Abstract
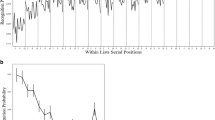
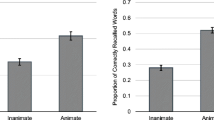
A series of five experiments was conducted to investigate the temporal aspects of human memory consolidation of symbolic material through the administration of amphetamine. Subjects had to recall or recognise unrelated words from a previously presented list. The first experiments support the conjecture, based on animal studies, that amphetamine enhances long-term memory performance. Subsequently, enhancement is demonstrated with oral administration before learning, as well as with intramuscular injection after learning. It is shown that improved recall cannot be explained solely by general arousal or attentional processes, but must be due to consolidation. By introducing different test delays we show that consolidation of symbolic material can be modulated by amphetamine during the 1st hour after learning. In a final experiment we demonstrate that the memory enhancement applies to recall as well as to recognition. The implications of the present results are discussed in the context of recent research on LTP processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39
Bliss TVP, Goddard GV, Riivis M (1983) Reduction of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of the rat following selective depletion of monoamines. J Physiol 334:475–491
Delanoy RL, Tucci DL, Gold PE (1983) Amphetamine effects on long term potentiation in dentate granule cells. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18:137–139
Duncan CP (1949) The retroactive effect of electroshock on learning. J Comp Physiol Psychol 42:32–44
Glanzer M (1972) Storage mechanisms in recall. In: Bower GH (ed) The psychology of learning and motivation: advances in research and theory. Academic Press, New York, pp 129–193
Gold PE, Van Buskirk RB (1975) Facilitation of time-dependent memory processes with posttrial epinephrine injection. Behav Biol 13:145–153
Gold PE, Delanoy RL, Merrin J (1984) Modulation of long-term potentiation by peripherally administered amphetamine and epinephrine. Brain Res 305:103–107
Hopkins WF, Johnston D (1984) Noradrenergic enhancement of long-term potentiation at mossy-fiber synapses in the hippocampus. J Neurophys 59:667–687
Janak PH, Martinez JL (1992) Cocaine and amphetamine facilitate retention of jump-up responding in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 41:837–840
Kesner RP, Bierley RA, Pebbles P (1981) Short-term memory: the role ofd-amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:673–676
Kleinsmith LJ, Kaplan S (1963) Paired-associate learning as a function of arousal and interpolated interval. J Exp Psychol 65:190–193
Krivanek JA, McGaugh JL (1969) Facilitating effects of pre- and posttrial amphetamine administration on discrimination learning in mice. Agents Actions 1:36–42
Martinez J, Jensen R, Messing RB, Vasquez BJ, Soumireu-Mourat B, Geddes D, Liang KC, McGaugh JL (1980) Central and peripheral actions of amphetamine on memory storage. Brain Res 182:157–166
McGaugh JL (1973) Drug facilitation of learning and memory. Annu Rev Pharmacol 13:229–241
McGaugh JL, Dawson RG (1971) Modification of memory storage processes. Behav Sci 16:45–63
McGaugh JL, Herz MJ (1972) Memory consolidation. Albion Publishing Company, San Francisco
Morimoto K, Otani S, Goddard G (1987) Effects of acute and long-term treatment with amphetamine on evoked responses and long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of anaesthetised rats. Brain Res 407:137–143
Murdock BB (1962) The serial-position effect of free recall. J Exp Psychol 64:482–488
Newhouse PA, Sunderland T, Tariot PN, Blumhardt CL, Weingartner H, Mellow A, Murphy DL (1988) Intravenous nicotine in Alzheimer's disease: a pilot study. Psychopharmacology 95:171–175
Oscos A, Martinez JL, McGaugh JL (1988) Effects of post-trainingd-amphetamine on acquisition of an appetitive autoshaped lever press response in rats. Psychopharmacology 95:132–134
Rapoport JL, Buchsbaum MS, Weingartner H, Zahn TP, Ludlow C, Mikkelsen EJ (1980) Dextroamphetamine: its cognitive and behavioural effects in normal and hyperactive boys and normal men. Arch Gen Psychiatry 37:933–943
Russell WR, Nathan PW (1946) Traumatic amnesia. Brain 69:280–300
Sanders AF, Wertheim AH (1973) The relation between physical stimulus properties and the effect of foreperiod duration on reaction time. Q J Exp Psychol 25:201–206
Spetch ML, Treit D (1984) The effect ofd-amphetamine on short-term memory for time in pigeons. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21:663–666
Squire LR (1982) The neuropsychology of human memory. Annu Rev Neurosci 5:241–273
Squire LR, Slater PC, Chace PM (1975) Retrograde amnesia: temporal gradient in very long-term memory following electrocon-vulsive therapy. Science 187:77–79
Wetzel DA, Squire LR, Janowsky DS (1981) Methylphenidate impairs learning and memory in normal adults. Behav Neural Biol 31:413–424
Wynn LC, Solomon RL (1955) Traumatic avoidance learning: acquisition and extinction in dogs deprived of normal peripheral autonomic function. Gen Psychol Monogr 52:241–284
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soetens, E., Hueting, J.E., Casaer, S. et al. Effect of amphetamine on long-term retention of verbal material. Psychopharmacology 119, 155–162 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246156
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02246156