Summary
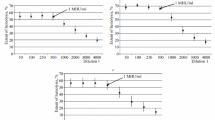
Sera from 93 patients with systemic scleroderma including incipient or prodromal acroscleroderma and from 43 healthy individuals were studied for cytotoxic effects on endothelial cells by means of three different in vitro methods. Inhibition of3H-thymidine incorporation by endothelium was caused by about 33% of sera, almost exclusively from patients with diffuse scleroderma and the transitional form: acroscleroderma—diffuse scleroderma. An antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity assay revealed cytotoxicity of about 37% of sera from patients with diffuse sceroderma and the transitional form but also of a proportion of sera from patients with CREST syndrome with pronounced vascular changes. Serum cytotoxic activity, revealed by both methods, was related with more frequent involvement of muscle and kidney in the patients. A direct51Cr release assay showed the cytotoxicity only in 4 of 68 cases in diffuse scleroderma with pronounced internal organ involvement. Thus, depending on the method used, various types of cytotoxicity could be detected in sera from patients with systemic scleroderma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LeRoy EC (1982) Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). J Invest Dermatol [Suppl] 79: 87–89
Fleischmajer R, Perlish JS, Duncan M (1983) Scleroderma. A model for fibrosis. Arch Dermatol 119: 957–962
Lee EB, Anhalt GJ, Voorhees JJ, Diaz LA (1984) Pathogenesis of scleroderma: current concepts. Int J Dermatol 23: 85–89
Kahaleh MB, LeRoy EC (1985) The vascular disease in scleroderma. In: Black CM, Myers AR (eds) Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Gower, New York, pp 242–248
Fleischmajer R, Perlish JS (1980) Capillary alterations in scleroderma. J Am Acad Dermatol 2: 161–170
Norton WL, Nadaro JM (1970) Vascular disease in progressive systemic scleroderma. Ann Intern Med 73: 317–324
Fleischmajer R, Perlish JS (1977)3H-Thymidine labeling of dermal endothelial cells in scleroderma. J Invest Dermatol 69: 379–382
Kazandjian S, Fiessinger JN, Camilleri JP, Dadoune JP, Housset E (1982) Endothelial cell renewal in skin of patients with progressive systemic sclerosis (PSS): an in vitro autoradiographic study. Acta Derm Venereol [Stockh] 62: 425–429
Majewski S, Skopinska-Rożewska E, Jablonska S, Polakowski I, Pawinska M, Marczak M, Szmurlo A (1985) Modulatory effect of sera from scleroderma patients on lymphocyte-induced angiogenesis. Arthritis Rheum 27: 1133–1139
Kahaleh MB, Sherer GK, LeRoy EC (1979) Endothelial injury in scleroderma. J Exp Med 149: 1326–1335
Kahaleh MB, LeRoy EC (1983) Endothelial injury in scleroderma. A protease mechanism. J Lab Clin Med 101: 553–560
Shanahan WR Jr, Korn JH (1982) Cytotoxic activity of sera from scleroderma and other connective tissue diseases. Lack of cellular and disease specificity. Arthritis Rheum 25: 1391–1395
Cohen S, Johnson AR, Hurd E (1983) Cytotoxicity of sera from patients with scleroderma. Effect on human endothelial cells and fibroblasts in culture. Arthritis Rheum 26: 170–178
Drenk F, Mensing H, Serbin A, Deicher H (1985) Studies on endothelial cell cytotoxic activity in sera of patients with progressive systemic sclerosis, Raynaud syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int 5: 259–263
Drenk F, Lubach D, Schwabe C, Deicher H (1987) Endothelial cytotoxic activity (ECA) in sera of patients with livedo racemosa generalisata Ehrmann. Arch Dermatol Res 279: 415–417
Blake DR, Winyard P, Scott DGI, Brailsford S, Blann A, Lunec J (1985) Endothelial cell cytotoxicity in inflammatory vascular disease — the possible role of oxidised lipoproteins. Ann Rheum Dis 44: 176–182
Summers GD, Weiss JB, Jayson MIV (1985) Failure of sera from patients with scleroderma to exhibit cytotoxicity towards human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Rheumatol Int 5: 9–13
Penning CA, Cunningham J, French MAH, Harrison G, Rowell NR, Hughes P (1984) Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of human vascular endothelium in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Immunol 58: 548–556
Subcommittee for Scleroderma Criteria of the ARA Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee (1980) Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum 23: 581–590
Jablonska S (1975) Scleroderma and pseudoscleroderma. Polish Medical Publishers, Warsaw
Rodnan GP, Jablonska S, Medsger TA Jr (1979) Classification and nomenclature of progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Clin Rheum Dis 5: 5–13
Beutner EH, Nisengard RL, Kumar V (1979) Defined immunofluorescence: basic concepts and their application to clinical immunodermatology. In: Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP, Bean SF (eds) Immunopathology fo the skin. Wiley, New York, pp 29–75
Tan EM, Rodnan GP, Garcia I, Moroi Y, Fritzler MJ, Peebles C (1980) Diversity of antinuclear antibodies in progressive systemic sclerosis: anti-centromere antibody and its relationship to CREST syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 23: 617–625
Jarzabek-Chorzelska M, Blaszczyk M, Jablonska S, Chorzelski TP, Kumar V, Beunter EH (1986) Scl 70 antibody — a specific marker of systemic sclerosis. Br J Dermatol 115: 393–401
Kaminski KJ, Nowaczyk M, Skopinska-Rożewska E, Kaminska G, Bem W (1981) Human peripheral blood T-lymphocyte subpopulations isolated on the basis of their affinity for sheep red blood cells differ in angiogenesis-inducing capability. Clin Exp Immunol 46: 327–331
Jaffe EA (1980) Culture of human endothelial cells. Transplant Proc [Suppl] 12: 49–53
Majewski S, Kaminski MJ, Szmurlo A, Kaminska G, Malejczyk J (1984) Inhibition of tumour-induced angiogenesis by systemically administered protamine sulphate. Int J Cancer 33: 831–833
Reynolds TB, Denison EK, Frankl HD, Lieberman FL, Peters RL (1971) Primary biliary cirrhosis with scleroderma, Raynaud's phenomenon and teleangiectasia. New Syndrome. Am J Med 50: 302–305
Salerni R, Rodnan GP, Leon DF, Shaver JA (1977) Pulmonary hypertension in the CREST syndrome variant of progressive systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Ann Intern Med 80: 394–399
Chorzelski TP, Jablonska S, Beutner EH, Blaszczyk M, Jarzabek-Chorzelska M, Kencka D, Krasny S, Kumar V, Tchórzewska H (1985) Anticentromere antibody: an immunological marker of a subset of systemic sclerosis. Br J Dermatol 113: 381–389
Lakomek HJ, Guldner HH, Bautz FA, Georz G, Kind P, Mensing H, Krüskemper HL (1987) Kernantikörper als serologische Marker der progressiven systemischen Sklerodermie (PSS). Hautarzt 38: 63–68
Nunzi E, Rebora A (1983) Are endothelial cells stimulated by autoantibodies in scleroderma? Acta Derm Venereol [Stockh] 63: 458–459
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majewski, S., Blaszczyk, M., Jabłonska, S. et al. Cytotoxic effects of sera from patients with systemic scleroderma: Comparison of three different in vitro methods. Rheumatol Int 10, 65–70 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02274785
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02274785