Summary
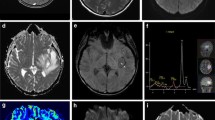
Computerized tomography (CT) was used to examine the timecourse of the propagation of extravasated contrast medium from small brain metastases into the peritumoural oedematous white matter, following infusion of 200 ml of meglumine amidtrizoate for 3 hours. Four patients with a metastatic brain tumour were examined. CT scans at identical levels were taken 1.5, 3, 6, 9, and 12 hours after start of contrast infusion. Following 4–7 days of dexamethasone treatment (8–12mg/day i.v.) the examination was repeated. A contrast-enhanced area was observed surrounding the clearly delineated tumours, expanding gradually in a circular fashion into the peritumoural white matter oedema. The expanding circular enhancement was measured planimetrically on the various scans. From these values, the increase in radius/hr respectively in volume/hr was calculated, assuming a spherical geometry. This enabled a determination of the rate of oedema fluid formation and of the speed of oedema fluid propagation. The formation rate of oedema fluid amounted to 0.5–3.2ml/hour and the speed of oedema fluid spreading to 1.9 mm/hour. Following treatment with dexamethasone the formation rate of oedema fluid is reduced by 30–50%. The important clinical implications of these new findings are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausman JI, Levin VA, Brown WE, Rall DP, Fenstermacher JD (1977) Brain tumor chemotherapy. Pharmacological principles derived from a monkey brain-tumor model. J Neurosurg 46: 155–164
Blasberg R, Patlak C, Shapiro W, Fenstermacher J (1979) Metastatic brain tumors: local blood flow and capillary permeability. Neurol (Minneap) 29: 547
Blasberg R, Gazendam J, Patlak CS, Fenstermacher JD (1980) Quantitative autoradiographic studies of brain edema and a comparison of multi-isotope autoradiographic techniques. In: Cervos-Navarro J, Ferszt T (eds) Brain edema. Raven Press, New York, pp 255–270
Bruce DA, Weeme C ter, Kaiser G, Langfitt T (1976) The dynamics of small and large molecules in the extracellular space and CSF following local cold injury of the cortex. In: Pappuis H-M, Feindel W (eds) Dynamics of brain edema. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 122–128
Crocker EF, Zimmerman RA, Phelps ME, Kuhl DE (1976) The effect of steroids on the extravascular distribution of radiographic contrast materials and Technetium pertechnetate in brain tumors as determined by computed tomography. Radiol 119: 471–474
Fenske A, Samii M, Reulen H-Jet al (1973) Extracellular space and electrolyte distribution in cortex and white matter of dog brain in cold induced edema. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 28: 81–94
Fletcher JW, George EA, Henry RE, Donati RM (1975) Brain scans, dexamethasone therapy and brain tumors. JAMA 232: 1261–1263
Gado MH, Phelps MLE, Coleman RE (1975) An extravascular component of contrast enhancement in cranial computer tomography. Radiology 177: 595–597
Hatam A, Bergström M, Yu ZY, Granholm L (1983) Effect of dexamethasone treatment on volume and contrast enhancement of intracranial neoplasms. J Comput Assist Tomogr 7: 295–300
Hirano A, Matsui T (1975) Vascular structure in brain tumors. Hum Path 6: 611–621
Hossmann KA, Blanik M, Wilmes F, Wechsler W (1980) Experimental peritumoral edema of the cat brain. In: Cervos Navarro J, Ferszt R (eds). Brain edema. Advances in neurology, vol 28. Raven Press, New York, pp 323–340
Ito U, Reulen H-J, Huber P (1986) Spatial and quantitative distribution of human peritumoral brain edema in computerized tomography. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 81: 53–60
Ito U, Tomita H, Kito K, Ueki Y, Inaba Y (1986) CT enhancement after prolonged high-dose contrast infusion in the early stage of cerebral infarction. Stroke 17: 424–430
Klatzo I, Chui E, Fujiwara K, Spatz M (1980) Resolution of vasogenic brain edema. In: Cervos-Navarro J, Ferszt R (eds) Brain edema. Raven Press, New York, pp 1359–1373
Lanksch WR (1982) The diagnosis of brain edema by computed tomography. In: Hartmann A, Brock M (eds) Treatment of cerebral edema. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 43–80
Long DM (1970) Capillary ultrastructure and the Blood-Brain Barrier in human malignant brain tumors. J Neurosurg 32: 127–151
Marmarou T, Takagi H, Shulman K (1980) Biomechanics of brain edema and effects on local cerebral blood flow. In: Cervos Navarro J, Ferszt R (eds) Brain edema. Raven Press, New York, pp 345–358
Oi S, Szper I, Wetzel N, Kim KS (1980) Analysis of peritumoral edema and contrast enhancement by computerized axial tomography. Noshinkeigeka 8: 935–941 (in Japanese)
Reulen H-J, Graham R, Spatz M, Klatzo I (1977) Role of pressure gradients and bulk flow in dynamics of vasogenic brain edema. J Neurosurg 46: 24–35
Reulen H-J, Tsuyumu M (1981) Pathophysiology of formation and natural resolution of vasogenic brain edema. In: Vlieger M de, Lange S de, Beks JWJ (eds) Brain edema. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 31–48
Tsuyumu M, Reulen H-J, Inaba Y (1985) Dynamics of fluid movement through brain parenchyma and into the CSF in vasogenic brain edema. In: Inaba Y, Klatzo I, Spatz M (eds) Brain edema. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg, pp 99–107
Yamada K, Bremer AM, West CR (1979) Effects of dexamethasone on tumor-induced brain edema and its distribution in the brain of monkeys. J Neurosurg 50: 361–367
Yamada K, Hayakawa T, Ushio Y, Kato A, Yamada N, Mogami H (1984) Peritumoral brain edema: Effects of methylprednisolone on local cerebral blood flow, glucose utilisation and capillary permeability. In: Go KG, Baethman A (eds) Plenum Press, New York London, pp 345–354
Yen MH, Wright D, Nakagawa N, Blasberg R, Patlak C, Fenstermacher J (1985) Effects of dexamethasone on the blood-brain distribution of 125J-Albumine and 14C-Alphaaminoisobutyric acid in vasogenic cerebral edema. In: Inaba Y, Klatzo I, Spatz M (eds) Brain edema. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 638–645
Yu ZY, Wrange O, Boethius J, Hatam A, Granholm L, Gustafsson JA (1981) A study of glucocorticoid receptors in intracranial tumors. J Neurosurg 55: 757–760
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, U., Reulen, H.J., Tomita, H. et al. Formation and propagation of brain oedema fluid around human brain metastases. A CT study. Acta neurochir 90, 35–41 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01541264
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01541264