Summary
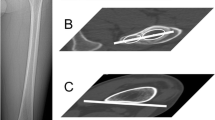
Three methods based on the fluoroscopic technique for measurement of tibial torsion were analyzed. The measurements were performed bilaterally in 100 normal adults. The values for bilateral tibial torsion were recorded and the values for the difference in torsion between the right and left tibia were calculated. The standard error of all investigated methods was found to be lower than published figures for computerized tomography and ultrasonic methods. The method found to be most convenient for routine use also presented the best repeatability. With this method, the standard error of a single determination of tibial torsion was estimated to be 0.7°.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clementz B-G (1987) A new method for routine measurement of the rotational deformity of a tibial fracture and the bilateral tibial torsion determined in a hundred normal adults. Acta Orthop Scand 58:443–444
Clementz B-G (1988) Tibial torsion measured in normal adults. Acta Orthop Scand 59:441–442
Le Damany P (1909) La torsion du tibia — normale, pathologique, expérimentale. J anat Physiol 45:598–615
Dupuis P-V (1951) La torsion tibiale — sa mesure, son intéretclinique, radiologique et chirurgical. Masson, Paris
Elftman H (1945) Torsion of the lower extremity. Am J Phys Anthropol 33:255–265
Elgeti H, Grote R, Giebel G (1980) Bestimmung der Tibiatorsion mit der axialen Computertomographie. Unfallheilkunde 83:14–19
Hutter CG, Scott W (1949) Tibial torsion. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 31:511–518
Jakob RP, Haertel M, Stüssi E (1980) Tibial torsion calculated by computerised tomography and compared to other methods of measurement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 62:238–242
Jend H-H, Heller M, Dallek M, Schoettle H (1981) Measurement of tibial torsion by computer tomography. Acta Radiol [Diagn] (Stockh) 22:271–276
Joseph B, Carver RA, Bell MJ, Sharrard WJW, Levick RK, Aithal V, Chacko V, Murthy SV (1987) Measurement of tibial torsion by ultrasound. J Pediatr Orthop 7(3):317–323
Laasonen EM, Jokio P, Lindholm TS (1984) Tibial torsion measured by computed tomography. Acta Radiol [Diagn] (Stockh) 25:325–329
Larsson K, Bergström B, van der Linden W (1983) A new method for measuring tibio-fibular torsion. Acta Univ Upsaliensis 469, Faculty of Medicine, Uppsala, Sweden
Mebs G, Schrems HTh (1973) Eine röntgenologische Methode zur Bestimmung des Torsionswinkels der Tibia. Arch Orthop Unfall-Chir 76:1–8
Rosen H, Sandick H (1955) The measurement of tibiofibular torsion. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 37:847–855
Staheli LT, Engel GM (1972) Tibial torsion—a method of assessment and a survey of normal children. Clin Orthop 86:183–186
Turner MS, Smillie IS (1981) The effect of tibial torsion on the pathology of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 63:396–398
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clementz, B.G., Magnusson, A. Fluoroscopic measurement of tibial torsion in adults. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 108, 150–153 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00934258
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00934258