Abstract
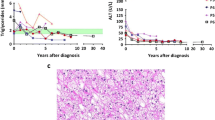
Type I glycogen storage disease (GSD-I) is due to the deficiency of glucose-6-phosphatase activity in the liver, kidney and intestine. Although kidney enlargement occurs in GSD-I, renal disease has not been considered a major problem until recently. In older patients (more than 20 years of age) whose GSD-I disease has been ineffectively treated, virtually all have disturbed renal function, manifested by persistent proteinuria; many also have hypertension, renal stones, altered creatinine clearance or a progressive renal insufficiency. Glomerular hyperfiltration is seen in the early stage of the renal dysfunction and can occur before proteinuria. In younger GSD-I patients, the hyperfiltration is usually the only renal abnormality found; and, in some patients, microalbuminuria develops before clinical proteinuria. The predominant underlying renal pathology is focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Renal stones and/or nephrocalcinosis are also common findings. Amyloidosis and Fanconi-like syndrome can occur, but rarely. The risk factors for developing the glomerulosclerosis in GSD-I include hyperfiltration, hypertension, hyperlipidemia and hyperuricemia. Dietary therapy with cornstarch and/or nasogastric infusion of glucose, aimed at maintaining normoglycemia, corrects metabolic abnormalities and improves the proximal renal tubular function. Long-term trial will be needed to assess whether the dietary therapy may prevent the evolution or the progression of the renal disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Y-T (1989) Disorders of carbohydrate metabolism (excluding diabetes). In: Kelley WN (ed) Textbook of internal medicine. Lippincott, Pennsylvania, pp 2270–2273
Hers H-G, Hoof F van, Barsy T de (1989) Glycogen storage diseases. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease, 6th edn, vol 1. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 425–452
Cohen J, Friedman M (1979) Renal tubular acidosis associated with type III glycogenosis. Acta Paediatr Scand 68: 779–782
DiMauro S (1978) Metabolic myopathies. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW, Ringel SP (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology. North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 175–234
Grunfeld JP, Ganeval D, Chanard J, Fardeau M, Dreyfus JC (1972) Acute renal failure in McArdle's disease. N Engl J Med 286: 1237
Bank WJ, Dimauro S, Rowland LP (1972) Renal failure in McArdle's disease. N Engl J Med 287: 1102
McDermott M, Piegari G, Hofeldt FD (1982) Acute renal failure in McArdle's disease. South Med J 75: 309–312
Fanconia VG, Bickel H (1949) Die chronische Aminoacidurie (Aminosäurediabetes oder nephrotisch-glukosurischer Zwergwuchs) bei der Glykogenose und der Cystinkrankheit. Helv Paediatr Acta 4: 359–396
Rotthauwe HW, Fichsel H, Heldt HW, Kirsten E, Reim M, Schmidt E, Schmidt FW, Wesemann W (1963) Glykogenose der Leber mit Aminoacidurie und Glucosurie: Klinische und biochemische Untersuchungen. Klin Wochenschr 41: 818–825
Odièvre M (1966) Glycogenose hépato-rénale avec tubulopathie congénitale: deux observations d'une entité nouvelle. Rev Int Hepatol 16: 1–70
Garty R, Cooper R, Tabachnik E (1974) The Fanconi syndrome associated with hepatic glycogenosis and abnormal metabolism of galactose. J Pediatr 85: 821–823
Brivet M, Moatti N, Corriat A, Lemonnier A, Odièvre M (1983) Defective galactose oxidation in a patient with glycogen storage disease and Fanconi syndrome. Pediatr Res 17: 157–161
