Summary
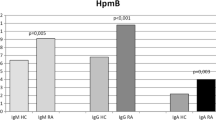
IgM, IgG and IgA class antibodies againstYersinia, Salmonella, Campylobacter andBorrelia were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in a group of 340 unselected patients with a recent inflammatory joint disease. The control group consisted of 340 and 100 healthy blood donors usingBorrelia-ELISA and other ELISAs, respectively. Of all the patients, 27.4% had increased antibody levels against at least one of the microbes tested. The prevalence of positive antibody levels was highest inYersinia antibodies (17.9%). The corresponding figures forSalmonella, Campylobacter andBorrelia were 7.0, 6.2 and 1.8%, respectively. Patients with entero-arthritis or clinically typical reactive arthritis who had not had gastrointestinal or urogenital symptoms previously had the highest prevalence of the microbial antibodies (67.6 and 40.7%, respectively). These findings indicate that arthritis may often have a reactive etiopathogenesis without recognized gastrointestinal infection, emphasizing the importance of microbial serology in the differential diagnosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toivanen A, Toivanen P (eds) (1988) Reactive arthritis. CRC, Boca Raton, Fla
Keat A (1983) Reiter's syndrome and reactive arthritis in perspective. N Engl J Med 309: 1606–1615
Valtonen VV, Leirisalo M, Pentikäinen PJ, Räsänen T, Seppälä I, Larinkari U, Ranki M, Koskimies S, Malkamäki M, Mäkelä PH (1985) Triggering infections in reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 44: 399–405
Stiernstedt G, Granström M (1985)Ixodes ricinus spirochete infection as the cause of postinfectious arthritis in Sweden. Scand J Rheumatol 14: 336–342
Steere A (1989) Lyme disease. N Engl J Med 321: 586–596
Weyand CM, Goronzy JJ (1989) Immune responses toBorrelia burgdorferi in patients with reactive arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 32: 1057–1064
Leirisalo M, Skylv G, Kousa M, Voipio-Pulkki LM, Suoranta H, Nissilä M, Hvidman L, Nielsen ED, Svejgaard A, Tiilikainen A, Lahtinen O (1982) Follow-up study on patients with Reiter's disease and reactive arthritis, with special reference to HLA-B27. Arthritis Rheum 25: 249–259
Hannu TJ, Leirisalo-Repo M (1988) Clinical picture of reactiveSalmonella arthritis. J Rheumatol 15: 1668–1671
Granfors K, Isomäki H, Essen R von, Maatela J, Kalliomäki JL, Toivanen A (1983)Yersinia antibodies in inflammatory joint diseases. Clin Exp Rheumatol 1: 215–218
Leino R (1982) Human yersiniosis. A clinical study with special reference to lymphocyte transformation inYersinia arthritis. Thesis, Turku, Finland
Ropes MW, Bennett GA, Cobb S, Jacox R, Jessar RA (1958) Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis 9: 175–176
Kellgren JH, Jeffrey MR, Ball J (1963) Clinical criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. In: Kellgren JH, Jeffrey MR, Ball J (eds) The epidemiology of chronic rheumatism, vol 1. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 326–327
Granfors K (1979) Measurement of immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG and IgA antibodies againstYersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay: persistence of serum antibodies during disease. J Clin Microbiol 9: 336–341
Granfors K, Ogasawara M, Hill JL, Lahesmaa-Rantala R, Toivanen A, Yu DTY (1989) Analysis of IgA antibodies to lipopolysaccharide inYersinia-triggered reactive arthritis. J Infect Dis 159: 1142–1147
Granfors K, Lahesmaa-Rantala R, Ståhlberg TH, Toivanen A (1989) Comparison of bacteria with and without plasmid-encoded proteins as antigens for measurement of immunoglobulin M, G and A antibodies toYersinia enterocolitica by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol 27: 583–585
Mäki-Ikola O, Heesemann J, Lahesmaa R, Toivanen A, Granfors K (in press) Combined use of released proteins and lipopolysaccharide in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for serological screening ofYersinia infections. J Infect Dis
Isomäki O, Vuento R, Granfors K (1989) Serological diagnosis ofSalmonella infections by enzyme immunoassay. Lancet 1: 1411–1414
Kosunen TU, Rautelin H, Pitkänen T, Pönkä A, Pettersson T (1983) Antibodies against an acid extract from a singleCampylobacter strain in hospitalized campylobacter patients. Infection 11: 189–191
Viljanen MK, Punnonen J (1989) The effect of storage of antigen-coated polystyrene microwells on the detection of antibodies againstBorrelia burgdorferi by enzyme immunoassay (EIA). J Immunol Methods 124: 137–141
van Bohemen ChG, Nabbe AJJM, Zanen HC, Goei The HS (1986) Serology and bacteriology in reactive arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 45: 262–263
Palombi L, Mancinelli S, Marazzi MC, Galeazzi M, Pasquini P, Gospodinoff A, Pana A (1989) Antimicrobial antibodies in patients with a non-specific arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 7: 659–660
Lapadula G, Covelli M, Numo R (1988) Antibacterial antibody pattern in seronegative spondyloarthropathies (SNSA). Clin Exp Rheumatol 6: 385–390
Kryger P, Hansen K, Vinterberg H, Pedersen FK (1990) Lyme borreliosis among Danish patients with arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 19: 77–81
Cooper C, Muhlemann M, Wright DJM, Hutchinson CA, Armstrong R, Maini RN (1987) Arthritis as manifestation of Lyme disease in England. Lancet I: 1313–1314
Kalliomäki JL, Leino R (1979) Follow-up studies of joint complications in yersiniosis. Acta Med Scand 205: 521–525
Marsal L, Winblad S, Wollheim FA (1981)Yersinia enterocolitica arthritis in southern Sweden: a four-year follow-up study. Br Med J 283: 101–103
Granfors K, Jalkanen S, Essen R von, Lahesmaa-Rantala R, Isomäki O, Pekkola-Heino K, Merilahti-Palo R, Saario R, Isomäki H, Toivanen A (1989)Yersinia antigens in synovial-cells from patients with reactive arthritis. N Engl J Med 320: 216–221
Granfors K, Jalkanen S, Lindberg AA, Mäki-Ikola O, Essen R von, Lahesmaa-Rantala R, Isomäki H, Saario R, Arnold WJ, Toivanen A (1990)Salmonella lipopolysaccharide in synovial fluid cells from patients with reactive arthritis. Lancet 335: 685–688
Schumacher HR Jr, Magge S, Cherian PV, Sleckman J, Ruthfuss S, Clayburne G, Streck M (1988) Light and electron microscopic studies on the synovial membrane in Reiter's syndrome: immunocytochemical identification of chlamydial antigen in patients with early disease. Arthritis Rheum 31: 937–946
Keat A, Thomas B, Dixey J, Osborn M, Sonnex C, Taylor-Robinson D (1987)Chlamydia trachomatis and reactive arthritis: the missing link. Lancet I: 72–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mäki-Ikola, O., Viljanen, M.K., Tiitinen, S. et al. Antibodies to arthritis-associated microbes in inflammatory joint diseases. Rheumatol Int 10, 231–234 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02274884
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02274884