Abstract
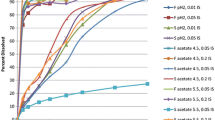
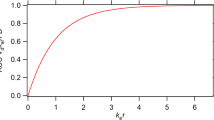
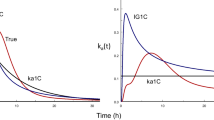
The performance of a novel method for determination of drug absorption characteristics was evaluated by Monte Carlo simulations. In bioavailability studies with use of this method, the test and the reference doses are administered within a time interval of hours. Estimates of bioavilability are obtained by fitting an appropriate model to the concentrationtime profile, which in its terminal portion is thus the summed concentration of the two doses. Drugs with different properties, mimicked by varying the kinetic rate constants (ka, λ1,and λ2),and experimental designs with different sets of conditions regarding the interval between doses, dose ratio, dose order, and duration of sampling, were simulated to determine what factors govern parameter estimation. The absorption characteristics of the simulated drugs could be adequately determined in experiments lasting for 12 hr or less, provided that a proper design was used. Fitting of a simpler or a more complex disposition model produced estimates with similar accuracy and precision to those noted with the true model. For some conditions the use of an improper absorption model resulted in slightly reduced accuracy, but as these fits were poor there was a clear need to try other models. In another set of simulations the use of the proposed method to assess the relative availability of two extravascular doses was evaluated. The relative rate and extent of absorption could be estimated with good precision for two formulations exhibiting a rapid to moderate rate of absorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Rowland. Intra-individual variability in pharmacokinetics. In: D. D. Breimer (ed.),Towards Better Safety of Drugs and Pharmaceutical Products, Elsevier/North-Holland, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980.
A. Grahnén. The impact of time-dependent phenomena on bioequivalence studies. In: D. D. Breimer and P. Speiser (eds),Topics in Pharmaceutical Sciences, Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985.
K. Kwan and A. Till. Novel method for bioavailability assessment.J. Pharm. Sci. 62:1494–1497 (1973).
A. E. Till, L. Z. Benet, and K. C. Kwan. An integrated approach to the pharmacokinetic analysis of drug absorption.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 2:525–544 (1974).
P. S. Collier and S. Riegelman. Estimation of absolute bioavailability assuming steady state apparent volume of distribution remains constant.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 11:205 (1983).
E. E. Dagrosa, P. Hadju, W. Heptner, and W. Rupp. The role of intrasubject variations in bioavailability studies.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 29:39 (1981).
R. A. Dederich, S. J. Szefler, and E. R. Green. Intrasubject variation in sustained-release theophylline absorption.J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 67:465–471 (1981).
A. Yacobi, R. G. Stoll, G. C. Chao, R. A. Schwartz, D. J. Weidler, J. W. Ayers, E. Sakmar, M. Hallmark, and J. G. Wagner. The assessment of the intrasubject variability in digoxin absorption in man from two oral dosage forms.J. Clin. Pharmacol. 21:301–310 (1981).
J. M. Strong, J. S. Dutcher, W. K. Lee, and A. J. Atkinson Jr. Absolute bioavailability in man of N-acetylprocainamide determined by a novel stable isotope method.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 18:613 (1975).
R. L. Wolen, The application of stable isotopes to studies of drug bioavailability and bioequivalence.J. Clin. Pharmacol. 26:419–424 (1986).
M. O. Karlsson and U. Bredberg. Estimation of bioavailability at a single occasion after semisimultaneous drug administration.Pharm. Res. 6:817–821 (1989).
K. C. Kwan, J. V. Bondi and K. C. Yeh. Bioavailability assessment under quasi- and nonsteady-state condition I. Theoretical considerations.J. Pharm. Sci. 64:1639–1642 (1975).
K. C. Yeh and K. C. Kwan. Bioavailability assessment under quasi- and nonsteady-state condition II. Study Designs.J. Pharm. Sci. 65:512–517 (1976).
J. V. Bondi, H. B. Hucker, K. C. Yeh and K. C. Kwan. Bioavailability assessment under quasi- and nonsteady-state condition III. Application.J. Pharm. Sci. 65:1657–1665 (1976).
Y. Bard.Estimators and Their Properties, in Nonlinear Parameter Estimation, Academic Press, New York, 1974, pp. 39–53.
ACSL.Advanced Continuous Simulation Language, Reference Manual, Mitchell and Gauthier Associates, Concord, MA, 1986.
Statistical Consultants. PCNONLIN and NONLIN84: Software for the statistical analysis of nonlinear models.Am. Statist. 40:52 (1986).
K. Iga, Y. Ogawa, T. Yashiki, and T. Shimamoto. Estimation of drug absorption rates using a deconvolution method with nonequal sampling times,J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 14:213–225 (1986).
J. Schmid, A. Prox, H. Zipp, and F. W. Koss. The use of stable isotopes to prove the saturable first-pass effect of methoxsalen.Biomed. Mass Spectrom. 7:560–564 (1980).
A. Grannen, M. Hammarlund, and T. Lundqvist. Implications of intraindividual variability in bioavailability studies of furosemide.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 27:595–602 (1984).
K.-C. Khoo, M. Gibaldi, and R. K. Brazzell. Comparison of statistical moment parameters to Cmax and tmax for detecting differences inin vivo dissolution rates.J. Pharm. Sci. 74:1340–1342 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlsson, M.O., Bredberg, U. Bioavailability estimation by semisimultaneous drug administration: A Monte Carlo simulation study. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 18, 103–120 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063554
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063554