Abstract
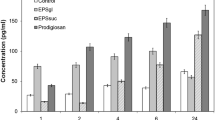
The antibody response against the antigen sheep red blood cells (SRBC) was investigated in mice pre-treated with formalin-killedParacoccidioides brasiliensis or with cell wall fractions of the fungus. Pre-treatment withP. brasiliensis, as well as with the F1 fraction and beta-glucan significantly increased the anti-SRBC antibody response in the experimental groups as compared to the control group that received only SRBC. This immunomodulatory effect varied with the different doses employed and with pre-treatment time. We conclude that the cell wall fractions ofP. brasiliensis might play an important role in the hypergammaglobulinemia associated with Paracoccidioidomycosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Restrepo A, Greer DL, Vasconcellos M. Paracoccidioidomycosis, a review. Review Med Vet Mycol 1973; 8: 97–123.
Musatti CC, Rezkallah RT, Mendes E, Mendes NF. ‘In vivo’ evaluation of cell-mediated immunity in patients with paracoccidioidomycosis. Cell Immunol 1976; 24: 365–78.
Robledo MA, Graybill JR, Ahrens J, Restrepo A, Drutz DL, Robledo M. Host defense against experimental paracoccidioidomycosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1982; 125: 563–7.
Chequer-Bou-Habib D, Daniel-Ribeiro C, Banic DM, Valle ACF, Galvao-Castro B. Polyclonal B cell activation in paracoccidioidomycosis. Mycopathologia 1989; 108: 89–93.
Chirara G, Maeda YY, Hamuro J. Current status and perspectives of immunomodulators of microbial origin. Int J Tissue React 1982; 4: 207–25.
Fava-Netto C. Contribuicao para o estudo imunologico de Blastomicose de Lutz (Blastomicose Sul-Americana). Rev Inst A Lutz 1961; 21: 99–194.
Kanetsuna F, Carbonell LM, Azuma I, Yamamura Y. Studies on thermal dimorphism ofParacoccidioides brasiliensis. J Bacteriol 1972; 110: 208–18.
Reiss E. Serial enzymatic hydrolysis of cell walls of two serotypes of yeast-formHistoplasma capsulatum with α-(1–3)-glucanase, β(1–3)-glucanase, pronase, and chitinase. Infect Immun 1977; 16: 181–8.
Avrameas S, Taudou B, Chuillon S. Glutaraldeyde, cyanuric chloride and tetrazotized o-dianisidine as coupling reagents in the passive hemagglutination test. Immunochemistry 1969; 6: 67–76.
Silva CL, Fazioli RA. AParacoccidioides brasiliensis polysaccharide having granuloma-inducing, toxic and macrophage stimulating activity. J Gen Microbiol 1985; 131: 1497–501
Di-Luzio NR. Immunopharmacology of glucan: a broad spectrum enhancer of host defense mechanisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1983; 131: 1497–506.
Wooles WR, Di-Luzio NR. The phagocytic proliferative response of the reticuloendothelial system following glucan administration. J Reticuloendothel Soc 1964; 1: 160–70.
Ferencik M, Kotulova D, Masler L, Bergendi L, Samdula J, Stefanovic J. Modulatory effect of glucans on the functional and biochemical activities of guinea-pig macrophages. Methods Find Exptl Clin Pharmacol 1986; 8: 163–66.
Carareto Alves LM, Figueiredo F, Brandao-Filho SL, Tincani I, Silva CL. The role of fractions fromParacoccidiodes brasiliensis in the genesis of inflammatory response. Mycopathologia 1987; 97: 3–7.
Jimenez-Finkel BE, Murphy JW. Induction of antigen-specific T suppressor cells by solubleParacoccidioides brasiliensis antigen. Infect Immun 1988; 56: 1912–19.
Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. Two types of mouse helper T-cell clone: Implications for immune regulation. Immunol Today 1987; 8: 223–27.
Mond JJ, Sorer I, Cossman J, Kessler S, Monjini PKA, Hansen C, Finkelman FD, Paul WE. Role of thymus in directing the development of a subset of B lymphocytes. J Exp Med 1982; 155: 924–36.
Mosmann TR, Cherwinski H, Bond MW, Giedlin MA, Coffman RL. Two types of murine helper T cell clone, I: Definition according to profiles of lymphokine activities and secreted proteins. J Immunol 1986; 136: 2348–57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, S.L., da Silva, M.F., Victoriano de Campos Soares, A.M. et al. Cell wall fractions fromParacoccidioides brasiliensis induce hypergammaglobulinemia. Mycopathologia 121, 1–5 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01103346
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01103346