Summary
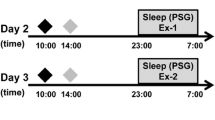
Acute loss of sleep produces few apparent physiological effects at rest. Nevertheless, many anecdotes suggest that adequate sleep is essential for optimum endurance athletic performance. To investigate this question, heavy exercise performance after 36 h without sleep was compared with that after normal sleep in eight subjects. During prolonged treadmill walking at about 80% of the\(\dot V_{O_2 } \) max, sleep loss reduced work time to exhaustion by an average of 11% (p=0.05). This decrease occurred despite doubling monetary incentives for subjects during work after sleeplessness. Subjects appeared to fall into “resistant” and “susceptible” categories: four showed less than a 5% change in performance after sleep loss, while four others showed decrements in exercise tolerance ranging from 15 to 40%. During the walk, sleep loss resulted in significantly greater perceived exertion (p<0.05), even though exercise heart rate and metabolic rate (\(\dot V_{O_2 } \) and\(\dot V_{CO_2 } \)) were unchanged. Minute ventilation was significantly elevated during exercise after sleep loss (p<0.05). Sleep loss failed to alter the continuous slow rises in\(\dot V_E \) E and heart rate that occurred as work was prolonged. These findings suggest that the psychological effects of acute sleep loss may contribute to decreased tolerance of prolonged heavy exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
åstrand P-O, Ryhming I (1954) A nomogram for calculation of aerobic capacity (physical fitness) from pulse rate during submaximal work. J Appl Physiol 7: 218–221
Bergstrom J, Hermansen L, Hultman E, Saltin B (1967) Diet, muscle glycogen, and physical performance. Acta Physiol Scand 71: 140–150
Borg G (1974) Perceived exertion. In: Wilmore JH (ed) Exercise and sports science reviews. Academic Press, New York, pp 131–153
Brodan B, Vostechovsky M, Kuhn M, Cepelak J (1969) Changes of mental and physical performance in sleep deprived healthy volunteers. Act Nerv Super 11: 175–181
Copes K, Rosentweig J (1972) The effects of sleep deprivation upon motor performance of ninth-grade students. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 12: 47–53
Costill DL, Gollnick PD, Jansson ED, Saltin B, Stein EM (1973) Glycogen depletion pattern in human muscle fibers during distance running. Acta Physiol Scand 89: 374–383
Costill DL, Dalsky GP, Fink WJ (1978) Effects of caffeine injection on metabolism and exercise performance. Med Sci Sports 10: 155–158
Dempsey JA, Gledhill N, Reddan WG, Forster HV, Hanson PG, Claremont AD (1977) Pulmonary adaptation to exercise: effects of exercise type and duration, chronic hypoxia, and physical training. Ann NY Acad Sci 301: 243–261
Ekblom B, Goldbarg AN, Gullbring B (1972) Response to exercise after blood loss and reinfusion. J Appl Physiol 33: 175–180
Fiorica V, Higgins EA, Iampietro PF, Lategola MT, Davis AW (1968) Physiological responses of men during sleep deprivation. J Appl Physiol 24: 167–176
Harris W, O'Hanlon JF (1972) A study of recovery functions in man. In: US Army Technical Memorandum, 10–72. Aberdeen Research and Development Center, Maryland
Heistad DD, Wheeler RC, Mark AL, Schmid PG, Abboud FM (1972) Effects of adrenergic stimulation on ventilation in man. J Clin Invest 51: 1469–1475
Hermansen L, Hultman E, Saltin B (1967) Muscle glycogen during prolonged severe exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 71: 129–139
Kleitman N (1963) Sleep and wakefulness. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Martin BJ, Gaddis GM (1981) Effects of sleep deprivation on exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc (in press)
Morgan WP (1973a) Psychological factors influencing perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports 5: 97–103
Morgan WP, Raven PB, Drinkwater BL, Horvath SM (1973b) Perceptual and metabolic responsivity to standard bicycle ergometry following various hypnotic suggestions. Int J Clin Exp Hypn 21: 86–101
Noble BJ, Metz KF, Pandolf KB, Cafarelli E (1973) Perceptual responses to exercise: a multiple regression study. Med Sci Sports 5: 104–109
Opstad PK, Aakvaag A, Rognum TO (1980) Altered hormonal response to short-term bicycle exercise in young men after prolonged physical strain, caloric deficit, and sleep deprivation. Eur J Appl Physiol 45: 51–62
Phillipson EA (1978) Respiratory adaptations in sleep. Annu Rev Physiol 40: 133–156
Pickett GF, Morris AF (1975) Effects of acute sleep and food deprivation on total body response time and cardiovascular performance. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 15: 49–56
Rowell LB (1974) Human cardiovascular adjustments to exercise and thermal stress. Physiol Rev 54: 75–159
Shephard RJ (1969) Learning, habituation, and training. Int Z Angew Physiol 28: 38–48
Sutton JR, Jones NL (1979) Control of pulmonary ventilation during exercise and mediators in the blood: CO2 and hydrogen ion. Med Sci Sports 11: 198–203
Walker JM, Floyd TC, Fein G, Cavness C, Lualhati R, Feinberg I (1978) Effects of exercise on sleep. J Appl Physiol 44: 945–951
Wasserman K (1978) Breathing during exercise. N Engl J Med 298: 780–785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by Public Health Service grant PHS S07 RR 5371, and by Grant DAMD-17-81-C-1023 from the U.S. Army
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, B.J. Effect of sleep deprivation on tolerance of prolonged exercise. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 47, 345–354 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02332962
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02332962