Hurvitz H, Elpeleg ON, Barash V, Kerem E, Reifen RM, Ruitenbee K, Mor C, Branski D (1989) Glycogen storage disease, Fanconi nephropathy, abnormal galactose metabolism and mitochondrial myopathy. Eur J Pediatr 149: 48–51
Holling HE (1963) Gout and glycogen storage disease. Ann Intern Med 58: 654–663
Sonobe H, Ogawa K, Takahashi I (1976) Familial nephropathy associated with hepatic type of glycogen storage disease. Acta Pathol Jpn 26: 727–738
Steim H, Zollinger HU (1967) Tödliche Schrumpfniere bei Glykogenspeicherkrankheit Typ von Gierke. Klin Wochenschr 45: 295–299
Nishio S, Oka K, Tanaka K, Imagawa E, Omae T (1981) Type 1 glycogenosis with contracted kidneys and liver cell adenoma. Acta Pathol Jpn 31: 873–881
Chen YT, Coleman RA, Scheinman JI, Kolbeck PC, Sidbury JB (1988) Renal disease in type I glycogen storage disease. N Engl J Med 318: 7–11
Alaupovic P, Fernandes J (1985) The serum apolipoprotein profile of patients with glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency. Pediatr Res 19: 380–384
Levy E, Thiabault LA, Roy CC, Bendayan M, Lepage G, Letarte J (1988) Circulating lipids and lipoproteins in glycogen storage disease type I with nocturnal intragastric feeding. J Lipid Res 29: 215–226
Greene HL, Slonim AE, O'Neill JA Jr., Burr IM (1976) Continuous nocturnal intragastric feeding for management of type I glycogenstorage disease. N Engl J Med 294: 423–425
Chen Y-T, Cornblath M, Sidbury JB (1984) Cornstarch therapy in type I glycogen-storage disease. N Engl J Med 310: 171–175
Wolfsdorf JI, Keller RJ, Landy H, Crigler JF Jr (1989) Glucose therapy of infants with type I glycogenosis (GSD): comparison of intermittent uncooked cornstarch (UCS) and continuous overnight glucose (COG) feedings. Pediatr Res 25: 205A
Baker L, Dahlem S, Goldfarb S, Kern EFO, Stanley CA, Egler J, Olshan JS, Heyman S (1989) Hyperfiltration and renal disease in glycogen storage disease, type I. Kidney Int 35: 1345–1350
Chen Y-T, Coleman RA, Scheinman JI (1988) Glomerular and tubular dysfunction in type I glycogen storage disease (GSD-I): improvement with cornstarch therapy. Am J Hum Genet 43: A3
Gehiig JJ, Wolfe JA (1988) Renal disease in type I glycogen storage disease. N Engl J Med 318: 1759–1760
Parscau L de, Guibaud P, Labrune P, Odièvre M (1990) Long term outcome of hepatic glycogen storage diseases: the French experience. J Inherited Metab Dis (in press)
Emmett M, Narins RG (1978) Renal transplantation in type I glycogenosis: failure to improve glucose metabolism. JAMA 239: 1642–1644
Jonas AJ, Verani RR, Howell RR, Conley SB (1988) Hypertension in a child with type Ia glycogen storage disease. Am J Kidney Dis II: 264–266
Verani R, Bernstein J (1988) Renal glomerular and tubular abnormalities in glycogen storage disease type I. Arch Pathol Lab Med 112: 271–274
Poe R, Snover DC (1988) Adenomas in glycogen storage disease type I: two cases with unusual histologic features. Am J Surg Pathol 12: 477–483
Kikuchi M, Haginoya K, Miyabayashi S, Igarashi Y, Narisawa K, Tada K (1990) Secondary amyloidosis in glycogen storage disease type Ib. Eur J Pediatr 149: 344–345
Matsuo N, Tsuchiya Y, Cho H, Nagai T, Tsuji A (1986) Proximal renal tubular acidosis in a child with type I glycogen storage disease. Acta Paediatr Scand 75: 332–335
Lampert F, Mayer H, Tocci PM, Nyhan WL (1967) Fanconi syndrome in glycogen storage disease. In: Nyhan WL (ed) Amino acid metabolism and genetic variation. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 353–362
