Summary
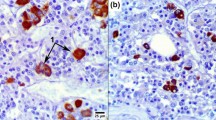
Three women with Cushing's disease caused by ACTH-producing adenoma, underwent transsphenoidal tumour resection. Many adenoma cells showed massive accumulation of microfilaments indistinguishable from Crooke's hyaline material by light and electron microscopy. We believe that these tumours represent variants of ACTH-producing adenomas, and the accumulation of microfilaments is due to cortisol dependency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergland, R. M., Torack, R. M., An ultrastructural study of follicular cells in the human anterior pituitary. Am. J. Path.57 (1969), 273–297.
Crcoke, A. C., A change in the basophilic cells of the pituitary gland common to condition which exhibit the syndrome attributed to basophilic adenoma. J. Path. Bact.41 (1935), 339–349.
DeCicco, F. A., Dekker, A., Yunis, E. J., Fine structure of the Crooke's hyaline change in the human pituitary gland. Arch. Path.94 (1972), 65–70.
Fisher, M. M., Phillips, M. J., Cytoskeleton of hepatocytes. In: Progress in liver disease, Vol. VI (Popper, H., Schaffner, F., eds.), p. 105. New York-San Francisco-London: Grune and Stratton. 1978.
Halmi, N. S., McCormick, W. F., Decker, D. A., The natural history of hyalization of ACTH-MSH cells in man. Arch. Path.91 (1971), 318–326.
Kepler, E. J., The relationship of “Crooke's changes” in the basophilic cells of the pituitary body to Cushing's syndrome (pituitary basophilism). J. Clin. Endocrinol.5 (1945), 70–75.
Kovacs, K., Corenblum, B., Sirek, A. M. T., Penz, G., Ezrin, C., Localization of prolactin in chromophobe pituitary adenomas: Study of human necropsy material by immunoperoxidase technique. J. Clin. Path.29 (1976), 250–258.
Kovacs, K., Horvath, E., Stratmann, I. E., Ezrin, C., Cytoplasmic microfilaments in the anterior lobe of the human pituitary. Acta Anat.87 (1976), 414–426.
Kovacs, K., Horvath, E., Bayley, A. T., Hassaram, S. T., Ezrin, C., Silent corticotroph cell adenoma with lysosomal accumulation and crinophagy. Am. J. Med.64 (1978), 492–499.
Kovacs, K., Horvath, E., Kerenyi, N. A., Sheppard, R. H., Light and electron microscopic adenomas of the pituitary adenoma in Nelson's syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Pathol.65 (1976), 337–343.
Lacy, P. E., Endocrine secretory mechanism: A review. Am. J. Pathol.79 (1975), 170–187.
Landolt, A. M., Ultrastructure of the human sella tumors. Acta Neurochir., Suppl. 22, p. 57. Wien-New York: Springer. 1975.
Olivier, L., Vila-Porcile, E., Racadot, O., Peilion, F., Racadot, J., Ultrastructure of the pituitary tumor cells: A critical study. In: The anterior pituitary, Vol. 7 (Tixier-Vidal, A., Farquhar, M. G., eds.), pp. 231–276. New York: Academic Press. 1975.
Ostlund, R. E., Jr., Leung, J. T., Kipnis, D. M., Muscle actin filaments bind pituitary secretory granules in vitro. J. Cell Biol.73 (1977), 78–87.
Ostlund, R. E., Jr., Contractil proteins and pancreatic secretion. Diabetes26 (1977), 245–254.
Porcile, E., Racadot, J., Ultrastructure des cellules de Crooke observées dans l'hypophyse humaine au cours de la maladie de Cushing. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris)263 (1966), 948–951.
Robert, F., Pelletier, G., Hardy, J., Pituitary adenomas in Cushing's disease; a histological ultrastructural and immunocytochemical study. Arch. Path. Lab. Med.102 (1978), 448–455.
Spencer, P. S., Schaumburg, H. H., Pathobiology of neurotoxic axonal degeneration. In: Physiology and pathobiology of the axons (Waxman, S. G., ed.), pp. 265–282. New York: Raven Press. 1978.
Spooner, B. S., Yamada, K. M., Wessells, N. K., Microfilaments and cell locomotion. J. Cell Biol.49 (1971), 595–613.
Wagermark, J., Wersall, J., Ultrastructural features of Crooke's changes in pituitary basophil cells. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand.72 (1968), 367–375.
Warner, T. S. C. F., Seo, I. S., Aggregates of cytofilaments as the cause of the appearance of hyaline tumor cells. Ultrastruct. Pathol.1 (1980), 395–401.
Wisniewski, H., Terry, R., Hirano, A., Neurofibrillary pathology. J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.29 (1970), 163–175.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research fellow supported by Conacyt and Hospital 20 de Noviembre (ISSSTE), Department of Pathology, Mexico D.F., Mexico.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felix, I.A., Horvath, E. & Kovacs, K. Massive Crooke's hyalinization in corticotroph cell adenomas of the human pituitary. Acta neurochir 58, 235–243 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01407130
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01407130