Abstract
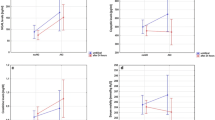
The diagnosis and evaluation of perinatal asphyxia can be problematic and objective means of assessing its severity are lacking. To study the validity of urinary uric acid as a marker of the degree of perinatal asphyxia, the ratio of urinary uric acid to creatinine (UA/Cr) in urine specimens obtained after birth was measured in two groups of infants. Eighteen term infants with Apgar scores ≤ 5 at 5 min and/or an umbilical cord blood pH ≤ 7.2, and a base deficit ≽ 12 meq/1 were compared to 50 healthy controls. The severity of the perinatal asphyxia was determined by using an ASPHYXIA SCORE. The UA/Cr was higher in the asphyxiated group when compared to controls. (2.06 ± 1.12, vs. 0.64 ± 0.48;P < 0.001). Within the perinatal asphyxia group, a significant correlation was found between the UA/Cr ratio and the asphyxia score. (r = 0.86,P < 0.01).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- UA/CR :
-
uric acid/creatinine
References
Bloom RS (1992) Delivery room resuscitation of the newborn. In: Fanaroff AA, Martin RJ (eds) Neonatal-perinatal medicine. Disease of the fetus and infant. Mosby Year Book, Toronto, pp 301–323
Buther AR (1975) The Jaffe reaction. Identification of the coloured species. Clin Chem Acta 59:227–232
Fossata P, Prencple L, Berti G (1980) Use of 3,5 Dichloro-2 hydroxybenzene sulforic and 4- aminophenazone chromogenic system in direct enzymatic assay of uric acid in serum and urine. Clin Chem 26:227–231
Hasday JD, Grum CM (1987) Nocturnal increase of urinary uric acid: Creatinine ratio. A biochemical correlate of sleep-associated hypoxemia. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:534–538
Marlow N (1992) Do we need an apgar score? Arch Dis Child 76:765–769
Mehes K, Horvath I, Szakolczai I (1981) Uric acid in a single urine sample from neonates with perinatal hypoxia. Acta Pediatr Hung 22:43–47
Portman RJ, Carter BS, Gaylord MS, Murphy MG, Thieme RE, Merenstein GB (1990) Predicting neonatal morbidity after perinatal asphyxia: A scoring system. Am J Obstet Gynecol 162:174–182
Poulsen JP, Rognum TO, Oyasaeter S, Saugstad OD (1990) Changes in oxypurine concentration in vitreous humor of pigs during hypoxemia and post-mortem. Pediatr Res 28:482–484
Poulsen JP, Oyasaeter S, Sanderud J, Rognum TO, Saugstad OD (1990) Hypoxanthine, xanthine, and uric Acid concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid, plasma, and urine of hypoxemic pigs. Pediatr Res 28:477–481
Press WH, Flannery BP, Tukolsky SA, Vetterling WT (1989) Statistical description of Data. Numerical recipes. In: Press WH (eds) Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, pp 454–497
Russell GAB, Jeffers G, Cooke RWI (1992) Plasma hypoxanthine: a marker for hypoxic-ischemic induced periventricular leucomalacia? Arch Dis Child 67:388–392
Saugstad CD (1988) Hypoxanthine as an indicator of hypoxia: Its role in health and disease through free radical production. Pediatr Res 23:143–150
Swanstrom S, Bratteby LE (1982) Hypoxanthine as a test of perinatal hypoxia as compared to lactate, base deficit, and pH. Pediatr Res 16:156–160
Thringer K (1983) Cord plasma hypoxanthine Aa measure of fetal asphyxia. Acta Pediatr Scand 72:231–237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bader, D., Gozal, D., Weinger-Abend, M. et al. Neonatal urinary uric acid/ceratinine ratio as an additional marker of perinatal asphyxia. Eur J Pediatr 154, 747–749 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02276720
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02276720