Abstract
Fourteen female patients 27.7 ± 10.0 years of age were studied by electrophysiological means before and during general anaesthesia. A mixture of thiopentone sodium, enflurane and nitrous oxide was used for anaesthesia. Electroretinogram (ERG) and visual evoked potentials (VEP) were recorded with electrodes placed on the lower lid and scalp and an averaging technique was used. The recordings were made under standard conditions with the pupils dilated, the eyes adapted to the dark and after 15–20 min stable anaesthesia.
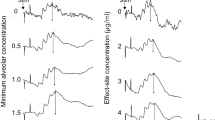
The latency of the a-wave did not change, whereas the b-wave was delayed (P<0.01). The amplitude of the a-wave tended to decrease; however, an increase of amplitude was also present. Therefore the change was not significant. The b-wave was unchanged.
Changes induced by anaesthesia were often noted in the shape of P130, where a change from V to W-form took place or the reverse. The latencies of the late components N180 and P220 were increased during anaesthesia (P=0.006 andP=0.001, respectively). No statistically significant change occurred in the N180 and P220 amplitudes. The amplitudes of N60 and P130 became smaller (P=0.002 andP=0.0003, respectively) during anaesthesia. The effect of enflurane on the components of the VEP seems to indicate a cortical site of action.
Zusammenfassung
Bei vierzehn Frauen mit einem durchschnittlichen Alter von 27.7 ± 10.0 Jahren wurden das Elektroretinogramm (ERG) sowie die visuell evozierten Potentiale (VEP) unter Standardbedingungen vor und während der Allgemeinanästhesie mit einer Thiopenton Natrium-Enfluran-Lachgas-Mischuing registriert. Die Ableitungsstelle für die VEP lag 2 cm über dem Inion (O0 des internationalen 10–20 Systems) in der okzipitalen Mittellinie. Die Ableitungselektrode für das ERG befand sich am Unterlid. Zur Mittelwertbildung wurde ein Summationselektronenrechner (Nokia) angewandt.
Die Aufzeichnungen wurden unter konstanten Bedingungen mit erweiterter Pupille sowie Dunkeladaptation des Auges 15–20 Minuten nach Verabreichung der Anästhesie durchgeführt. Die Latenz der a-Welle des ERGs blieb unverändert während sich die der b-Welle verlängerte (P<0.01). Die Amplitude der a-Welle tendierte zu einer Erniedrigung, jedoch kann auch eine erhöhte a-Welle vorkommen. Eine Signifikanz lag deshalb nicht vor. Die Amplitude der b-Welle blieb unverändert.
P130 der VEP zeigte eine Veränderung der Form von V in W Form und entgegengesetzt. Die späten Komponenten N180 und P220 waren verzögert (P=0.006 undP=0.001). Eine statistisch signifikante Veränderung der Amplituden von N180 und P220 konnte nicht festgestellt werden. Die Amplituden von N60 und P130 wurden kleiner (P=0.002 undP=0.003). Die Veränderungen der späten Komponente der visuell evozierten Potetentale während der Allgemeinanaesthesie mit Enfluran deuten auf einen kortikalen Einfluß hin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam N, Collins CJ (1979) Alterations by enflurane of electrophysiologic correlates of search in short-term memory. Anesthesiology 50:93–97
Black GW (1979) Enflurane. Br J Anaesth 51:627–637
Burchiel KJ, Stockard JJ, Myers RR, Bickford RG (1975) Visual and auditory evoked responses during enflurane anesthesia in man and cats. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 39: 434
Clark DL, Rosner BS (1973) Neurophysiologic effect of general anesthetics. I. The electroendephalogram and sensory evoked responsed in man. Anesthesiology 38:564–582
Conover WJ (1971) Practical non parametric statistics. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 206–209
Kending JJ, Trudell JR (1974) Approaches to a theory of anaesthetic action. In: Scientific Foundations of Anaesthesia. William Heinemann Medical Books, London
Raitta C, Karhunen U, Seppäläinen AM, Naukkarinen M (1979) Changes in the electroretinogram and visual avoked potentials during general anaesthesia. Albrecht von Graefes Arch Klin Exp Ophthalmol 211:139–211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raitta, C., Karhunen, U. & Seppäläinen, A.M. Changes in the electroretinogram and visual evoked potentials during general anaesthesia using enflurance. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 218, 294–296 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02150441
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02150441