue culture. Exp. molec. Path.1, 397–416 (1962)
Morecki, R., Porro, R. S.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Identification of virions in paraffin-embedded tissues. Arch. Neurol (Chic.)22, 253–258 (1970)
Mosher, M. B., Schall, G. L., Wilson, J.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: Positive brain scan. J. Amer. med. Ass.218, 226 (1971)
Muller, J., Watanabe, I.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. A virus disease? Amer. J. clin. Path.47, 114–123 (1967)
Navarro, J. C., Genth, J., Gullotta, F.: Leucoencephalopatia multifocale progressiva: Isopatologia ed ultrastruttura. Acta neurol. (Napoli)24, 572–577 (1972)
Narayan, O., Weiner, L. P., Herndon, R. M., Penney, J. B.: Etiology of progressive multifical leukoencephalopathy: identification of a papovavirus. New Engl. J. Med.289, 1278–1282 (1973)
Oshiro, L. S., Rose, H. M., Morgan, C., Hsu, K. C.: Electron microscopic study of the development of simian virus 40 by use of ferritin-labeled antibodies. J. Virol.1, 384–399 (1967)
Padgett, B. L., Walker, D. L., ZuRhein, G. M., Eckroade, R. J., Dessel, B. H.: Cultivation of papova-like virus from human brain with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Lancet1971 I, 1257–1260
Preskorn, S. H., Kepes, J., Bopp, W. J., Watanabe, I.: Propagation of JC virus in glia cells in PML (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy). 33rd Ann. Proc. Electron Microscopy Soc. Amer. Las Vegas, Nevada, (ed. G. W. Bailey), pp. 328–329. (Abstract, 1975)
Shirabe, T., Nagamatsu, K., Kuroiwa, Y., Kikuchi, M., Yoshida, H.: An autopsy case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Advanc. Neurol. Sci. (Tokyo)16, 504–514 (1972)
Silverman, L., Rubinstein, L. J.: Electron microscopic observations on a case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)5, 215–224 (1965)
Smith, J. L.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Arch. Ophthal.62, 828 (1959)
Tarsey, D., Holden, E. M., Segarra, J. M., Calabresi, P., Feldman, R. G.: I-Iodo-2′-deoxyuridine (IUDR; NSC-39661) given intraventricularly in the treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Cancer Chemother. Rep.57, 73–78 (1973)
Tomiyasu, U., Bakker, R. N., Wallman, J.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy and the “Slow Viruses”. Bull. Los Angeles neurol. Soc.33, 59–69 (1968)
Vanderhaeghen, J. J., Perier, O.: Leukoencephalite multifocale Progressive: mise en evidence de particules virales par la microscopie electronique. Acta neurol. belg.65, 816–837 (1965)
Walker, D. L., Padgett, B. L., ZuRhein, G. M., Albert, A. E., Marsh, R. F.: Human papovavirus (JC): induction of brain tumors in hamsters. Science181,674–676 (1973)
Weiner, L. P., Herndon, R. M., Narayan, O., Johnson, R. T., Shah K., Rubinstein, L. J., Preziosi, T. J., Conley, F. K.: Isolation of virus related to SV40 from patients with progressive multifocal leukoencephalpathy. New Engl. J. Med.286, 385–390 (1972)
Woodhouse, M. A., Dayan, A. D., Burston, J., Caldwell, I., Adams J. H., Melcher, D., Urich, H.: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: electron microscopic study of four cases. Brain90, 863–870 (1967)
ZuRhein, G. M.: Polyoma-like virions in a human demyelinating disease. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)8, 57–68 (1967)
ZuRhein, G. M.: Association of papova-virions with a human demyelinating disease. (Progressive multifocal leukodystrophy.) Progr. med. Virol.11, 185–247 (1969)
ZuRhein, G. M., Chou, S. M.: Particles resembling papovaviruses in human cerebral demyelinating disease. Science148, 1477–1479 (1965)
ZuRhein, G. M., Chou, S. M.: Papova virus in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. In: Infections of the nervous system, Ch. 17. Res. Publ. Ass. nerv. ment. Dis.44, 307–362 (1968)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by Veterans Administration Research Project, U. S. A. No. 9242-01.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, I., Preskorn, S.H. Virus-cell interaction in oligodendroglia, astroglia and phagocyte in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol 36, 101–115 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685273
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685273