Chen YT, Scheinman JI, Park HK, Coleman RA, Roe CR (1990) Amelioration of proximal renal tubular dysfunction in type I glycogen storage disease with dietary therapy. N Engl J Med 323: 590–593
Restaino I, Stanley C, Baker L, Weiss R, Kaplan BS (1990) Renal tubular abnormalities and nephrocalcinosis in patients with type Ia glycogen storage disease. Pediatr Res 27: 337A
Ditzel J, Schwartz M (1967) Abnormally increased glomerular filtration rate in short-term insulin-treated diabetic subjects. Diabetes 16: 264–267
Mogensen CE (1976) Renal function changes in diabetes. Diabetes 25: 872–879
Goldszer RC, Sweet J, Cotran RS (1984) Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Annu Rev Med 35: 429–449
Brenner BM, Meyer TW, Hostetter TH (1982) Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N Engl J Med 307: 652–659
Hostetter TH, Rennke HG, Brenner BM (1982) The case for intrarenal hypertension in the initiation and progression of diabetic and other glomerulopathies. Am J Med 72: 375–380
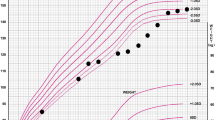
Chen YT, Feinstein KA, Coleman RA, Effman EL (1990) Variability of renal length in type I glycogen storage disease. J Inherited Metab Dis 13: 259–262
Beck LH (1986) Requiem for gouty nephropathy. Kidney Int 30: 280–287
Keane WF, Kasiske BL, O'Donnell MP (1988) Hyperlipidemia and the progression of renal disease. Am J Clin Nutr 47: 157–160
Peric-Golia L, Peric-Golia M (1983) Aortic and renal lesions in hypercholesterolemic adult male virgin Sprague-Dawley rats. Atherosclerosis 46: 57–65
French SW, Yamanaka W, Ostwald R (1967) Dietary induced glomerulosclerosis in the guinea pig. Arch Pathol 83: 204–210
Wellmann K, Volk BW (1970) Renal changes in experimental hypercholesterolemia in normal and in subdiabetic rabbits. Lab Invest 22: 144–155
Kasiske BL, O'Donnell MP, Cleary MP, Keane WF (1988) Treatment of hyperlipidemia reduces glomerular injury in obese Zucker rats. Kidney Int 33: 667–672
Moorhead JF, Chan MK, El-Nahas M, Varghese A (1982) Lipid nephrotoxicity in chronic progressive glomerular and tubulo-interstitial disease. Lancet II: 1309–1311
Keen H, Chlouverakis C, Fuller J, Jarrett RJ (1969) The concomitants of raised blood sugar: studies in newly-detected hyperglycaemics. Guy's Hosp Reports 118: 247–254
Fernandez J, Jansen H, Jansen TC (1979) Nocturnal gastric drip feeding in glucose-6-phosphatase deficient children. Pediatr Res 13: 225–229
Nikkila EA, Huttunen JK, Ehnholm C (1977) Postheparin plasma lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes 26: 11–15
Chen YT, Scheinman JI (1990) Hyperglycemia associated with lactic acidemia in a renal allograft recipient with type I glycogen storage disease. J Inherited Metab Dis (in press)
Addis T (1948) Glomerular nephritis: diagnosis and treatment. Macmillan, New York
Ihle BU, Becker GJ, Whitworth JA, Charlwood RA, Kincaid-Smith PS (1989) The effect of protein restriction on the progression of renal insufficiency. N Engl J Med 231: 1773–1777
Baker L, Kern EFO, Olshan J, Goldfarb S, Dahlem ST (1988) Pilot study of captopril in patients with renal disease associated with glycogen storage disease, type I (GSD-I). Pediatr Res 23: 388A
Taguma Y, Kitamoto Y, Futaki G, Veda H, Monma H, Ishizaki M, Takahashi H, Sekino H, Sasaki Y (1985) Effect of captopril on heavy proteinuria in azotemic diabetics. N Engl J Med 313: 1617–1620
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, YT. Type I glycogen storage disease: Kidney involvement, pathogenesis and its treatment. Pediatr Nephrol 5, 71–76 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00852851
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00852851