Summary
Specialised gastrointestinal absorption of amoxicillin has been suggested in man and has been demonstrated in animals. In order to study the rate and extent of amoxicillin absorption, six healthy subjects were given 500 mg IV and two oral doses (500 mg and 3 g as a suspension). Absorption kinetics was analysed by compartmental modelling, noncompartmental methods and by calculation of absorption rates using deconvolution.
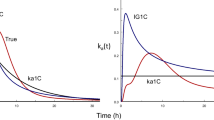
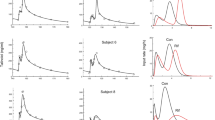
Dose-dependency of the extent of amoxicillin absorption was observed, with a lower than expected mean maximum plasma concentration (49%), and fraction of the dose absorbed (39%) after the 3 g dose calculated from the 500 mg dose, assuming kinetic linearity. Zero-order kinetics of absorption was apparent in some subjects after the 500 mg dose, both from model fitting and absorption rate profile. However, no pattern consistent with pure first-order or zero-order absorption was observed after both oral doses in any individual. The dose-dependency of amoxicillin absorption was confirmed by a trend to an increased time of absorption for the high dose.
The results show the variable nature and nonlinearity of the gastrointestinal absorption of amoxicillin and indicate the involvement of a number of factors, in addition to simple diffusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsuji A, Nakashima E, Kagami I, Honjo N, Yamana T (1977) Effect of dose-concentration on the absorption of amoxicillin and ampicillin from the rat intestine. J Pharm Pharmacol 29: 707–708
Tsuji A, Nakashima E, Hamano S, Yamana T (1978) Physicochemical properties of amphoteric β-lactam antibiotics: I. Stability, solubility, and dissolution behavior of amino penicillins as a function of pH. J Pharm Sci 67: 1059–1065
Kimura T, Endo H, Yoshikawa M, Muranishi S, Sezaki H (1978) Carrier-mediated transport systems for aminopenicillins in rat small intestine. J Pharmacobiodyn 1: 262–267
Nakashima E, Tsuji A, Kagatani S, Yamana T (1984) Intestinal absorption mechanism of amino-β-lactam antibiotics: III. Kinetics of carrier-mediated transport across the rat small intestine in situ. J Pharmacobiodyn 7: 452–464
Sjövall J, Alván G, Westerlund D (1985) Dose-dependent absorption of amoxicillin and bacampicillin. Clin Pharmacol Ther 38: 241–250
Sjövall J, Alván G, Westerlund D (1985) Oral cyclacillin interacts with the absorption of oral ampicillin, amoxicillin, and bacampicillin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29: 495–502
Simmons NA, Cawson RA, Clarke CA, Eykyn SJ, Guedes AM, Littler WA, McGowan DA, Oakley CM, Shanson DC (1986) Prophylaxis of infective endocarditis. Lancet 1: 1267
Nord CE, Edlund C (1990) Impact of antimicrobial agents on the intestinal microflora. J Chemother 2: 218–237
Sjövall J, Alvdn G, Åkerlund JE, Svensson JO, Paintaud G, Nord CE, Angelin B (1992) Dose-dependent absorption of amoxicillin in patients with ileostomy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 43: 277–281
Metzler CM (1987) Extended least squares (ELS) for pharmacokinetic models. J Pharm Sci 76: 565–571
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (1982) Pharmacokinetics. Dekker, New York
Sjövall J, Westerlund G, Alván G (1985) Renal excretion of intravenously infused amoxicillin and ampicillin. Br J Clin Pharmacol 19: 191–201
Riegelman S, Collier P (1980) The application of statistical moment theory to the evaluation of in vivo dissolution time and absorption time. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 8: 509–534
Iga K, Ogawa Y, Yashiki T, Shimamoto T (1986) Estimation of drug absorption rates using a deconvolution method with nonequal sampling times. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 14: 213–225
Reigner BG, Couet W, Guedes JP, Fourtillan JB, Tozer TN (1990) Saturable rate of cefatrizine absorption after oral administration to humans. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 18: 17–34
Boxenbaum HG, Riegelman S, Elashoff RM (1974) Statistical estimations in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 2: 123–148
Schuirmann D (1987) A comparison of the two one-sided test procedure and the power approach for assessing the equivalence of average bioavailability. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 15: 657–680
Tsuji A, Nakashima E, Kagami I, Yamana T (1981) Intestinal absorption mechanism of amphoteric β-lactam antibiotics: II. Michaelis-Menten kinetics of cyclacillin absorption and its pharmacokinetic analysis in rats. J Pharm Sci 70: 772–777
Sjövall J, Alván G, Huitfeldt B (1986) Intra- and inter-individual variation in pharmacokinetics of intravenously infused amoxicillin and ampicillin to elderly volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 21: 171–181
Welling PG, Huang H, Koch PA, Craig WA, Madsen PO (1977) Bioavailability of ampicillin and amoxicillin in fasted and nonfasted subjects. J Pharm Sci 66: 549–552
Veng-Pedersen P (1990) Reply to “Comments on two recent deconvolution methods”: II. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 18: 491–495
Verotta D (1990) Comments on two recent deconvolution methods. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 18: 483–499
Dalhoff A, Koeppe P, von Kobyletzki D (1981) Untersuchungen zur Pharmakokinetik von Amoxicillin nach intravenöser, intramuskulärer und oraler Applikation. Arzneimittelforschung 31: 1148–1157
Sinko PJ, Leesman GD, Amidon GL (1991) Predicting fraction dose absorbed in humans using a macroscopic mass balance approach. Pharm Res 8: 979–988
Couet WR, Reigner BG, Guedes JP, Tozer TN (1991) Theoretical model for both saturable rate and extent of absorption: simulations of cefatrizine data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 19: 271–285
Wagner JG (1973) Properties of the Michaelis-Menten equation and its integrated form which are useful in pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1: 103–121
Westphal JF, Deslandes A, Bogard JM, Carbon C (1991) Reappraisal of amoxicillin absorption kinetics. J Antimicrob Chemother 27: 647–654
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paintaud, G., Alván, G., Dahl, M.L. et al. Nonlinearity of amoxicillin absorption kinetics in human. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 43, 283–288 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02333024
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02333024