Summary
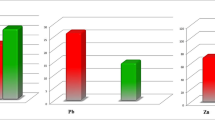
Iron-binding proteins (lactoferrin, transferrin and ferritin) and free iron were measured in synovial fluid (SF) from 30 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and 20 osteoarthritis (OA) patients. The iron-binding proteins except transferrin were significantly increased in RA SF as compared with OA SF. Similarly, free iron was also significantly higher in RA SF than in OA SF, whereas the ferritin saturation index, transferrin saturation index and bound iron were more significantly decreased in RA SF than in OA SF. These results suggest that RA SF contains sufficient micromolar amounts of free iron to allow hydroxyl radical formation. Also the capacity of iron-binding proteins to bind free iron is inadequate in the presence of a large amount of iron-binding proteins which are present in RA SF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muirden, K.D., Senator, G.B. Iron in the synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis and other joint diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 1968, 27, 38–47.
Blake, D.R., Gallagher, P.J., Potter, A.R. et al. The effect of synovial iron on the progression of rheumatoid disease. Arthritis Rheum 1984, 27, 495–501.
Halliwell, B., Gutteridge, J.M.C. Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. Biochem J 1984, 219, 1–14.
Halliwell, B. The biological effect of the superoxide radical and its products. Bull Eur Physopathol Respir 1981, 17, 2–28.
Burkhardt, H., Schwingel, M. Oxygen radicals as effectors of cartilage destruction. Arthritis Rheum 1986, 29, 379–387.
Wallis, W.J., Simkin, P.A., Nelp, W.B. Protein traffic in human synovial effusions. Arthritis Rheum 1987, 30, 57–63.
Biemond, P., Antonius, J.G., Swaak, A.J.G., et al. Protective factors against oxygen free radicals and hydrogen peroxide in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum 1984, 27, 760–765.
Ropes, N.W., Bennett, G.A., Gobb, S., et al. Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis 1958, 9, 175–176.
Hansen, N.E., Malmquist, J., Thorell, J. Plasma myeloperoxidase and lactoferrin measured by radioimmunoassay: Relations to neutrophil kinetics. Acta Med Scand 1975, 198, 437–443.
Bennett, R.M., Mohla, C. A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for the measurement of lactoferrin in human plasma: variations with age, sex and disease. J Lab Clin Med 1976, 88, 156–166.
Gutteridge, J.M.C, Rowley, D.A., Halliwell, B. Superoxide-dependent formation of hydroxyl radicals in the presence of iron salts. Biochem J 1981, 199, 263–265.
Young, D.S.W., Hickx, J.M. Method for the automatic determination of serum iron. J Clin Pathol 1965, 18, 98–102.
Zuyderhoudt, F.M.J., Linthorst, C., Hengeveld, P. On the iron content of human serum ferritin, especially in acute viral hepatitis and iron overload. Clin Chim Acta 1978, 90, 93–99.
Biemond, P., Swaak, A.J.G., van Eijk H.G. Intraarticular ferritin bound iron in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1986, 29, 1187–1193.
Cazzola, M., Huebers, H.A., Sayers, M.H. et al. Transferrin saturation, plasma iron turnover and transferrin uptake in normal humans. Blood 1985, 66, 935–939.
Hay, F.C., Nineham, L.J., Roitt, I.M. Routine assay for the detection of immune complexes of known immunoglobulin class using solid phase C1q. Clin Exp Immunol 1976, 24, 396–400.
Kent, J.F., Fife, E.H. Precise standardization of reagents for complement fixation. Am J Med 1963, 12, 103–116.
Platts-Mills, T.A.E., Ishizuka, K. Activation of the alternative pathway of human complement by rabbit cells. J Immunol 1974, 113, 348–358.
Henson, P.M., Zanolair, B., Schwartzman, et al. Intra-cellular control of human neutrophil secretion. J Immunol 1978, 121, 851–855.
