Summary
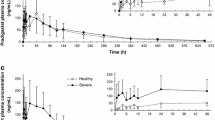
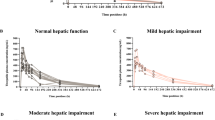
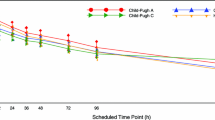
The elimination kinetics of disopyramide was studied in 9 patients with decreased hepatic function (DHF) due to histologically verified cirrhosis of the liver, and in 11 patients with ischaemic heart disease (IHD). Disopyramide 100 and 150 mg was given intravenously as a bolus to the patients with IHD and DHF, respectively, followed by a continuous infusion of disopyramide 0.3 (DHF group) and 0.4 mg · min−1 (IHD group) until steady-state was achieved. A significant (p<0.001) positive correlation between the percentage unbound and total serum concentration of disopyramide was demonstrated in both groups. The percentage of unbound disopyramide at a total serum concentration of 5.9 µmol·l−1 was 45.5% and 19.4% in the DHF and IHD groups, respectively. A negative correlation (r=−0,751,p<0.05, and r=−0.827,p<0.01 in the IHD and DHF patients, respectively) between the free fraction of disopyramide and alpha1-acid glycoprotein was observed. The serum concentration of alpha1-acid glycoprotein, the major binding protein of disopyramide, was significantly lower in the patients with DHF. The clearance of unbound disopyramide and its total volume of distribution and half-life were significantly lower in the DHF patients. No difference in total elimination clearance could be demonstrated. The clinical implication of the present findings appear to be that the dosage of disopyramide should be reduced by 25% when it is given intravenously to patients with decreased hepatic function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hinderling PH, Garrett ER (1976) Pharmacokinetics of the antiarrhythmic disopyramide in healthy humans. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 4: 199–230
Bryson SM, Whiting B, Lawrence JR (1978) Disopyramide serum and pharmacologic effect kinetics applied to the assessment of bioavailability. Br J Clin Pharmacol: 409–419
Hinderling PH, Bres J, Garrett ER (1974) Protein binding and erythrocyte partitioning of disopyramide and its monodealkylated metabolite. J Pharmacol Sci 63: 1684–1690
Burk M, Peters U (1983) Disopyramide kinetics in renal impairment: Determinants of interindividual variability. Clin Pharmacol Ther 34: 331–340
Johnston A, Henry JA, Warrington SJ, Hamer NAJ (1980) Pharmacokinetics of oral disopyramide phosphate in patients with renal impairment. Br J Clin Pharmacol 10: 245–248
Lima JJ, Boudoulas H, Blanford M (1981) Concentration-dependence of disopyramide binding to plasma protein and its influence on kinetics and dynamics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 219: 741–747
Bredesen JE, Kierulf P (1984) Relationship between alfa1-acid glycoprotein and plasma binding of disopyramide and mono-N-dealkyldisopyramide. Br J Clin Pharmacol 18: 779–784
Deano DA, Wu D, Mautner RK, Sherman RH, Ehsani AE, Rosen KM (1977) The antiarrhythmic efficacy of intravenous therapy with disopyramide phosphate. Chest 71: 597–606
Bonde J, Bødtker S, Angelo HR, Svendsen TL, Kampmann JP (1985) Kinetics of disopyramide after intravenous injection to patients with myocardial infarction or heart insufficiency. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 56: 278–282
Bonde J, Pedersen LE, Bødtker S, Angelo HR, Svendsen TL, Kampmann JP (1985) The influence of age and smoking on the elimination of disopyramide. Br J Clin Pharmacol 20: 453–458
Buchmann I, Storstein L, Bredesen JE, Berstad K, Lunde PKM (1982) Disopyramide pharmacokinetics in alcoholic liver disease. Acta Med Scand 42: 655 [Suppl]
Ilett KF, Madsen BW, Woods JD (1979) Disopyramide kinetics in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Clin Pharmacol Ther 26: 1–7
Barre J, Houin G, Rosenbaum J, Zini R, Dhumeaux D, Tillement JP (1984) Decreased alfa1-acid glycoprotein in liver cirrhosis: Consequences for drug protein binding. Br J Clin Pharmacol 18: 652–53
Cleve H, Strohmeyer G (1967) Quantitative Variationen von serum Glykoproteinen bei pathologischen Prozessen; Bestimmung von saurem alfa1-Glycoprotein, Gc and alfa2-Makroglobulin mit der radialen Immunodiffusion. Klin Wochenschr 20: 1051–1054
Hiramatsu S, Kojima J, Okada TT, Inai S, Ohmori K (1976) The serum protein profile in chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and liver cancer. Acta Hepato-Gastroenterol 23: 177–182
Cunningham JL, Shen DD, Shudo I, Azarnoff DL (1977) The effects of urin pH and plasma protein binding on the renal clearance of disopyramide. Clin Pharmacokinet 2: 373–383
Hansen JES, Lihme A, Bøg-Hansen TC (1984) The microheterogeneity components of orosomucoid and the dissociation constants and mobilities of concanavalin A/orosomucoid complexes in crossed affinoimmunoelectrophoresis with free concanavalin A. Electrophoresis 5: 196–201
Andersen I, Thorsen S (1977) The application of the reaction rate analyser LKB 8600 as an automatic coagulometer. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 37: 7–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonde, J., Graudal, N.A., Pedersen, L.E. et al. Kinetics of disopyramide in decreased hepatic function. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 31, 73–77 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00870990
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00870990