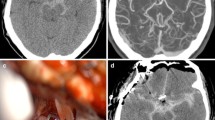
Summary
Supratentorial complications of infratentorial surgery are rare. In the last 3 years we have operated on 187 patients with infratentorial lesions and have observed an incidence of 3.7% of supratentorial haemorrhages. Postoperative intrcranial air, as shown by early postoperative CT control, was encountered mainly in a subdural frontal location and within the interhemispheric fissure. We performed no surgical decompression of the air accumulation because of the lack of clinical symptoms.
Predisposing factors for the development of supratentorial complications remote from the surgical area are hypertonia, female sex, brain atrophy and preoperative shunting procedures. Measures to avoid these complications are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albin, M. S., Babinski, M., Maroon, J. C., Jannetta, P. J., Anesthetic management of posterior fossa surgery in the sitting position. Acta Anaesth. Scand.20 (1976), 117–128.
Albright, L., Reigel, D. H., Management of hydrocephalus secondary to posterior fossa tumors. J. Neurosurg.46 (1977), 52–55.
Ameli, N. O., Sodeify, N., Anterior fossa extradural haematoma following ventriculography through posterior burr-holes. Acta Neurochir. (Wien)13 (1965), 464–468.
Arnason, O., Jakobsson, K. E., Lindgren, S., Extracerebral nonhaemorrhagic expansive complications of intracranial surgery. Acta Neurochir. (Wien)67 (1983), 231–238.
Driesen, W., Elies, W., Epidural and subdural haematomas as a complication of internal drainage of cerebrospinal fluid in hydrocephalus. Acta Neurochir. (Wien)30 (1974), 85–93.
Frera, C., Supratentorial extradural haematomas secondary to ventricular decompression. Acta Neurochir. (Wien)20 (1969), 31–35.
Grundy, B. L., Spetzler, R. F., Subdural pneumocephalus resulting from drainage of cerebrospinal fluid during craniotomy. Anesthesiology52 (1980), 269–271.
Haft, H., Liss, H., Mount, L. A., Massive epidural hemorrhage as a complication of ventricular drainage. J. Neurosurg.17 (1960), 49–54.
Haines, S. J., Maroon, J. C., Jannetta, P. J., Supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage following posterior fossa surgery. J. Neurosurg.49 (1978), 881–886.
Higazi, I., Epidural hematoma as complication of ventricular drainage. J. Neurosurg.20 (1963), 527–528.
Hitselberger, W. E., House, W. F., A warning regarding the sitting position for acoustic tumor surgery. Arch. Otolaryng.106, 1980.
Jan, M., Gouaze, A., Elie, A., Lapierre, F., Santini, J. J., Hématome extra-dural après ponction ventriculaire au course d'une intervention sur la fosse postérieure. Neurochirurgie24 (1978), 137–139.
Leunda, G., Cabezudo, J. M., Areitio, E., Vaquero, J., Gilsanz, F., Subdural tension pneumocephalus after posterior fossa operation: Is the inverted bottle phenomen on the only causative factor? Surg. Neurol.15 (1981), 303–305.
Lunsford, L. D., Maroon, J. C., Sheptak, P. E., Albin, M. S., Subdural tension pneumocephalus. J. Neurosurg.50 (1979), 525–527.
Osborn, A. G., Daines, J. H., Wing, S. D., Anderson, R. E., Intracranial air on computerized tomography. J. Neurosurg.48 (1978), 355–359.
Raggio, J. F., Fleischer, A. S., Sung, Y. F., Hoffmann, J. C., Expanding pneumocephalus due to nitrous oxide anesthesia. Neurosurgery4 (1979), 261–263.
Saidman, L. J., Eger, E. I., Change in cerebrospinal fluid pressure during pneumoencephalography under nitrous oxide anesthesia. Anesthesiology26 (1965), 67–72.
Sanchez, J. J., Redondo, P. C., Lopez, J. F., Alvarez, A. D., Tratamiento del hematoma subdural cronico el metodo de Ectors. Revista Espanola de Oto-Neuro-Oftalmologia y Neurocirugia, Valencia28 (161), (1970), 10–16.
Spetzler, R. F., Wilson, C. P., Dural fistulas and their repair. In: Neurological Surgery (Youmans, J. R., ed.), pp. 2222–2227. Philadelphia-London-Toronto-Mexico City-Sydney-Tokyo: B. Saunders Comp. 1982.
Tindall, G. T., Craddock, A., Greenfield, J. C., Effects of the sitting position on blood flow in the internal carotid artery of man during general anesthesia. J. Neurosurg.26 (1967), 383–389.
Toung, T., Donham, R. T., Lehner, A., Alano, J., Campbell, J., Tension pneumocephalus after posterior fossa craniotomy: Report of four additional cases and review of postoperative pneumocephalus. Neurosurgery12 (1983), 164–168.
Weiss, R. M., Massive epidural hematoma complicating ventricular decompression. J. Neurosurg.21 (1964), 235–236.
Yasargil, M. G., Subokzipitale-transmeatale mikrotechnische Exstirpation des Akustikusneurinoms. In: Kopf- und Hals-Chirurgie, Bd. 3 (Naumann, H. H., Hrsg.), S. 545–587. Stuttgart: Thieme. 1976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harders, A., Gilsbach, J. & Weigel, K. Supratentorial space occupying lesions following infratentorial surgery early diagnosis and treatment. Acta neurochir 74, 57–60 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01413279
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01413279