Lansbury, J. Method for evaluating rheumatoid arthritis. In: Arthritis and Allied Conditions, 9th ed., Editors: Hollander, J.L., McCarty, D.J.Jr., Philadelphia, Lea & Febiger, 1979, 141–142.
Blake, D.R., Bacon, P.A., Eastham, E.J. et al. Synovial fluid ferritin in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J 1980, 281, 715–716.
Bennett, R.M., Eddie-Quartey, A.C., Holt, P.J.L. Lactoferrin-An iron-binding protein in synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum 1973, 16, 186–190.
Lentner, C. Geigy Scientific Tables, 8th ed., 1981, 160
Halliwell, B., Gutteridge, J.M.C., Blake, D. Metal ions and oxygen radical reactions in human inflammatory joint disease. Phil Trans R Soc Lond [Biol] 1985, 311 (1152), 659–671.
Gutteridge, J.M.C. Fate of oxygen free radicals in extra-cellular fluids. Biochemical society transactions 1982, 10, 72–73.
Baldwin, D.A., Jenny, E.R., Aisen, P. The effect of human transferrin and milk lactoferrin on hydroxyl radical formation from superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. J Biol Chem 1984, 259, 13391–13394.
Gutteridge, J.M.C, Paterson, S.K., Segal, A.W. et al. Inhibition of lipid peroxidation by the ironbinding protein lactoferrin. Biochem J 1981, 199, 259–261.
Levick, J.R. Permeability of rheumatoid and normal human synovium to specific plasma proteins. Arthritis Rheum 1981, 24, 1550–1560.
Muirden, K.D., Fraser, J.R.E., Clarris, B. Ferritin formation by synovial cells exposed to haemoglobin in vitro. Ann Rheum Dis 1967, 26, 251–259.
Bennett, R.M., Williams, E.D., Lewis, S.M., Holt, P.J.L. Synovial iron deposition in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 1973, 16, 298–304.
Mowat, A.G., Hothersall, T.E. Nature of anemia in rheumatoid arthritis. VIII. Iron content of synovial tissue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and in normal individuals. Ann Rheum Dis 1968, 27, 345–350.
Biemond, P., Van Eijik, H.G., Swaak, A.J.G. et al. Iron mobilization from ferritin by superoxide derived from stimulated polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest 1984, 73, 1576–1579.
Etherington, D.J., Pugh, G., Silver, I.A. Collagen degradation in an experimental inflammatory lesion: studies on the role of the macrophage. Acta Biol Med Germ 1981, 40, 1625–1631.
Blake, D.R., Hall, N.D., Bacon, P.A. et al. The importance of iron in rheumatoid disease. Lancet 1981, 21, 1142–1143.
Kontoghiorghes, G.J. Iron mobilization from lactoferrin by chelators at physiological pH. Biochim Biophys Acta 1986, 882, 267–270.
Andrews, F.J., Morris, C.J., Kondratowicz, G. et al. Effect of iron chelation on inflammatory joint disease. Ann Rheum Dis 1987, 46, 327–333.
Ambruso, D.R., Johnston, R.B. Jr. Lactoferrin enhances hydroxyl radical production by human neutrophils, neutrophil particulate fraction, and an enzymatic generating system. J Clin Invest 1981, 67, 352–360.
Robbins, D.L., Feigal, D.W., Leek, J.C. Relation of serum IgG rheumatoid factor to IgM rheumatoid factor and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 1986, 13, 259–262.
Mallya, R.K., Vergani, D., Tee, D.E.H. et al. Correlation in rheumatoid arthritis of concentrations of plasma C3d, serum rheumatoid factor, immune complexes and C-reactive protein with each other and with clinical features of disease activity. Clin Exp Immunol 1982, 48, 747–753.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadzadeh, N., Shingu, M. & Nobunaga, M. Iron-binding proteins and free iron in synovial fluids of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol 8, 345–351 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02030347
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02030347