Abstract
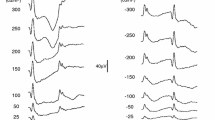
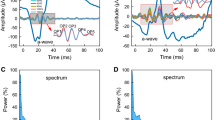
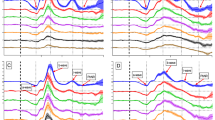
The effect of filter bandwith on the multifocal electroretinogram was assessed by means of theoretical calculation, electronic simulation and real multifocal electroretinogram recordings. Waveform distortion by high-pass filtering on simulated square waves, normal electroretinogram waveforms and negative electroretinogram waveforms was demonstrated. The theory of the effect of differentiation on electroretinographic waveform shape by electronic filtering indicates that little effect would be observed by changing the input filter cut-off for normal electroretinographic waveform shapes. However, negative electroretinogram waveforms are differentiated when the high-pass filter setting is increased. The differentiation effect artificially recreates a positive component that could be mistaken as a b-wave component. To eliminate this effect when recording multifocal electroretinograms, a high-pass filter setting of less than 1 Hz should be used to preserve the true electroretinographic waveform shape.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bush RA, Sieving PA. A proximal retinal component in the primate photopic ERG a-wave. Invest Opthalmol Vis Sci 1994; 35: 635–45.
Bush RA, Sieving PA. Inner retinal contributions to the primate photopic fast flicker electroretinogram. J Opt Soc Am 1996; 13: 557–65.
Karwoski CJ, Xu X, Yu H. Current-source density analysis of the electroretinogram of the frog: methodological issues and origin of components. J Opt Soc Am 1996; 13: 549–56.
Robson JG, Frishman LJ. Photoreceptor and bipolar-cell contributions to the cat electroretinogram: a kinetic model for the early part of the flash response. J Opt Soc Am 1996; 13: 613–22.
Hood DC, Birch DG. B-wave of the scotopic (rod) electroretinogram as a measure of the activity of human on-bipolar cells. J Opt Soc Am 1996; 13: 623–33.
Miyake Y, Yagasaki K, Horiguchi M. Congenital stationary night blindness with negative electroretinogram: a new classification. Arch Ophthalmol 1986; 104: 1023–20.
Hayakawa M, Imai Y, Wakita M, Kato K, Yanashima K, Miyake Y, Kanai A. A Japanese pedigree of autosomal dominant congenital stationary night blindness with variable expressivity. Opthalmic Paediatr Genet 1992; 13: 211–7.
Jensen H, Warburg M, Sjo o, Schwartz M. Duchenne muscular dystrophy: negative electroretinograms and normal dark adaptation. Reappraisal of assignment of X linked incomplete congenital stationary night blindness. J Med Genet 1995; 32: 348–51.
Matsui Y, Katsumi O, Sakaue H, Hirose T. Electroretinogram b/a wave ratio improvement in central retinal vein obstruction. Br J Opthalmol 1994; 78: 191–8.
Sakaue H, Katsumi O, Hirose T. Electroretinographic findings in fellow eyes of patients with central retinal vein occlusion. Arch Ophthalmol 1989; 107: 1459–620.
Shimazaki J, Matsuhashi M. Familial retinoschisis in female patients. Doc Opthalmol 1987; 65: 393–400.
Murayama K, Kuo CY, Sieving PA. Abnormal threshold ERG response in X-linked juvenile retinoschisis: evidence for a proximal retinal original of the human STR. Clin Vision Sci 1991; 6: 317–22.
Cideciyan AV, Jacobson SG. Negative electroretinograms in retinitis pigmentosa. Invest Opthalmol Vis Sci 1993; 34: 3253–63.
Miyake Y, Shiroyama N, Horiguchi M, Saito A, Yagasaki K. Bull's-eye maculopathy and negative electroretinograms. Retina 1989; 9: 210–5.
Hiros T, Katsumi O, Pruett RC, Sakaue H, Mehta M. Retinal function in birdshot retinochoroidopathy. Acta Opthalmol 1991; 69: 327–37.
Weleber RG, Miyake Y. Familial optic atrophy with negative electroretinograms. Arch Opthalmol 1992; 110: 640–5.
Marmor MF. Negative-type electroretinogram from cisplatin toxicity. Doc Opthalmol 1993; 84: 237–46.
Fujii N, Shiono T, Wada Y, Nakazawa M, Tamai M, Yamada N. Autosomal dominant cone-rod dystrophy with negative electroretinogram. Br J Opthalmol 1995; 79: 916–21.
Sutter EE, Tran D. The field topography of ERG components in man. I: the photopic luminance response. Vision Res 1992; 32: 433–446.
Kondo M, Miyake Y, Horiguchi M, Suzuki S, Tanikawa A. Clinical evaluation of multifocal electroretinogram. Invest Opthalmol Vis Sci 1995; 36: 2146–50.
Usui S, Nagasaka E. Spatial distribution of local flash electroretinogram by multi-input stimulation. Doc Opthalmol 1994; 88: 57–63.
Marmor MF, Zrenner E. Standard for clinical electroretinography. Doc Opthalmol 1995; 89: 199–210.
Kretschmann UH, Ruther KW, Zrenner E. Observations regarding the waveform of the ERG recorded with the m-sequence stimulation technique 1996. Invest Opthalmol Vis Sci 1996; 37(suppl): 346. Abstract
Hood DC, Seiple W, Holpigian K, Greenstein V, Carr RE. A comparison of the components of multi-focal and full field ERGs. Proceedings XXXIV ISCEV Symposium 1996, Tubingen, Germany.
Bradman MS, Evans AL, Montgomery DMI, Keating D, Damato BE, Cluckie A, Allan D. A personal computer based visual evoked potential stimulus and recording system. Doc Opthalmol 1994; 86: 81–93.
Hawlina M, Konec B. New noncorneal HK-loop electrode for clinical electroretinography. Doc Opthalmol 1992; 81: 253–9.
Parks S, Keating D, Williamson TH, Evans AL, Elliott AT, Jay JL. Functional imaging of the retina using the multifocal ERG: a control study. Br J Opthalmol 1996; 80: 831–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keating, D., Parks, S., Evans, A.L. et al. The effect of filter bandwidth on the multifocal electroretinogram. Doc Ophthalmol 92, 291–300 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02584083
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02584083